R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT GUI Reference
Trace Menu
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 170
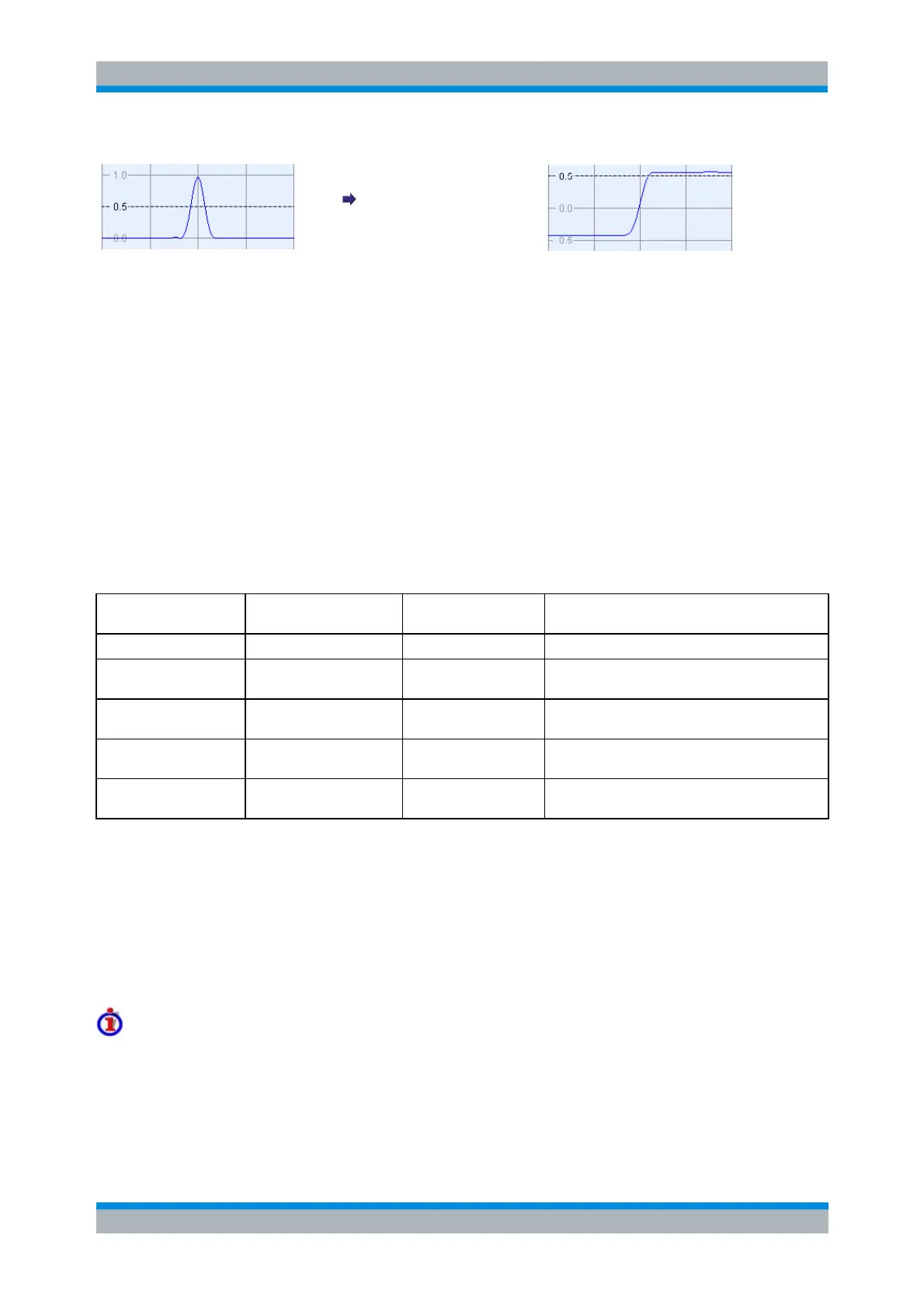
Integrate impulse response
Obtain step response
The step response is recommended for impedance measurements and for the analysis of discontinuities
(especially inductive and capacitive discontinuities). The impulse response has an unambiguous
magnitude and is therefore recommended for most other applications.
Please note that the unambiguous range for the step response is half of the unambiguous range for the
impulse response, meaning that the unambiguous range for the step response is Δt = 1/(2Δf), where Δf is
the spacing between two consecutive frequency points.
CALCulate<Chn>:TRANsform:TIME:STIMulus
Windows in the Frequency Domain
The finite sweep range in a frequency domain measurement with the discontinuous transitions at the start
and stop frequency broadens the impulses and causes sidelobes (ringing) in the time domain response.
The windows offered in the Define Transform dialog can reduce this effect and optimize the time domain
response. The windows have the following characteristics:
Low First Sidelobe
(Hamming)
Response resolution: separation of closely
spaced responses with comparable amplitude
Good compromise between pulse width and
sidelobe suppression
Dynamic range: separation of distant responses
with different amplitude
Arbitrary Sidelobes
(Dolph-Chebychev)
User defined between 10
dB and 120 dB
1.2 (at 32 dB sidelobe
suppression)
Adjustment to individual needs; tradeoff between
sidelobe suppression and impulse width
CALCulate<Chn>:TRANsform:TIME:WINDow
CALCulate<Chn>:TRANsform:TIME:DCHebyshev
Low Pass Settings
The Low Pass Settings dialog can be used to change the current grid of sweep points (that may or may
not be harmonic) to obtain a harmonic grid for lowpass time domain transforms.
Harmonic grid
A harmonic grid is formed by a set of equidistant frequency points f
i
(i = 1...n) with spacing Δf and the
additional condition that f
1
= m · Δf with m < 0.2 · n. In other words, all frequencies f
i
must be harmonics of
the frequency gap Δf. Furthermore, the number of extrapolated points including the DC value must be less
than 20 percent of the measured points.
 Loading...
Loading...