3.4 ZONE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL ELEMENTS
The zone current differential element picks up if there is a fault in a zone on the busbar and the following
thresholds are exceeded:
● The bias slope characteristic defined by the k2 setting in the GROUP X DIFF PROTECTION
column
● The differential current threshold defined by the ID>2 setting in the GROUP X DIFF PROTECTION
column
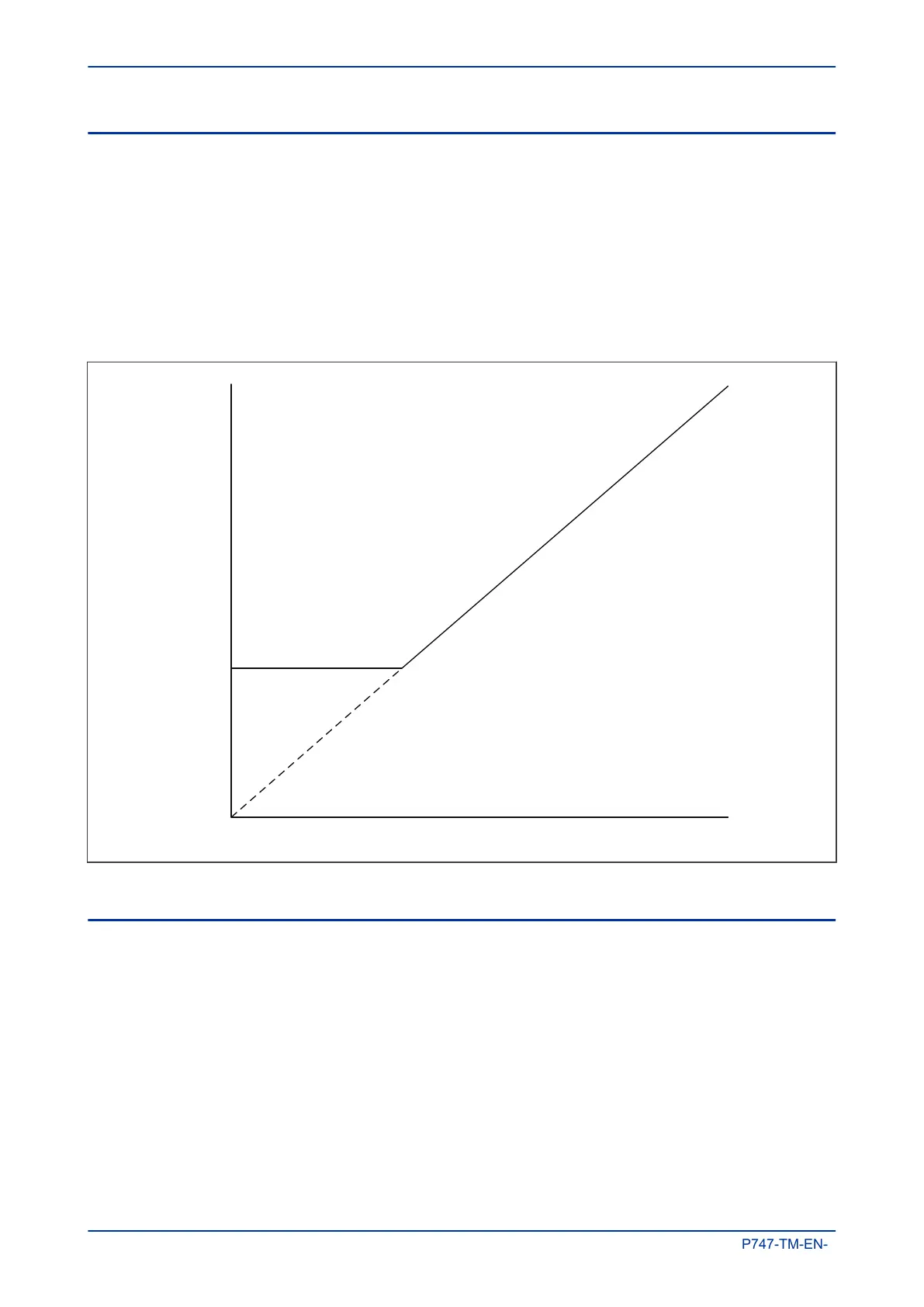
The following diagram shows the bias characteristic for the zone current differential, where:
Idiff is the vector sum of all the currents entering and leaving the zone.
Ibias is proportional to the scalar sum of all the currents entering and leaving the zone.
Tripping area
Idiff
Restrain area
K2 = 20% to 90%
Ibias
ID>2
E00718
Figure 31: Zone tripping characteristic.
3.5 CHECK ZONE
The check zone element ensures that a busbar zone trip signal is correct. This avoids unnecessarily tripping
a zone and affecting busbar stability. Individual zone elements compare currents entering and leaving the
zone, whereas the check zone element compares all currents entering and leaving the whole busbar.
Therefore the sum of zone fault currents should equal the checkzone fault current for the whole busbar. If it
does not, the error may be due to a distorted zone trip signal. To trip a section of the busbar, both the current
differential zone element and the check zone element must indicate a fault.
Chapter 5 - Protection Functions MiCOM P747
106 P747-TM-EN-1

 Loading...
Loading...