D.4
SEL-751A Relay Instruction Manual Date Code 20100129
DNP3 Communications
Introduction to DNP3
DNP3 also supports static polling: simple polling of the present value of data
points within the remote. By combining event data, unsolicited polling, and
static polling, you can operate your system in one of the four access methods
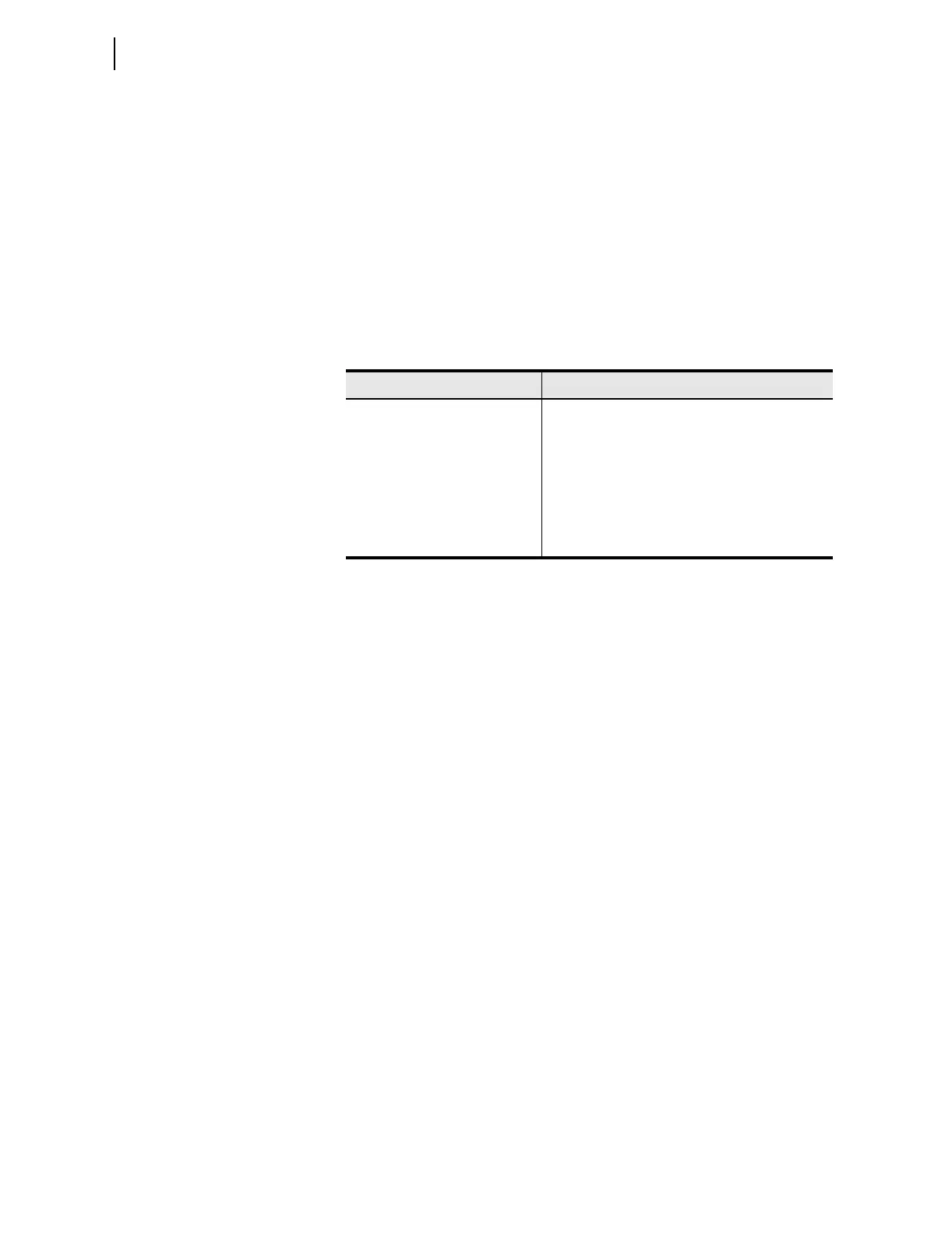
shown in Table D.3.
The access methods listed in Table D.3 are listed in order of increasing
communication efficiency. With various trade-offs, each method is less
demanding of communication bandwidth than the previous one. For example,
unsolicited report-by-exception consumes less communication bandwidth
than polled report-by-exception because that method does not require polling
messages from the master. In order to properly evaluate which access method
provides optimum performance for your application, you must also consider
overall system size and the volume of data communication expected.
Binary Control
Operations
DNP3 masters use Object 12, control device output block, to perform DNP3
binary control operations. The control device output block has both a trip/
close selection and a code selection. The trip/close selection allows a single
DNP3 index to operate two related control points such as trip and close or
raise and lower. Trip/close pair operation is not recommended for new DNP3
devices, but is often included for interoperability with older DNP3 master
implementations.
The control device output block code selection specifies either a latch or pulse
operation on the point. In many cases, DNP3 remotes have only a limited
subset of the possible combinations of the code field. Sometimes, DNP3
remotes assign special operation characteristics to the latch and pulse
selections. Table D.14 describes control point operation for the SEL-751A.
Conformance Testing
In addition to the protocol specifications, the DNP Users Group has approved
conformance-testing requirements for Level 1 and Level 2 devices. Some
implementers perform their own conformance specification testing, while
some contract with independent companies to perform conformance testing.
Conformance testing does not always guarantee that a master and remote will
be fully interoperable (that is, work together properly for all implemented
features). Conformance testing does help to standardize the testing procedure
and move the DNP3 implementers toward a higher level of interpretability.
Table D.3 DNP3 Access Methods
Access Method Description
Polled static Master polls for present value (Class 0) data only
Polled report-by-exception Master polls frequently for event data and
occasionally for Class 0 data
Unsolicited report-by-exception Remote devices send unsolicited event data to the
master, and the master occasionally polls for Class 0
data
Quiescent Master never polls and relies on unsolicited reports
only

 Loading...
Loading...