R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT GUI Reference
Channel Menu
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 328
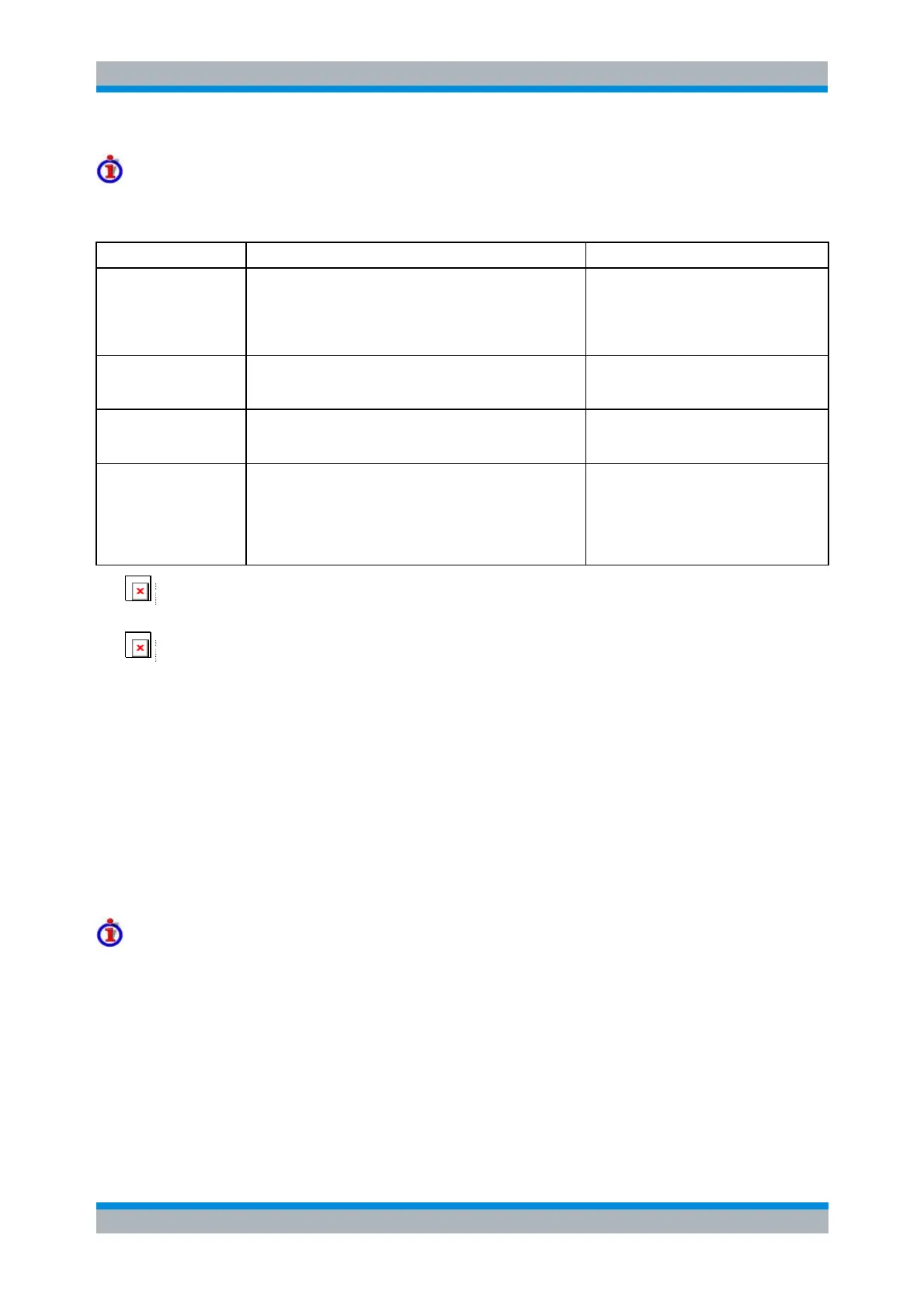
Finding the best test setup
The alternative test setups place different requirements on the NWA receivers and the additional
equipment.
Lowpass / highpass filter requirements
Port 2, forward
measurement (port 1 -->
port 2)
RF signal is converted to IF by the MUT and passes the
coupler at NWA port 2 as well as the MEAS mixer before it
reaches the measurement receiver.
--> Reduced accuracy for network analyzers with an upper
frequency limit > 20 GHz and IF frequencies <600 MHz.
The distance between the two IF bands
increases with the LO frequency.
--> Moderate filter requirements for
"standard" measurement scenarios where
f
RF
>> f
IF
, f
LO
>> f
IF
.
Port 2, reverse
measurement (port 2 -->
port 1)
Port 1, forward
measurement (port 1 -->
port 2)
Port 1, reverse
measurement (port 2 -->
port 1)
IF signal is converted to RF by the MUT and passes the
coupler at NWA port 2 as well as the MEAS mixer before it
reaches the measurement receiver.
--> Reduced accuracy for network analyzers with an upper
frequency limit > 20 GHz and RF frequencies <600 MHz.
The distance between the two RF bands
decreases if a smaller IF frequency is
chosen.
--> High filter requirements for "standard"
measurement scenarios with low IF
frequencies.
Avoid test setup "Port 2", if you use a network analyzer with an upper frequency limit > 20 GHz
and work at IF frequencies <600 MHz.
Avoid test setup "Port 1", if the edge of your lowpass or highpass filter is not steep enough to
clearly separate the two RF bands in the reverse measurement.
Example: RF frequency: 1.1 GHz ... 1.2 GHz, LO Frequency: 1.0 GHz, IF = RF – LO (Down, USB). An
R&S ZVA24 network analyzer is used.
--> IF = 100 MHz ... 200 MHz. For best accuracy in the forward measurement, use test setup "Port 1". In
the reverse measurement, this test setup requires a highpass filter with a cutoff 900 MHz < f
c
< 1.1 GHz.
Mixer Power Cal...
The Vector Mixer Measurement Power Calibration wizard controls the power calibration of the vector
mixer measurement. A power calibration ensures accurate levels of the mixer input signals (RF, IF, and
LO source power calibration). The necessary calibration steps are automatically performed across the
entire frequency range of the active mixer measurement (Set Frequencies).
Mixer Power Cal procedure and example
Due to the different frequency ranges of the input and output signals and the external equipment needed,
the mixer power calibration must be performed in several steps. For the standard test setup where the RF
and LO signals are provided by port 1 and an external generator, respectively, where the RF signal is
swept, and where the IF signal is analyzed at port 2, the following test setups are required:
1. Source power calibration for the RF signal. A power sensor is connected to port 1. The RF power
(red) is calibrated over the selected RF sweep range.
 Loading...
Loading...