9328900990 Rev L BE1-951 Testing and Maintenance 13-49
Step 3: Connect a current source to Terminals D1 and D2 (A-phase input). Slowly increase the current
applied to the A-phase input until OUT2 (and subsequently OUT1) closes. Compare the applied
current to the current values listed in
Table 13-73. Verify that pickup occurred between the
lower and upper limits for your relay.
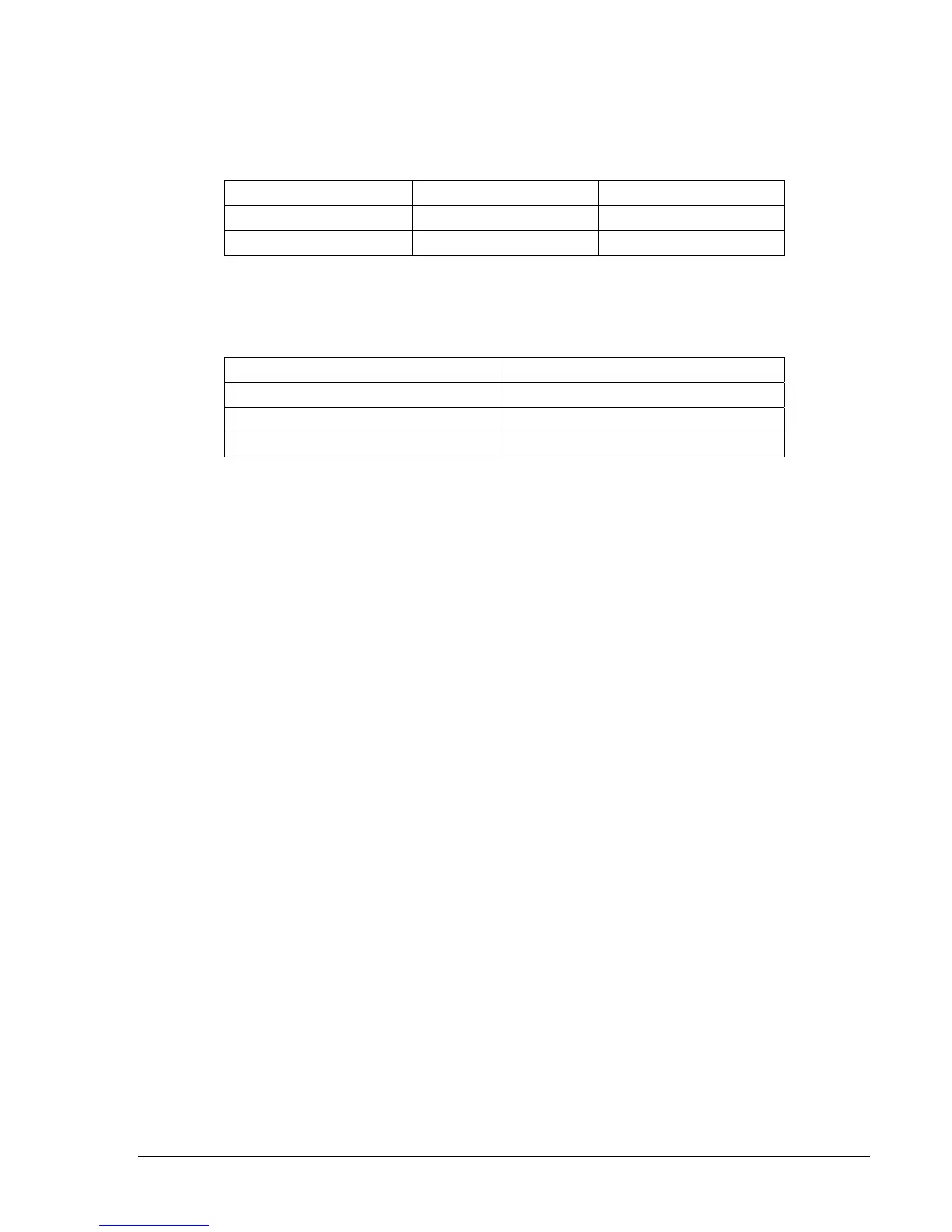
Table 13-73. BF Pickup Limits
Sensing Type Lower Pickup Limit Upper Pickup Limit
A or B (1 A) 0.09 A 0.11 A
D, E, or F (5 A) 0.45 A 0.55 A
Step 4: Transmit the commands in
Table 13-74 to set the BF time delay.
Table 13-74. BF Time Delay Commands
Command Purpose
A= Gains write access.
SP-BF=100m Set BF time delay at 100 milliseconds.
EXIT;Y Exit and save settings.
Step 5: Verify the BF time delay by applying the pickup current obtained in Step 3 for the duration given
in the following steps:
A. Apply pickup current to phase A for 4 cycles (67 ms at 60 Hz). No trip should occur.
B. Apply pickup current to phase A for 5 cycles (83 ms at 60 Hz). No trip should occur.
C. Apply pickup current to phase A for 7 cycles (117 ms at 60 Hz). A BF trip should occur. Use
the RS-LGC command to retrieve an SER report and verify that a BF trip was logged 100
milliseconds ±0.5 percent (+1¼, -¼) after application of pickup current.
Step 6: (Optional.) De-energize relay input IN3. This will block the breaker fail logic and cause OUT1
and OUT2 to open. Verify that relay Outputs OUT1 and OUT2 remain open (BF element does
not operate) even though pickup current is applied. De-energize IN3 and verify that OUT2 (and
subsequently OUT1) closes. Remove current from phase A.
Step 7: (Optional.) Apply pickup current to phase A. OUT2 and OUT1 should close. De-energize IN4
and verify that OUT1 and OUT2 open. Remove current from phase A.
Step 8: Energize IN4 and apply 0.7 A of current to the phase A current input and measure the time
between the application of current and OUT1 closing. OUT2 should have closed immediately
when current was applied. Verify that the BF timer operated within the specified accuracy of ±5
percent or +1¼, -¼ cycles, whichever is greater.
Step 9: (Optional.) Repeat Steps 3 through 8 for the phase B and phase C elements.
Virtual Switches (43)
Purpose: To verify operation of the 43/143/243/343 virtual switches.
Reference Commands: SL-43/143/243/343, CS/CO-43/143/243/343
To test virtual switches, we verify each mode of operation but do not verify each of the four virtual
switches. In your testing, you may substitute any or all of the switches as desired. If you give an invalid
command such as CS-243=1/CO-243=1 when Switch 243 is programmed for mode 3 operation, the relay
will reject the command and return an INVALID PARAMETER message through the ASCII command
interface. For more information about virtual switch operation, see Section 4, Protection and Control,
Virtual Switches. You may verify operation of virtual switches by monitoring the programmed output
contacts, HMI Screen 1.5.4 or by using the RS-LGC command to retrieve logic variable data from the
SER. You also may use the RG-STAT command. See Section 6, Reporting and Alarm Functions, for
more information about reports.
 Loading...
Loading...