5: Square (Fixed boost with square characteristic)
A fixed square frequency to voltage characteristic is used as shown below. When the |OutputFrequency (05.001)| is below MotorRatedFrequency (05.006)
the OutputVoltage (05.002) is given by:
OutputVoltage (05.002) = LowFrequencyVoltageBoost (05.015) + [(MotorRatedVoltage (05.009) - LowFrequencyVoltageBoost (05.015)) x ( |
OutputFrequency (05.001) | / MotorRatedFrequency (05.006))
2
]
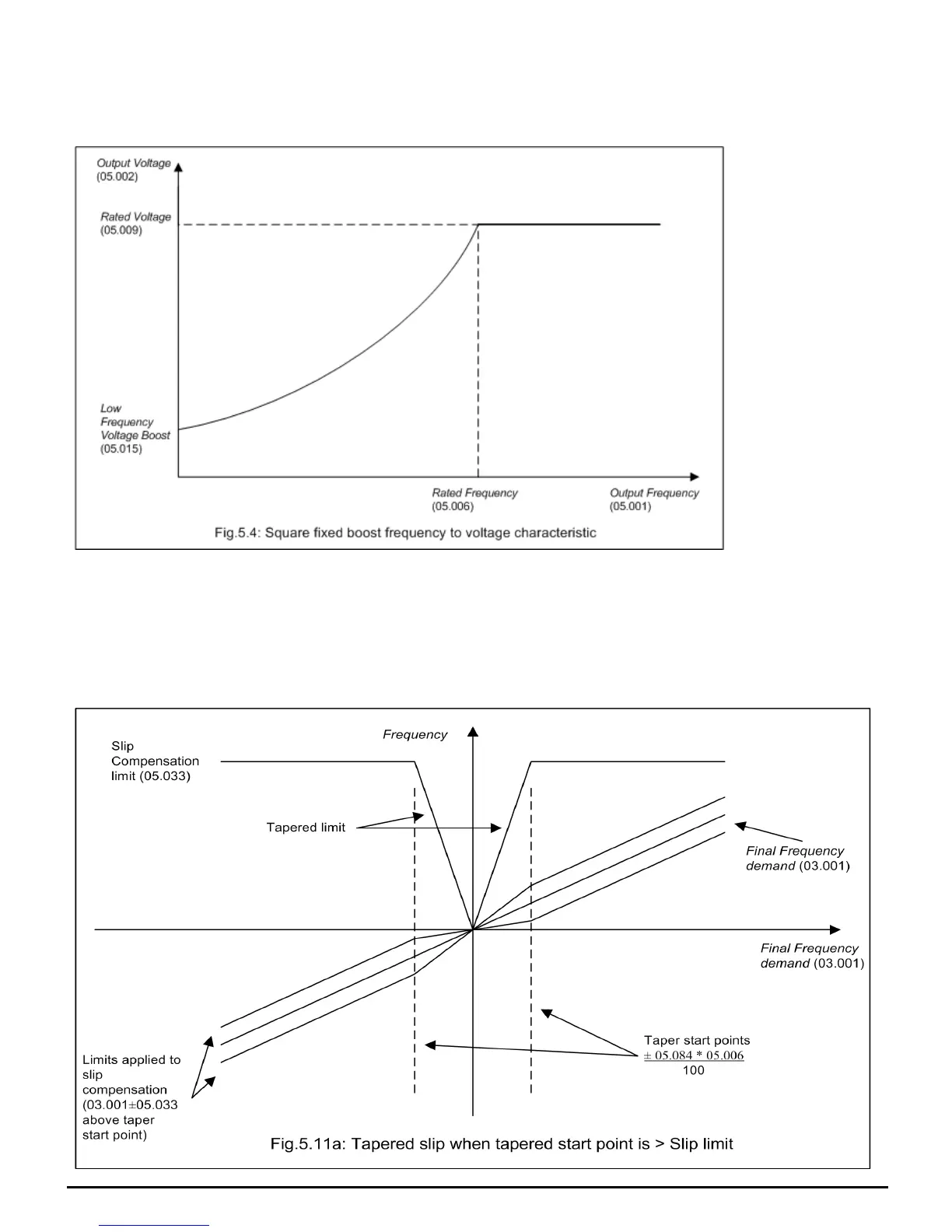
6: Fixed boost with tapered slip limit
Normally, slip compensation calculations do not allow the final output frequency to be opposite in sign to the final frequency reference. This can be an issue in
some applications where good torque control is required close to zero speed. In this mode of operation this limitation is removed.
To give even better control of the amount of slip being applied close to zero speed LowFrequencyEstimatorThreshold,LowFrequencyTorqueadjustment
(05.084) can be used to taper the slip compensation limit ( SlipCompensationLimit (05.033) ) down to 0 at zero frequency demand.
If the slip limit taper start point set by LowFrequencyEstimatorThreshold,LowFrequencyTorqueadjustment (05.084) is > SlipCompensationLimit
(05.033) then there is still no slip compensation applied in the opposite direction to the final frequency demand (see Fig 5.11a), but if the slip limit taper start
point set by LowFrequencyEstimatorThreshold,LowFrequencyTorqueadjustment (05.084) is < SlipCompensationLimit (05.033) then a controlled amount
of slip compensation can be applied in the opposite direction to the final frequency demand (see Fig 5.11b)

 Loading...
Loading...
















