R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT GUI Reference
Channel Menu
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 397
analyzer generates both stimulus modes according to what the measurement of the selected
quantity requires.
The power levels of the two sources are swept symmetrically around the equilibrium state |a
k
| =
|a
l
|, where r dB = 0 dB (see also Wave Quantities and Ratios in True Differential Mode).
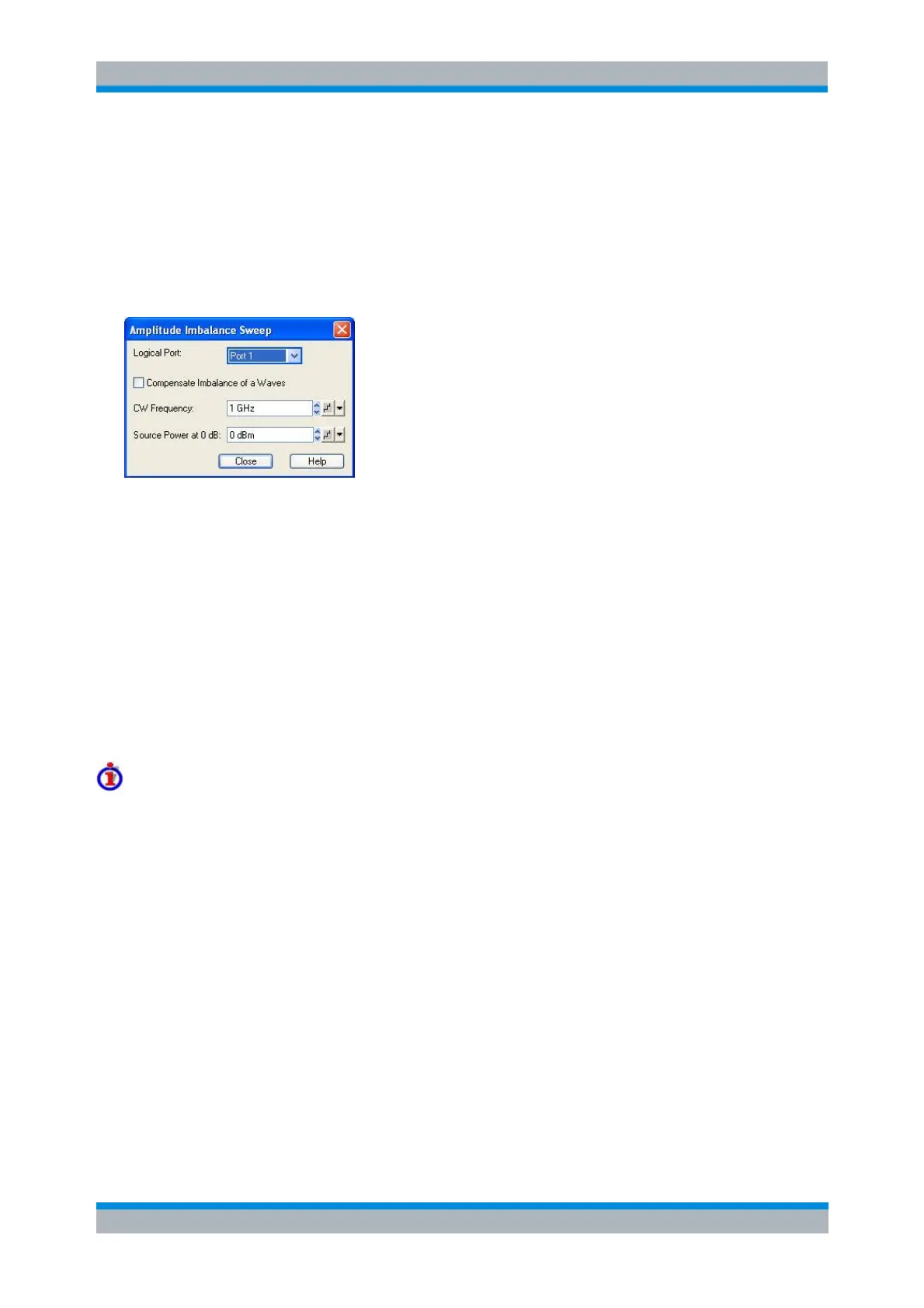
At least one logical port must be defined, and the true differential mode must be active to enable the
amplitude imbalance sweep. Activating the sweep (Channel – Sweep – Sweep Type: Amplitude
Imbalance) opens the following configuration dialog:
Logical Port selects the swept logical port.
Compensate Imbalance of a Waves selects the calculation method for S-parameters, ratios and
derived quantities; see background information below.
CW Frequency defines the frequency of all stimulus signals, which is constant over the entire
sweep. This setting is identical with the CW frequency for power, time and CW mode sweeps.
Source Power at 0 dB defines a constant power reference, corresponding to the channel power
P
ch
in the tables in section Source Power in True Differential Mode. The swept power range
(Channel – Stimulus – Start, Channel – Stimulus – Stop) of the involved single-ended sources is
defined relative to the reference value. This setting is identical with the constant channel base
power for frequency, time and CW mode sweeps.
The power range for the amplitude imbalance sweep is independent of the power range for power
sweeps.
Compensate Imbalance of a Waves
Since the mixed-mode S-parameters of a linear balanced DUT depend only on the DUT itself, they will be
independent of the amplitude or phase imbalance of the stimulus signal. So looking for example at S
dd21
of
a differential amplifier in phase imbalance sweep will not reveal the amplitude reduction of the differential
output signal caused by unequal lengths of the balanced input line conductors. This length asymmetry
corresponds to a phase imbalance increasing over frequency.
In order to see the effect of such a phase or amplitude imbalance, modified S-parameters are required.
The modification is done in such a way that if e.g. the imbalance of port 1 is swept, the imbalance of the a
wave of port 1 is compensated before the S-parameters are calculated. The effect of the compensation is
a constant amplitude of the differential or common mode stimulus wave of port 1 over the imbalance
sweep range. This reflects the situation of the user applying a stimulus signal of known nominal amplitude
to the DUT, but getting at the output only the amplified differential contents in this signal, which depends
on the imbalance. Usually, S-parameters of balanced devices measured with active imbalance
compensation will exhibit a maximum or minimum at zero imbalance.
The imbalance compensation is not only performed for mixed-mode S-parameters, but also for the
imbalance-swept a wave itself when it is selected as a measured quantity, as well as for ratios including
that wave.
 Loading...
Loading...