R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT GUI Reference
Channel Menu
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 390
CALCulate<Ch>:TRANsform:VNETworks:PPAir:DEEMbedding:DEFine
CALCulate<Ch>:TRANsform:VNETworks:PPAir:DEEMbedding:DELete
CALCulate<Ch>:TRANsform:VNETworks:PPAir:EMBedding:DEFine
CALCulate<Ch>:TRANsform:VNETworks:PPAir:EMBedding:DELete
True Differential Mode (R&S ZVA and R&S ZVT)
Differential transmission lines and circuits are widely used, because their characteristics give them a lower
susceptibility to electromagnetic interference. Linear balanced devices can be tested with sufficient
accuracy using the virtual differential mode, where the vector network analyzer generates unbalanced
stimulus signals and uses a mathematical transformation to convert unbalanced wave quantities into
balanced S-parameters. A different behavior is expected for nonlinear balanced devices, where the
transmission characteristics of the DUT may depend on how closely the stimulus signal matches real
operating conditions.
With option R&S ZVA-K6, True Differential Mode, the vector network analyzer can generate true
differential and common mode stimuli at arbitrary reference planes in the test setup and determine mixed-
mode S-parameters, wave quantities and ratios. It is also possible to perform true differential
measurements on frequency-converting DUTs or to use true differential mode in combination with external
frequency converters (see background information in section Balanced Ports and Port Groups – True Diff
Mode). Moreover the true differential mode provides two additional sweep types, the amplitude imbalance
and phase imbalance sweeps. Like the virtual differential mode, the true differential mode requires a port
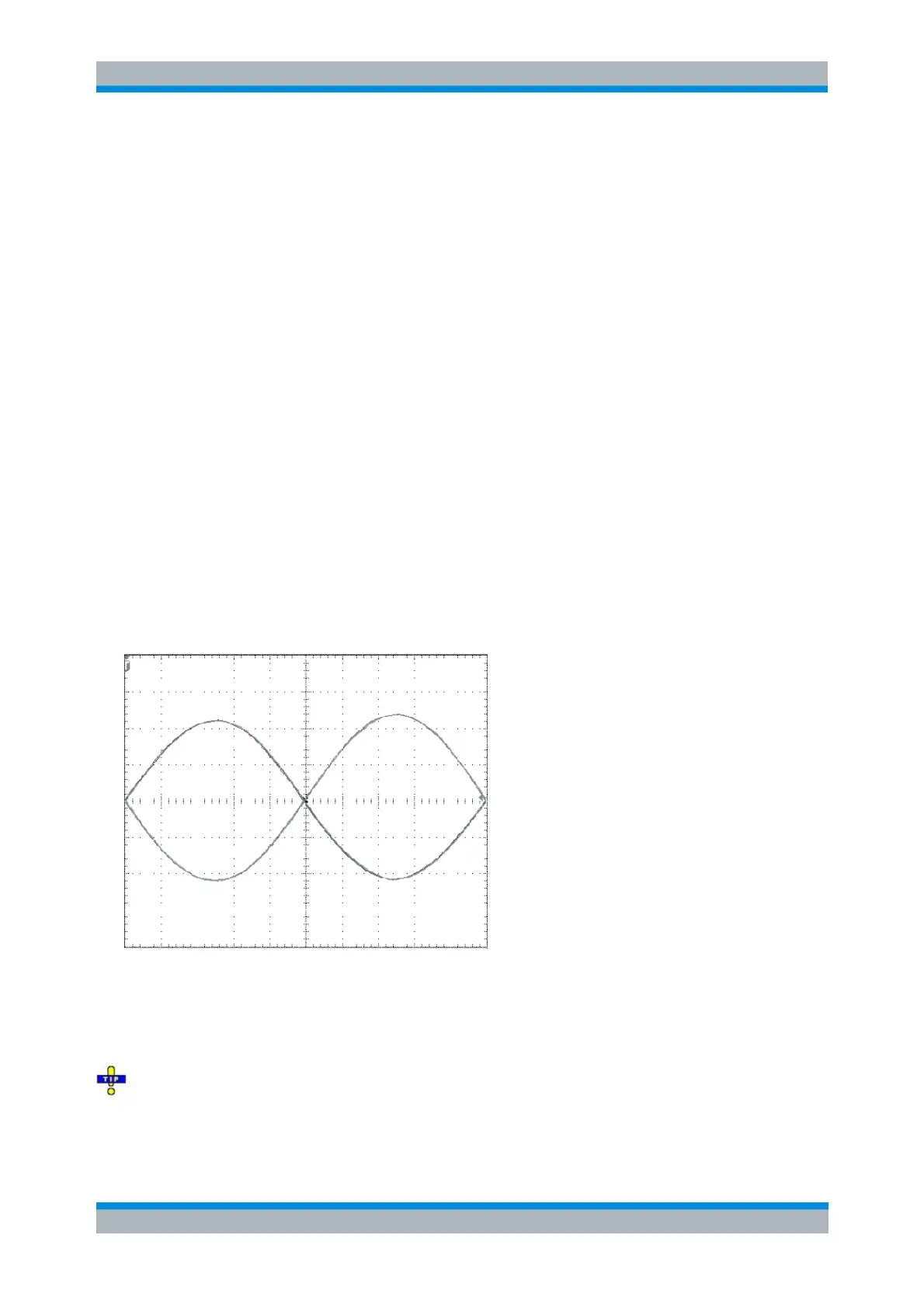
configuration with at least one balanced port. The differential mode signal that the analyzer generates in
true differential mode is shown below (the plot shows the waveforms of the two single-ended sources
measured vs. ground).
True differential mode requires an analyzer with at least two independent internal sources, i.e. a minimum
of 3 ports. To activate true differential mode, open the Balanced Ports and Port Groups dialog to define a
balanced port configuration, then select the True Diff Mode tab (Channel – Mode – Port Configuration... –
Balanced Ports and Port Groups... – True Diff Mode – True Differential Mode: On). Refer to chapter
Measurement Examples for details.
On R&S ZVA67 and on R&S ZVA24/40 network analyzers with four ports and four generators (order
nos. 1145.1110.28/48), all ports have independent internal sources. You can use true differential mode
with an arbitrary combination of two source ports. Note, however, that in converter mode all converter
ports must be configured for active power control, i.e. the power control method must not be set to None
 Loading...
Loading...