Bit no. Bit Mask (hex) Alarm Description
15 0x00008000 unused
16 0x00010000 unused
17 0x00020000 unused
18 0x00040000 unused
19 0x00080000 unused
20 0x00100000 unused
21 0x00200000 unused
22 0x00400000 unused
23 0x00800000 unused
24 0x01000000 unused
25 0x02000000 unused
26 0x04000000 unused
27 0x08000000 unused
28 0x10000000 unused
29 0x20000000 unused
30 0x40000000 unused
31 0x80000000 unused
2.2.4 FAULT RECORD EVENTS
An event record is created for every fault the IED detects. This is also known as a fault record.
The event type description shown in the Event Text
cell for this type of event is always Fault Recorded.
The IED contains a separate register containing the latest fault records. This provides a convenient way of
viewing the latest fault records and saves searching through the event log. You access these fault records
using the Select Fault setting, where fault number 0 is the latest fault.
A fault record is triggered by the Fault REC TRIG signal DDB, which is assigned in the PSL. The fault
recorder records the values of all parameters associated with the fault for the duration of the fault. These
parameters are stored in separate Courier cells, which become visible depending on the type of fault.
The fault recorder stops recording only when:
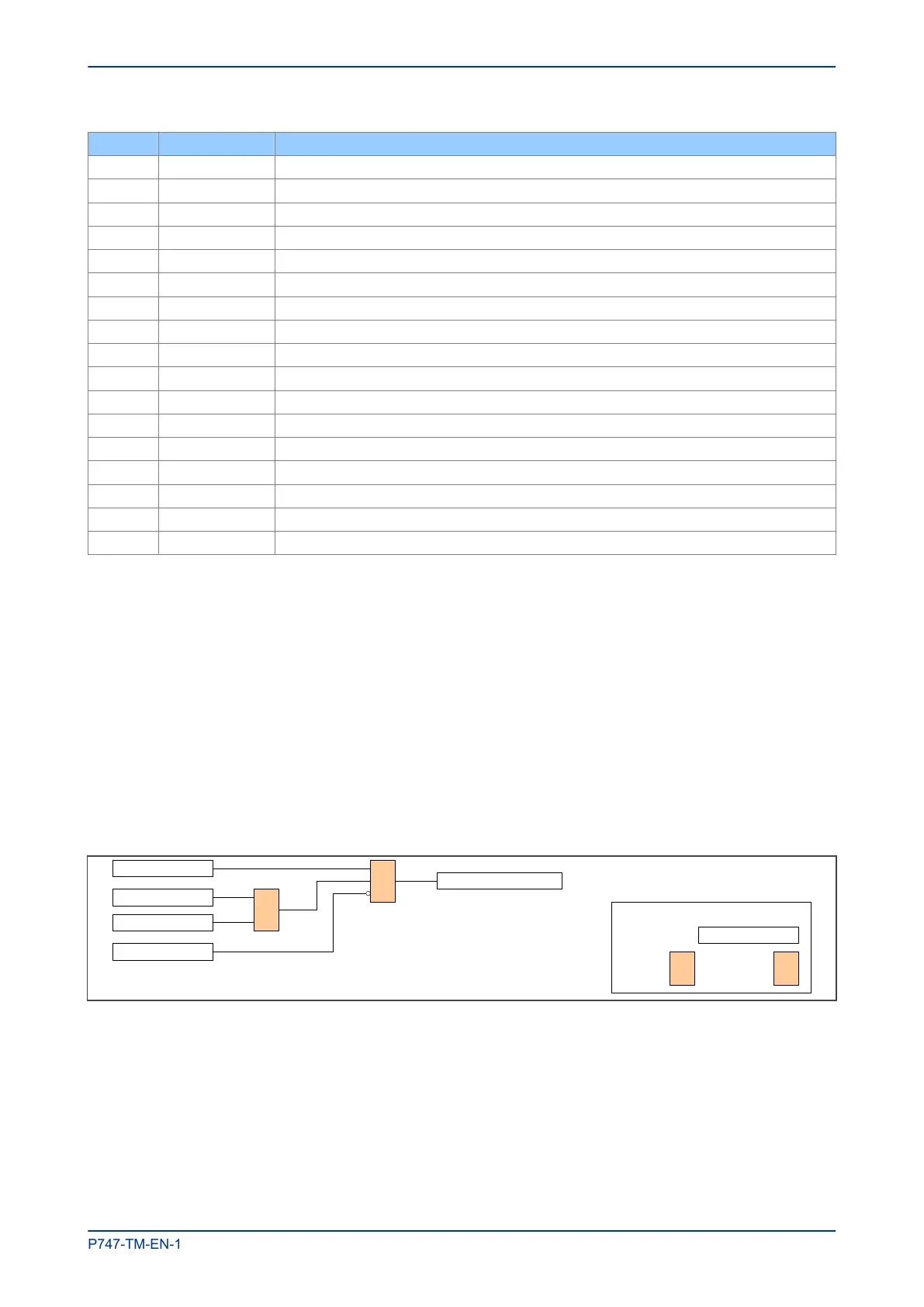
The Start signal is reset AND the undercurrent is ON OR the Trip signal is reset, as shown below:
V01234
Key:
I
nternal function
&
A
ND gate
OR gate
1
&
Start signal resets
Undercurrent is ON
Trip signal resets
1
Fault recorder stops recording
Fault recorder trigger
Figure 39: Fault recorder stop conditions
The event is logged as soon as the fault recorder stops. The time stamp assigned to the fault corresponds to
the start of the fault. The timestamp assigned to the fault record event corresponds to the time when the fault
recorder stops.
MiCOM P747 Chapter 6 - Monitoring and Control
P747-TM-EN-1 155

 Loading...
Loading...