11
11-7
A-D Converters
32180 Group User's Manual (Rev.1.0)
A-D conversion interrupt or DMA transfer request
ADiIN0
Completed here when operating
in single-shot scan mode
ADiDT0
10-bit A-Di Data Register
Conversion
starts
(Note 1)
ADiIN1
ADiINn-1
ADiINn
ADiDT1 ADiDTn-1 ADiDTn
During continuous scan mode
<n-channel scan>
i=0, 1
n=0–15
Note 1: A-D0 conversion start: Software trigger → Started by setting the A-D0 conversion start bit to "1"
Hardware trigger → Started by input event bus 3, input event bus 2,
output event bus 3 or TIN23S signal input
A-D1 conversion start: Software trigger → Started by setting the A-D1 conversion start bit to "1"
Hardware trigger → Started by input event bus 3, input event bus 2,
TID1_udf/ovf or TIN23S signal input
Figure 11.1.5 Operation of A-D Conversion in Scan Mode
11.1 Outline of A-D Converters
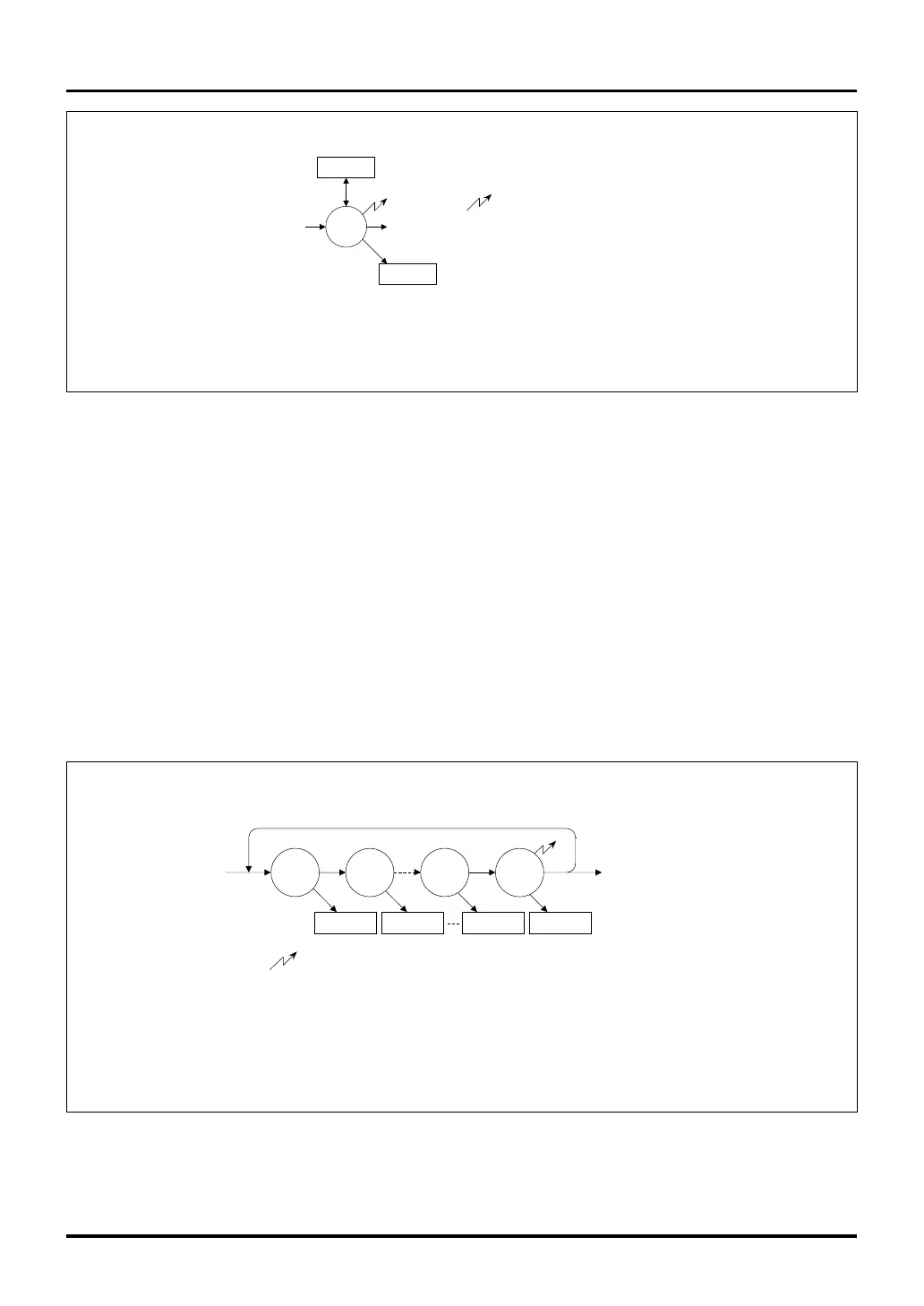
Figure 11.1.4 Operation in Single Mode (Comparate)
(2) Scan Mode
In scan mode, the analog input voltages on two or more selected channels from channel 0 (ADiIN0, i = 0 or 1)
to the channel (channels 0–15) selected by the A-D Scan Mode Register 1 scan loop select bit are sequen-
tially A-D converted.
There are two types of scan mode: “Single-shot scan mode” in which A-D conversion is completed after
performing one cycle of scan operation, and “Continuous scan mode” in which scan operation is continued
until halted by setting the A-D scan mode register 0’s A-D conversion stop bit to "1".
These types of scan mode are selected using A-D Scan Mode Register 0. The channels to be scanned are
selected using A-D Scan Mode Register 1. The selected channels are scanned sequentially beginning with
channel 0.
An A-D conversion interrupt or DMA transfer request can be generated when one cycle of scan operation is
completed.
A-D conversion interrupt
or DMA transfer request
Note 1: Comparate operation is started by writing a comparison value to the Successive
Approximation Register (ADiSAR)
ADiINn
Completed
ADiCMP
A-Di Comparate
Data Register
Conversion
starts
(Note 1)
ADiSAR
A-D Successive Approximation Register
Comparate result
ADiCMP=0 (ANn > ADiSAR)
ADiCMP=1 (ANn < ADiSAR)
i=0,1
n=0–15

 Loading...
Loading...











