18
Chap.1 b Master
1) Characteristics of the master
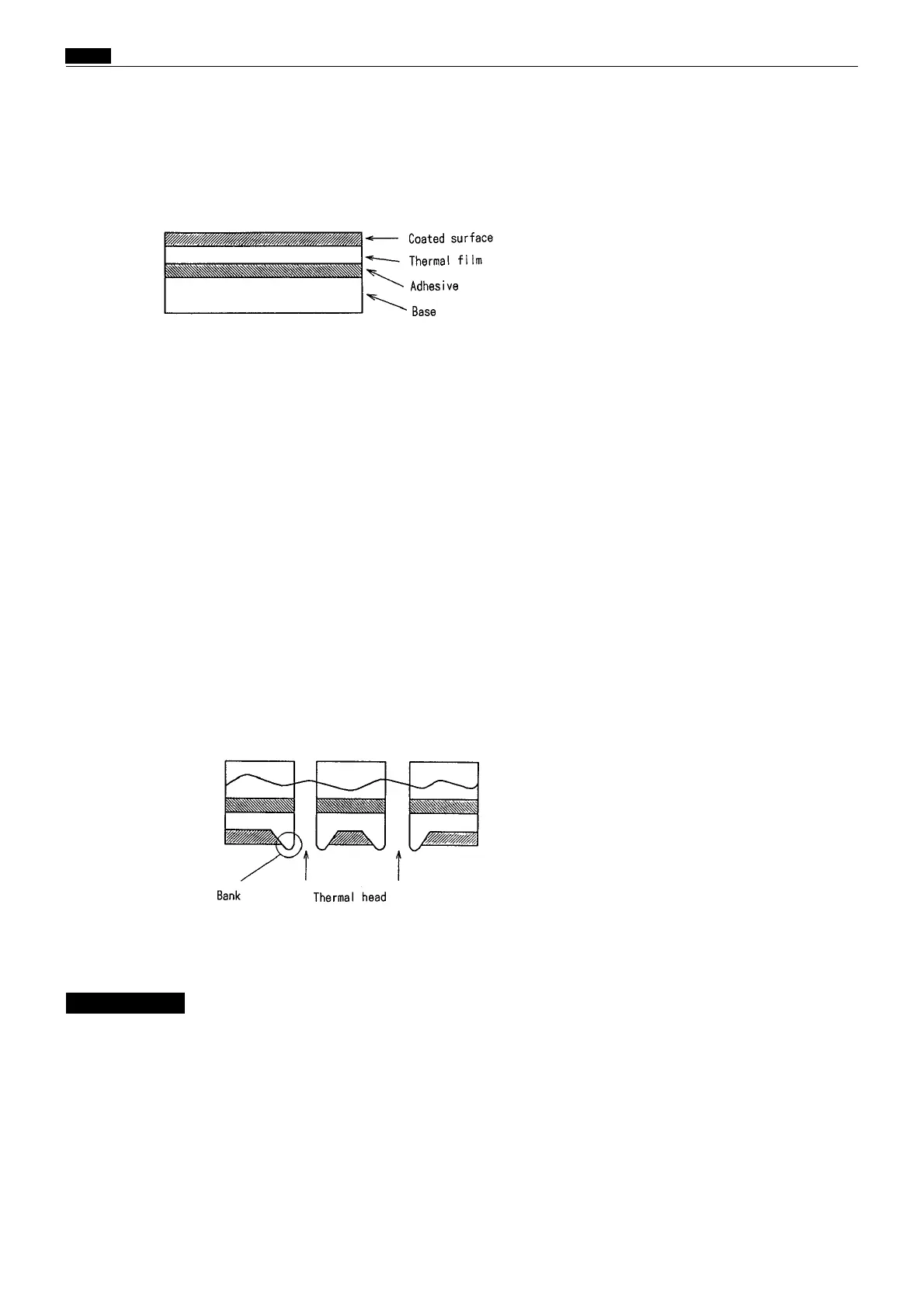
(1) Structure of the thermal master
(2) Functions and materials of the layers
Coated surface …… Prevents the film from fusing, being damaged due to friction,being peeled,
and being conveyed defectively due to electric static charge.
Material: silicon fluorine mold lubricant
Thermal film …… Holes are made by the heat of the thermal head.
Material: Polyethylene terephthalate (polyester)
Adhesive ………… 1] Adheres the film to the base.
2] Does not prevent ink from seeping.
3] Increases impression endurance.
Base ……………… 1] Base material for the master. Fibrous layer
2] Ink seeps the base.
(3) Cross section of the master during platemaking
Holes are made on the coated surface, thermal film and adhesive, while base fiber, base material
for the master, is left.
A part of the film fused by the thermal head is stuck to the head or banks up.
(4) Printed image
As the image consists of innumerable dots, it is taken as a continuous line through our eye.
INPORTANT :
•Precautions to be taken in dealing in the master.
(1) Do not put a heavy thing on the box in which masters are packed.
•This may damage the master and may cause defective platemaking.
(2) Do not leave the master as it is after it is taken out.
•Foreign objects are stuck to the master and this may cause defective platemaking.
(3) Keep the master from direct sunlight, too high or low temperature and too high or low humidity.
(Desirable storage temperature and humidity: 5-35 °C, 20-80%)
• If the master curls, defective plate attachment may occur.
bMaster
 Loading...
Loading...











