Operation Principles D1 Servo Drive User Manual
3-4 HIWIN MIKROSYSTEM CORP.
(2) Using PWM command
PWM command is transformed into current command to control the force and torque of motor. The
corresponding current of full PWM can be set in the servo drive.
3.1.4 Stand-alone mode
The servo drive has one high-speed digital signal processor (DSP), so the servo drive is able to do path
planning. Select stand-alone mode when user would like the servo drive to be tested alone or operate
without controller. In stand-alone mode, servo loops are handled by the servo drive.
3.2 Encoder types
Encoder plays an essential role in controlling servo motor. With position and angle information provided
by encoder, the servo drive is able to control servo loops. The commonly-used encoders are optical scale
and magnetic scale which obtain current position by means of optics and variation of magnetic field. The
position signal obtained by optical scale or magnetic scale is transformed into digital signal or analog
signal. Normally optical scale or magnetic scale may support either digital signal output or analog signal
output.
3.2.1 Digital type
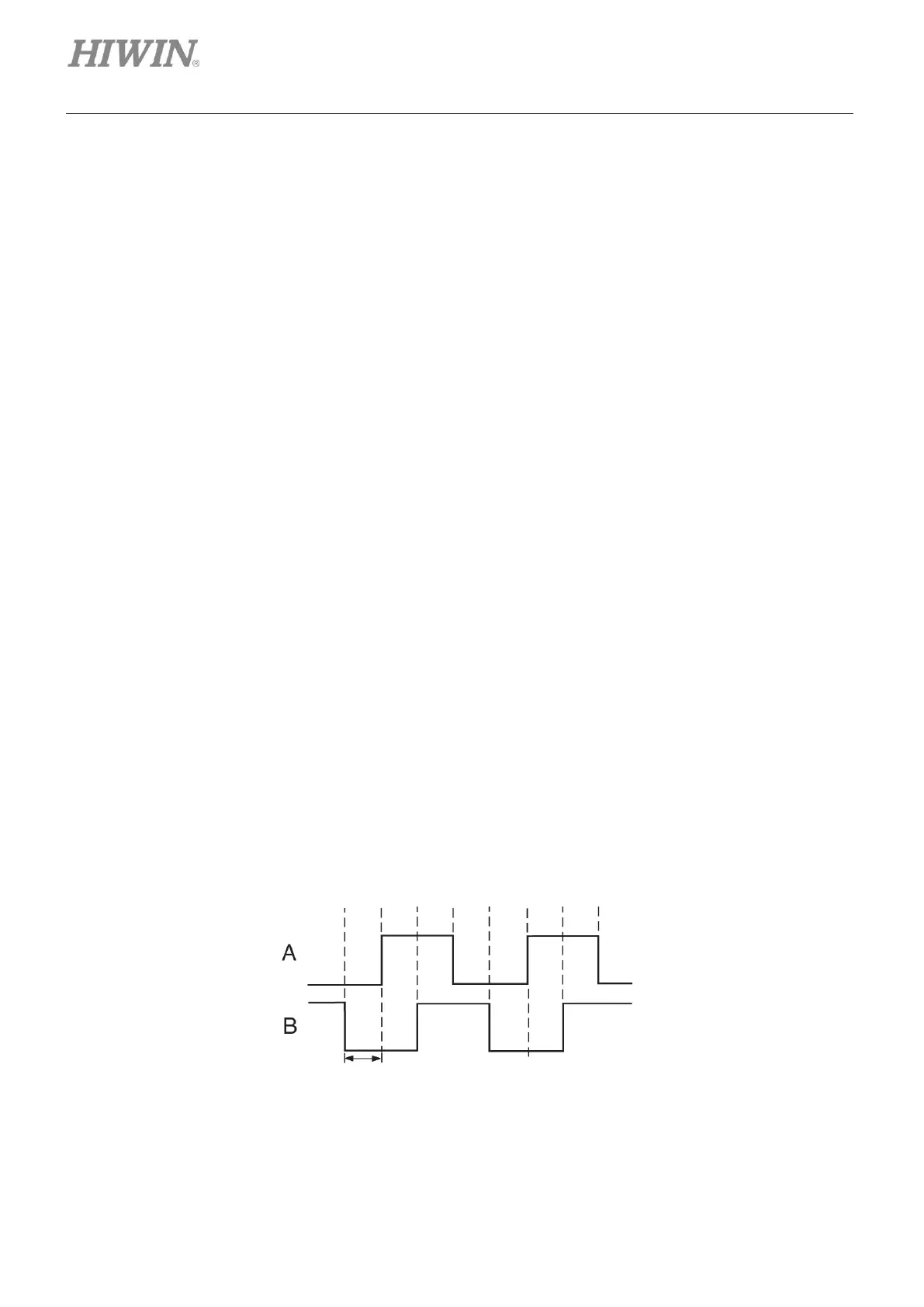
Digital encoder (or incremental encoder) normally outputs TTL RS422 differential signal. TTL RS422
differential signal includes two digital pulses with 90 degrees phase difference. Its resolution definition is
shown in figure 3.2.1.1. The resolution of linear optical scale is usually 1 um.
Figure3.2.1.1
 Loading...
Loading...