Functional Description
Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential UG0677 User Guide Revision 9.0 57
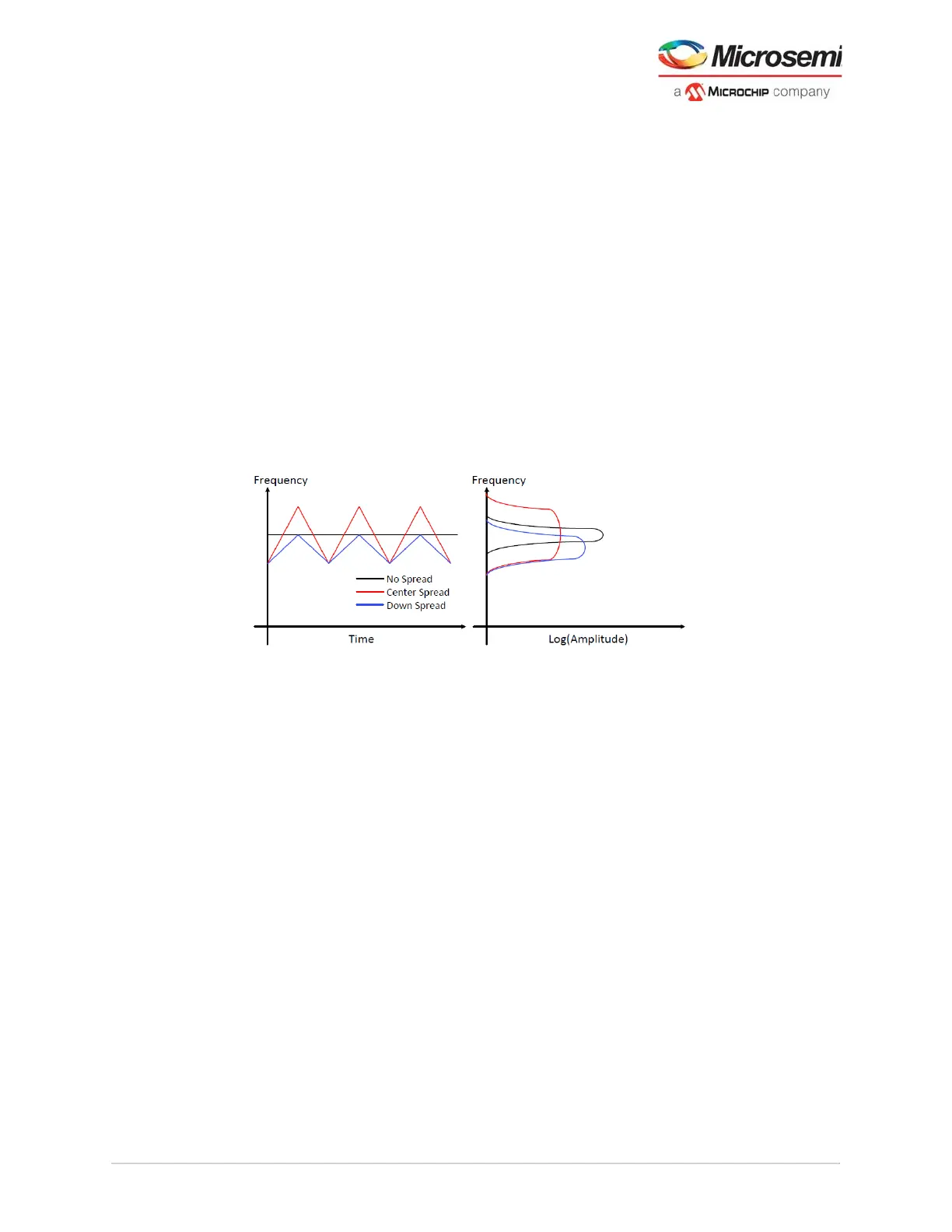
3.5.2 Spread Spectrum Clocking
TxPLL produces spread spectrum clock generation (SSCG). SSCG uses a modulated output clock signal
to reduce peak EMI. The lowering of peak EMI enables significant reduction in expensive shielding cost
or reduce interference with other sensitive circuits. By modulating the PLL, the resulting spectrum at
each clock harmonic is made broad-band or flattened, and reduced in amplitude from 10 db to 20 dB,
depending on frequency and modulation amplitude.
TxPLL is configured in Fractional-N mode to preserve the accuracy of modulation to the targeted
modulation frequency. The SSCG works by modulating the feedback divider value (Divval) of the TxPLL,
thus modulating the PLLs output frequency and introducing a noise source or wave table.
Setting the modulation mode (Center versus Down) and modulation amplitude depend on the amount of
EMI reduction desired and the timing margin for circuits running on the spread clock domain.
SSCG is optionally implemented using the Libero TxPLL configurator by setting the modulation
frequency, modulator spread mode (Center and Down spread), Spread/Divval, and Wave table.
See Libero Configurators, page 81.
The following figure shows the frequency versus time and the resulting amplitude in the frequency
domain.
Figure 39 • Spread Spectrum Clocking Modulation Mode

 Loading...
Loading...