The circuitry fail element is time delayed by default. This prevents any conflict with the tripping characteristic
if there is a genuine busbar fault. If the circuitry fail element picks up, it triggers an alarm. This can be used
to block tripping of the zone differential protection elements.
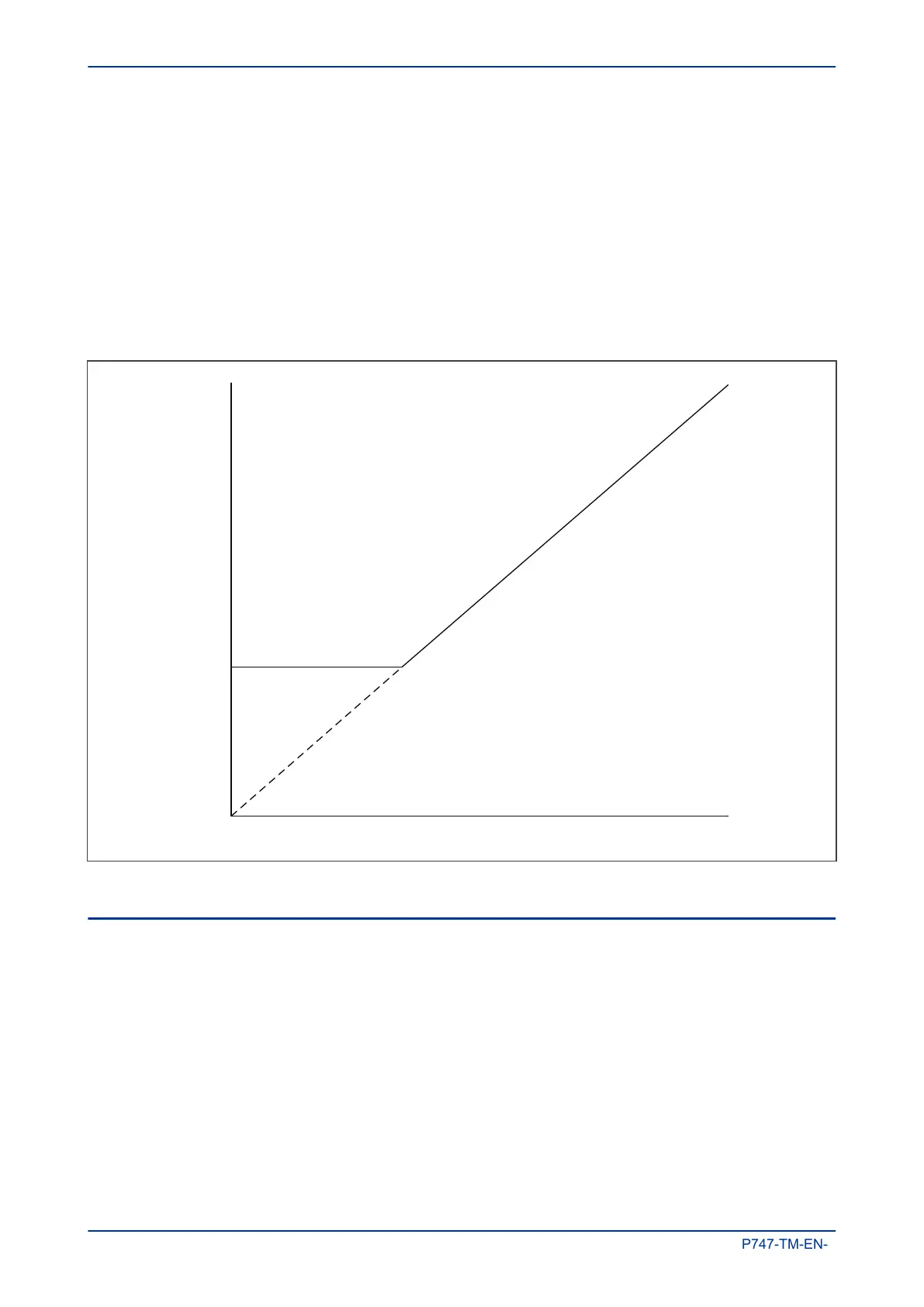
The circuitry fail element uses a dual slope differential characteristic. This is defined by the settings ID>1 and
k1 in the GROUP X DIFF PROTECTION column. If the ratio of differential to bias current exceeds the ID>1
and k1
settings, but does not exceed the ID>2 and k2 settings, for the duration of the ID>1 Alarm Timer
setting, a circuitry fail alarm is raised. The ID>1 Alarm Timer delay is set to 5 seconds by default.
The following diagram shows the bias characteristic for the circuitry fail element, where:
Idiff is the vector sum of all the currents entering and leaving the zone.
Ibias is proportional to the scalar sum of all the currents entering and leaving the zone.
Circuitry fail alarm area
Idiff
Circuitry ok area
Ibias
E00720
k1 = 0% to 50%
ID>1
Figure 33: Circuitry check characteristic.
3.7 CURRENT PHASE COMPARISON CHECK
Unless there is a fault, the current flowing into the busbar equals the current flowing out. If an external
(through) fault occurs, the busbar protection should not trip. However, if the external fault current is large
enough to saturate one or more of the CTs in the scheme, differential current appears. The biased current
differential characteristic provides stability for saturation of CTs for external faults. However, if the
characteristic is set too high, the protection may fail to operate for internal faults.
To prevent unnecessary tripping it is necessary to detect heavy saturation of CTs for external faults. This is
done using a current phase comparison function to supervise the differential decision. Tripping is blocked for
faults that are considered to be external with heavy CT saturation, but the block is removed if an evolving
internal fault is detected.
If a CT saturates, the relative phase angles between the currents entering and leaving the protected zone
exceed 90 deg and the current exceeds the threshold PhComp Thresh. These values can be used to verify
Chapter 5 - Protection Functions MiCOM P747
108 P747-TM-EN-1

 Loading...
Loading...