R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT GUI Reference
Trace Menu
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 130
if no combination of passive source or load can cause the circuit to oscillate.
The K-factor provides a necessary condition for unconditional stability: A circuit is unconditionally
stable if K>1 and an additional condition is met. The additional condition can be tested by means
of the stability factors μ
1
and μ
2
.
The μ
1
and μ
2
factors both provide a necessary and sufficient condition for unconditional stability:
The conditions μ
1
>1 or μ
2
>1 are both equivalent to unconditional stability. This means that μ
1
and
μ
2
provide direct insight into the degree of stability or potential instability of linear circuits.
References: Marion Lee Edwards and Jeffrey H. Sinsky, "A New Criterion for Linear 2-Port Stability Using
a Single Geometrically Derived Parameter", IEEE Trans. MTT, vol. 40, No. 12, pp. 2303-2311, Dec. 1992.
CALCulate<Ch>:PARameter:MEASure "<Trace_Name>", "KFAC21" |
"MUF121" | "MUF221" | ...
[SENSe<Chn>:]FUNCtion[:ON] "...:POWer:KFACtor | MUFactor1 |
MUFactor2"
Create new trace and select name and measurement parameter:
CALCulate<Ch>:PARameter:SDEFine "<Trace_Name>", "SY11" | "SY12" |
"SY21" | "SY22"
Imbalance...
Opens a dialog to select the imbalance for balanced ports. This result is available in the simulated (virtual)
differential mode but not in true differential mode.
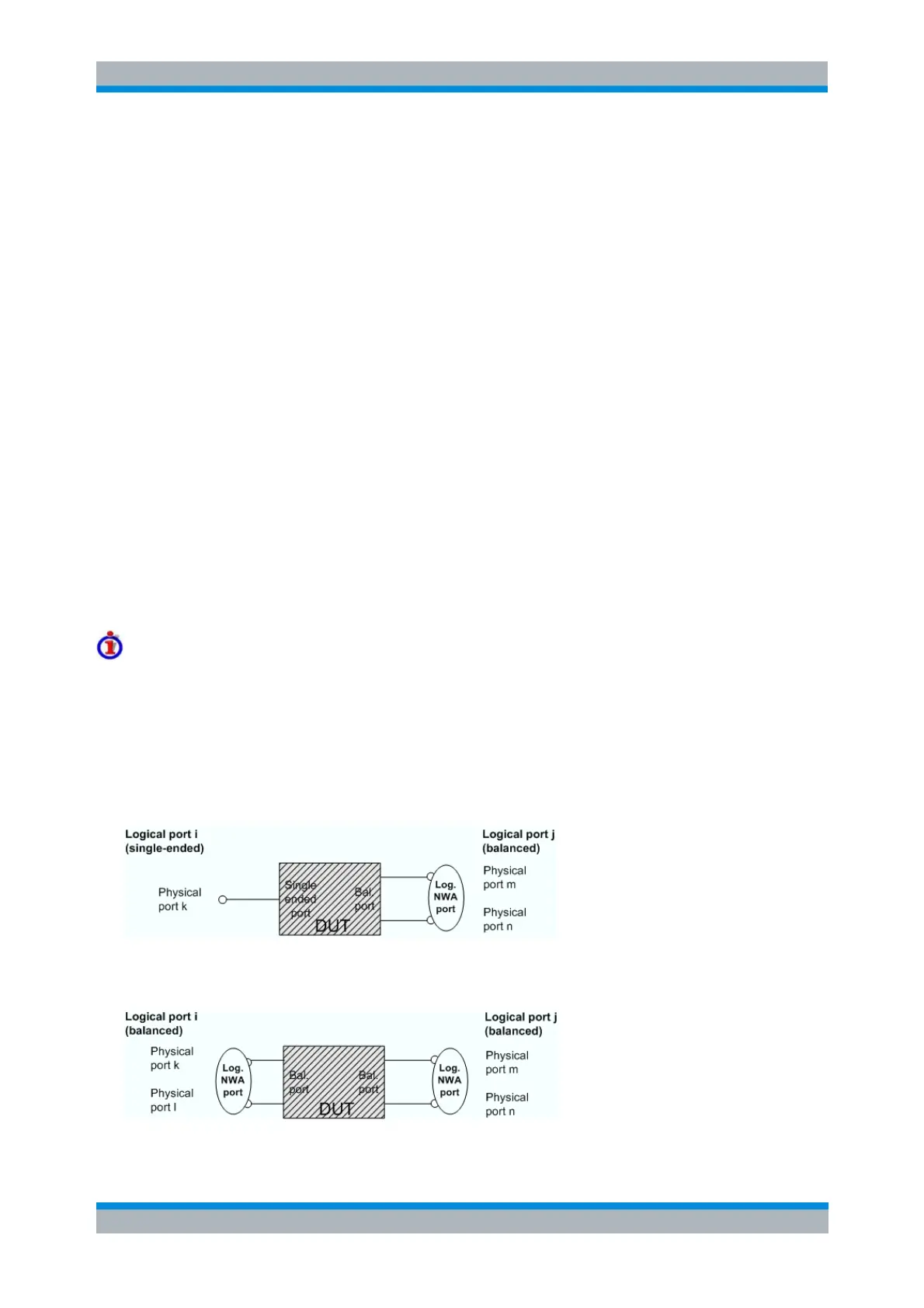
Definition of imbalance parameters
An ideal unbalance-balance transformer (balun) converts an unbalanced signal into a balanced one and
vice versa. When it is driven with an unbalanced signal at its physical port k, unbalanced signals with
equal amplitude and opposite phase appear at the physical ports m and n.
This means that the ratio –S
mk
/S
nk
of the physical transmission coefficients of an ideal balun equals to 1.
This ratio is called imbalance; it is a measure for the deviation of the balun from ideality. The definition of
the imbalance of a DUT with one or two balanced ports and physical port numbers m < n, k < l is given
below.
The imbalance of a DUT with a single ended logical input port i and a balanced logical output port
j is defined as Imb ji = –S
mk
/S
nk
and Imb ij = –S
km
/S
kn
.
 Loading...
Loading...