R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT GUI Reference
Channel Menu
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 489
Recommendation ("Default" configuration)
The port assignments must establish a
connection between all calibrated analyzer ports.
For n calibrated analyzer ports, n – 1 connections
are required. A star-shaped configuration with a
central port fulfills this requirement (see One Path
Two Port Calibration). Another option is to
connect the calibration unit between ports 1 and
2, ports 2 and 3 and so forth
1)
.
Assign the analyzer port with the lowest port number (e.g. port
1) to port 1 of the calibration unit. Subdivide the remaining n – 1
analyzer ports into groups of m – 1 ports with increasing port
numbers. Create a separate port assignment for each group;
leave port 1 of the calibration unit connected to the analyzer
port with the lowest port number and connect the ports of each
of the port groups to the remaining m – 1 ports of the calibration
unit.
One Path
Two Port
Calibration
The node port must be included in all port
assignments. The calibration unit must be
connected between the node port and all other
calibrated analyzer ports (star-shaped
calibration). For n calibrated analyzer ports, n – 1
connections between the node port and the other
ports are required.
Additional condition: The cal unit port assigned to
a given analyzer port must be the same
2)
.
Assign the node port to port 1 of the calibration unit. Subdivide
the remaining n – 1 analyzer ports into groups of m – 1 ports.
Create a separate port assignment for each group; leave port 1
of the calibration unit connected to the node port and connect
the ports of each of the port groups to the remaining m – 1
ports of the calibration unit.
1) The general condition is that every port is connected at least once, and that the connections form no
cycles (the connections correspond to a "tree" in graph theory). This condition can be fulfilled with two-port
calibration units (or cal unit characterizations) only; cal units with more ports involve cycles.
2) This rule minimizes the number of re-connections between the calibration stages.
Full n-Port Calibration: The number of re-connections between the calibration stages is minimized if
you always assign the same cal unit port to a given analyzer port. This rule is applied in the examples
below.
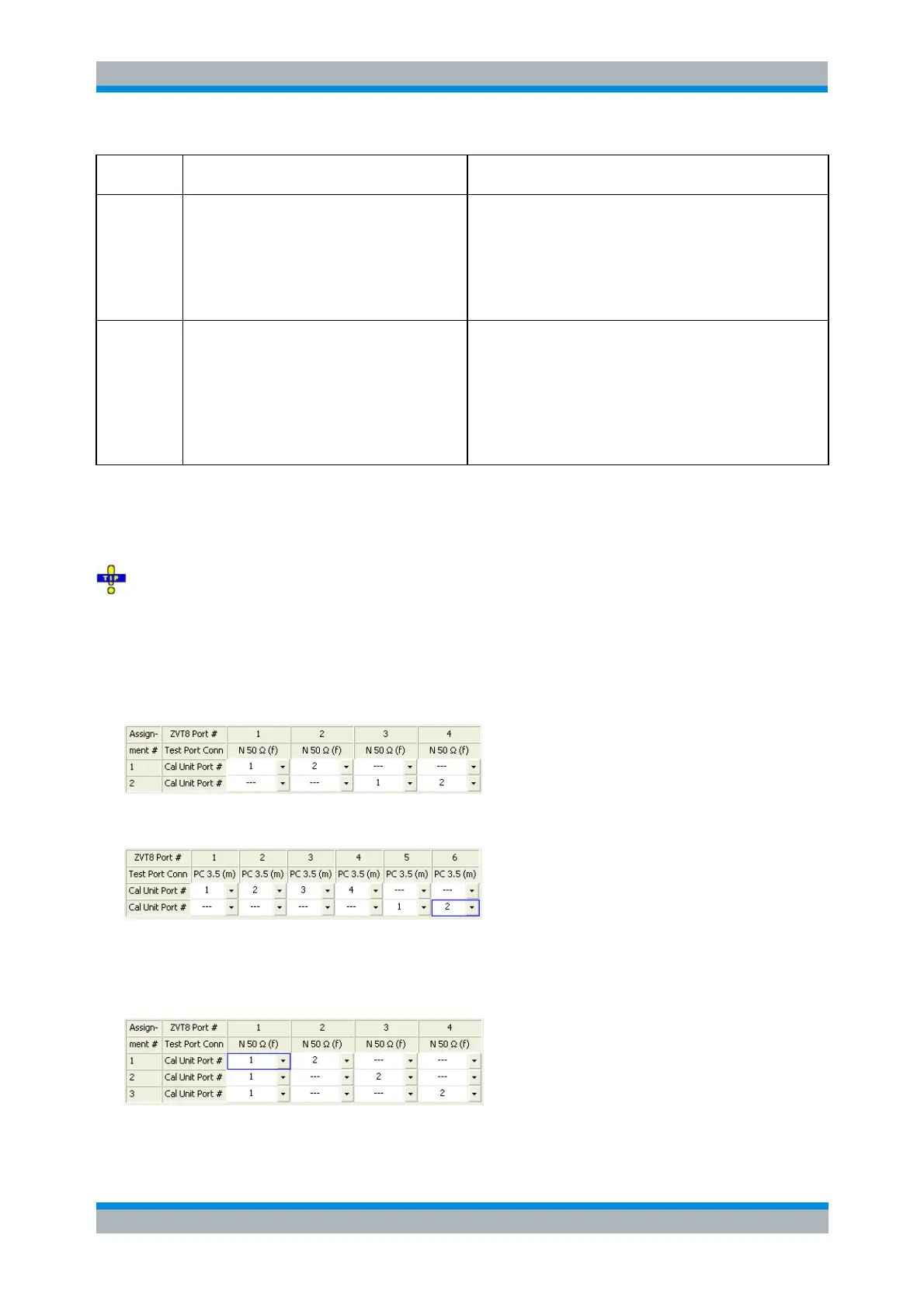
Example 1: Full One Port calibration
The following example shows a valid port assignment for a Full One Port calibration of four analyzer ports
using a two-port calibration unit.
The same for six calibrated analyzer ports and a four-port calibration unit.
Example 2: Full n-Port calibration
The following examples show a valid port assignment for a Full n-Port calibration of four analyzer ports
using a two-port calibration unit.
 Loading...
Loading...