APPENDIX
241
Quality factor (Q) and Dissipation factor (D)
The quality factor measures energies consumed by relative
frequency. In general, the better a circuit's quality factor the better
its selectivity.
The dissipation factor is the reciprocal of quality factor. It is the
signal angle loss by a capacitor (or inductor) and acting frequency
at a fixed temperature. Phase shifts caused by time lag between an
externally applied voltage and current generated may result in loss
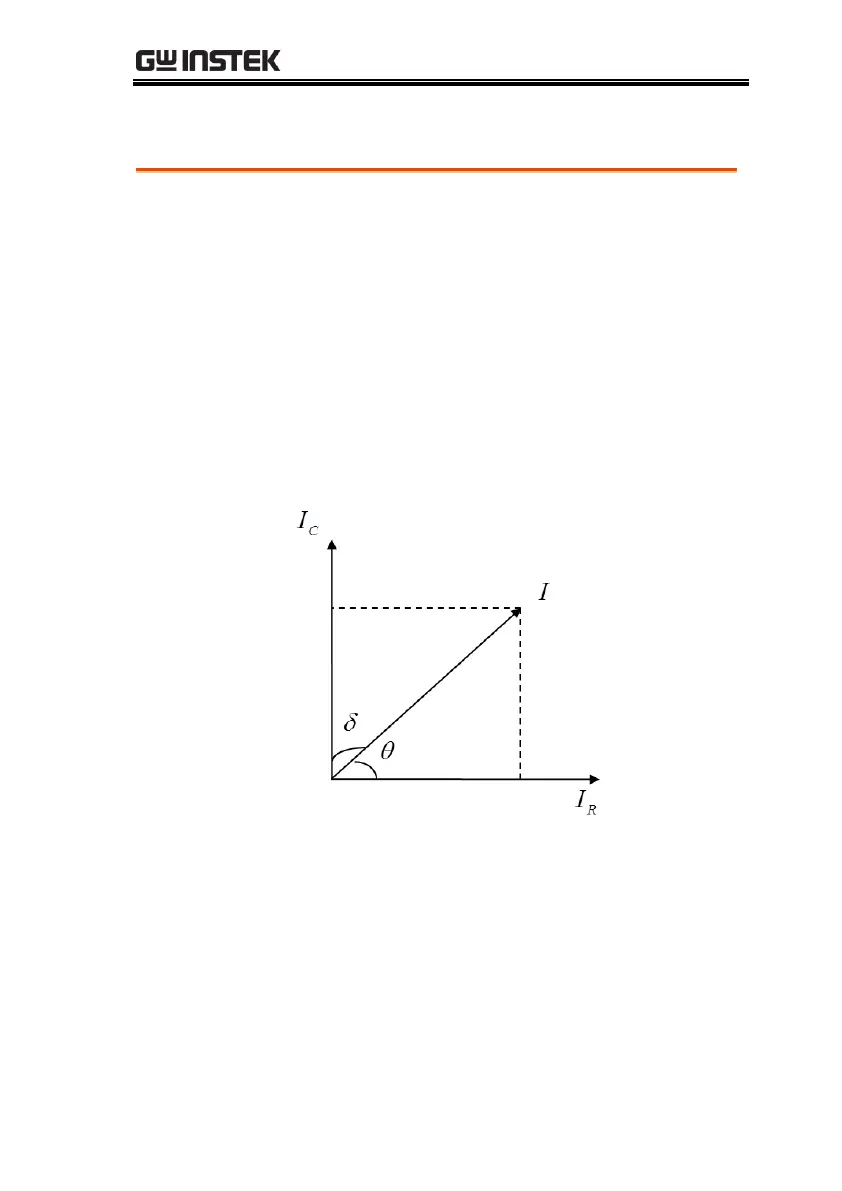
of current and energy dissipation. Here the total current (I) is the
sum of the charging current (Ic) by a 90 ゚ voltage phase shift and
loss current (IR) of the same voltage. The loss angle is the angle δ
between the total current and charging current and tanδ the
dissipation factor (symbol: D) as shown in the figure below:

 Loading...
Loading...











