VLANVLAN
Allows you to set a VLAN Identifier (VIDVID), a Drop Eligible Indicator (DEIDEI) and
a Priority Code Point (PCPPCP).
Displays a Tag Protocol Identifier (TPIDTPID).
I-TagI-Tag
Allows you to set a VLAN Identifier (VIDVID), a Drop Eligible Indicator (DEIDEI), a
Priority Code Point (PCPPCP) and a User Customer Address (UCAUCA).
Displays a Tag Protocol Identifier (TPIDTPID).
Dst MACDst MAC
The
MAC-in-MAC destination address
can either be specified manually, or be
decided based on an ARP/NDP lookup.
When Layer 3 is set to IPv4, select the ARPARP check box to enable the ARP.
When Layer 3 is set to IPv6, select the NDP(NS/NA)NDP(NS/NA) check box to enable the
NDP.
The !! button is an
instant
button which when touched will perform an ARP or
NDP lookup immediately, instead of waiting until the transmitter starts.
Src MACSrc MAC
Allows you to specify the
MAC-in-MAC source address
.
EthertypeEthertype
Shows the type automatically depending on layer configuration. If the value is
selectable, select the value by touching the field.
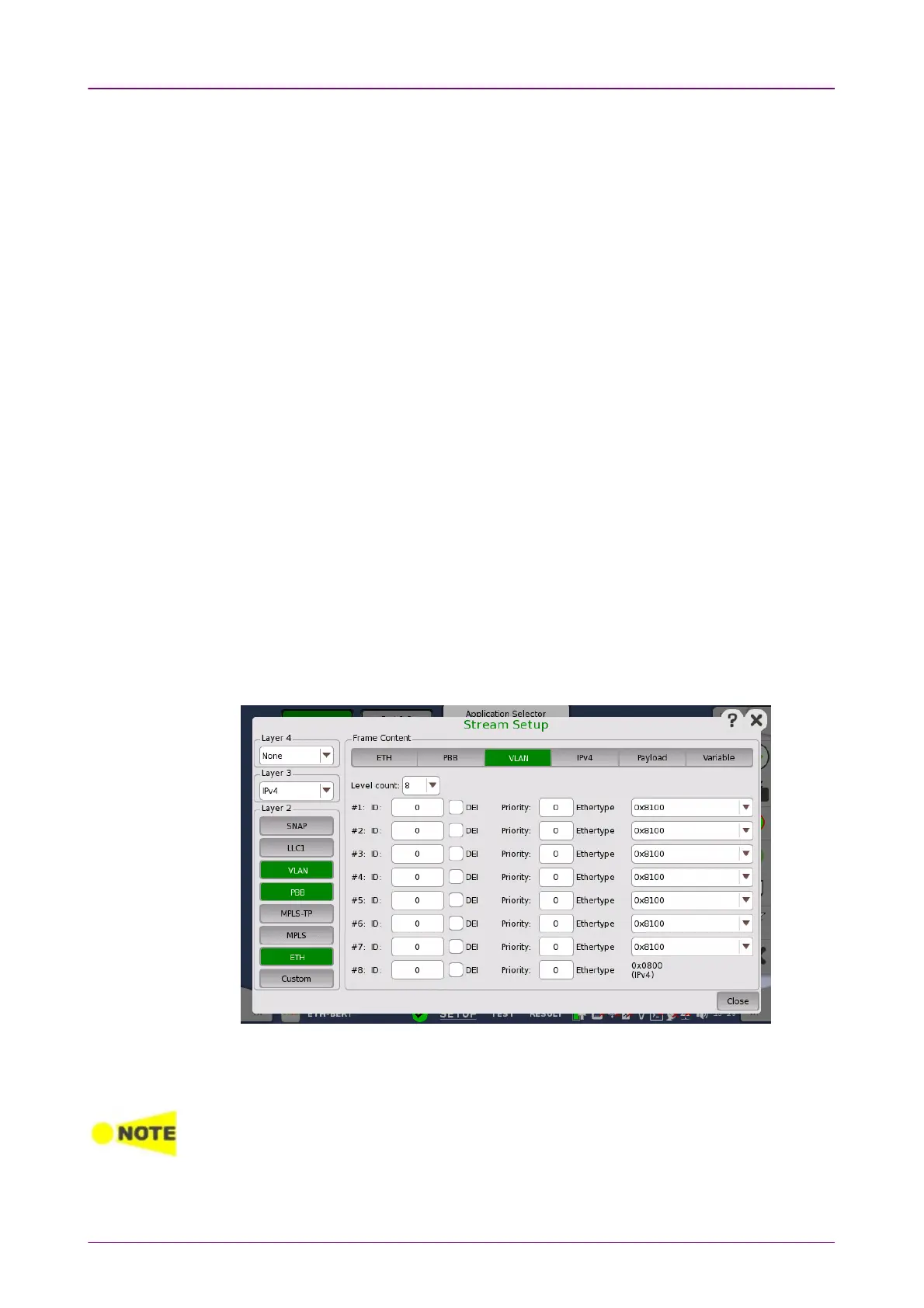
Touching the VLANVLAN layer button displays the parameters available for the
Virtual LAN
protocol layer.
Virtual LAN (VLAN) is used to create independent logical networks within a
physical network. When enabled, it adds a 16 bit IEEE 802.1Q field and a 16
bit Ethertype field to the header. The 802.1Q is separated into 3 parts.
VLAN affects the Ping and RFC2544/Router Latency test, i.e. when VLAN is enabled,
only frames with VLAN tag will be accepted. Furthermore, Ping replies will only be sent if
the Ping request contains the same VLAN ID as the one selected.
Level countLevel count
 Loading...
Loading...