11
11-38
A-D Converters
32180 Group User's Manual (Rev.1.0)
Start dummy Execution cycle
A-D conversion
start trigger
Convert operation
starts
Transferred to the
comparate data register
End dummy
Completed
11.3 Functional Description of A-D Converters
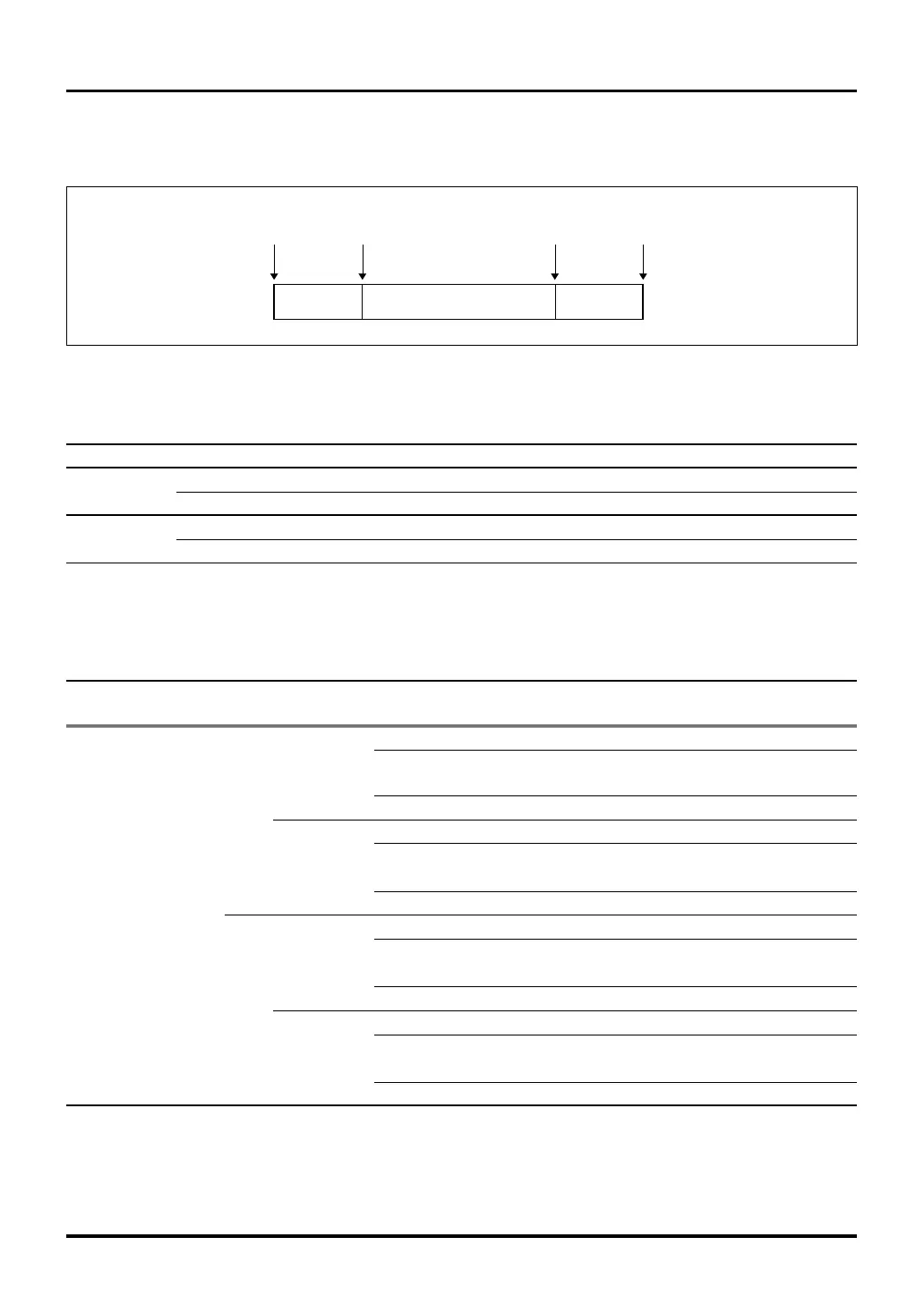
Figure 11.3.5 Conceptual Diagram of A-D Conversion Time during Comparator Mode
Table 11.3.4 Conversion Clock Periods during Comparator Mode Unit: BCLK
Conversion speed Start dummy Execution cycle End dummy
Slow mode Normal speed 4 42 1
Double speed 4 24 1
Fast mode Normal speed 4 18 1
Double speed 4 12 1
(4) A-D conversion time
A total A-D conversion time in various modes are shown in the table below.
Table 11.3.5 A-D Conversion Time (Total Time) Unit: BCLK
Conversion start method Conversion speed Conversion mode (Note 1) Conversion time When fast sample-
and-hold enabled
Software and Normal speed Single mode 299 191
hardware triggers n-channel single-shot scan/ (298 × n)+1 (190 × n)+1
(Note 2) continuous scan mode
Slow Comparator mode 47 47
Mode Double speed Single mode 173 101
n-channel single-shot scan/ (172 × n)+1 (100 × n)+1
continuous scan mode
Comparator mode 29 29
Normal speed Single mode 131 95
n-channel single-shot scan/ (130 × n)+1 (94 × n)+1
continuous scan mode
Fast Comparator mode 23 23
Mode Double speed Single mode 89 53
n-channel single-shot scan/ (88 × n)+1 (52 × n)+1
continuous scan mode
Comparator mode 17 17
Note 1: For single mode and comparator mode, this indicates an A-D conversion or comparate time per channel. For single-
shot and continuous scan modes, this indicates an A-D conversion time per scan loop.
Note 2: This indicates a time from when a register write cycle has finished to when an A-D conversion completion interrupt
request is generated, or a time from when an event bus or other MJT event has occurred to when an A-D conversion
completion interrupt request is generated.
(3) Calculating the conversion time during comparator mode
The following schematically shows the method for calculating the conversion time during comparator mode.

 Loading...
Loading...











