R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT GUI Reference
Trace Menu
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 131
The imbalance of a DUT with a balanced logical input port i and a balanced logical output port j is
defined as Imb ji = –(S
mk
– S
nk
)/(S
ml
– S
nl
) and Imb ij = –(S
km
– S
kn
)/(S
lm
– S
ln
).
In general the imbalance is a quantity with two numeric indices numbering the logical output port and the
logical input port of the DUT during the measurement (Imb<out><in>).
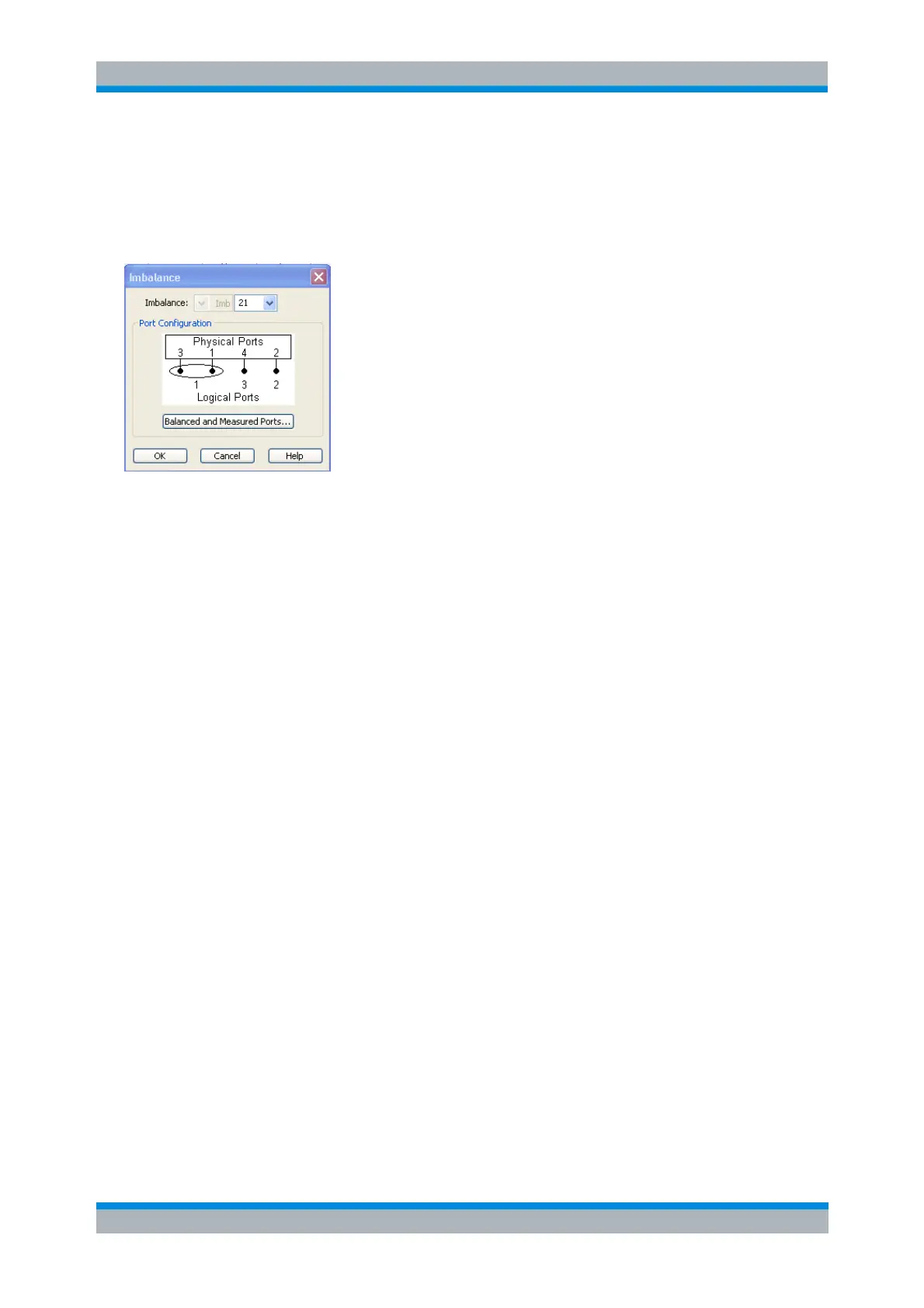
The Imbalance dialog provides the following settings:
Imbalance selects the imbalance parameter Imb
<out><in>
to be measured.
Balanced and Measured Ports opens the Balanced Port and Port Groups dialog to define the
properties of the test ports. Single-ended (unbalanced) impedance parameters are assigned to
the physical test ports of the analyzer. Balanced impedance parameters are assigned to logical
test ports. Selecting a balanced port configuration with logical test ports means that the
unbalance-balance conversion is switched on and that the analyzer provides mixed mode
parameters. A unbalance-balance conversion is a prerequisite for the calculation of imbalance
parameters.
CALCulate<Ch>:PARameter:MEASure "<Trace_Name>", "IMB21" |
"IMB12" ...
Create new trace and select name and measurement parameter:
CALCulate<Ch>:PARameter:SDEFine "<Trace_Name>", "IMB21" |
"IMB12" ...
All S-Params
Displays all S-parameters S
<out><in>
that the analyzer can calculate according to its port configuration.
Reflection parameters S
ii
are displayed in Smith charts; transmission parameters are displayed in
Cartesian (dB Mag) diagrams. For a four-port analyzer with four single-ended ports:
 Loading...
Loading...