R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT GUI Reference
Channel Menu
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 256
independently for the individual segments.
Due to this flexibility Segmented Frequency sweeps are suitable for any detailed analysis of a DUT at
specified frequencies. In a Cartesian diagram the measurement result is displayed as a trace over a linear
frequency scale ranging from the lowest to the highest frequency point of all segments. The following
example shows a Segmented Frequency sweep with 3 segments in the stimulus range between 300 kHz
and 4 GHz, the forward transmission parameter S
21
as measured quantity, and a dB Mag scaled y-axis. In
the frequency ranges between the sweep segments the trace is displayed as a straight line.
[SENSe<Ch>:]SWEep:TYPE SEGMent
[SENSe<Chn>:]FUNCtion[:ON] "XFRequency:..."
Power
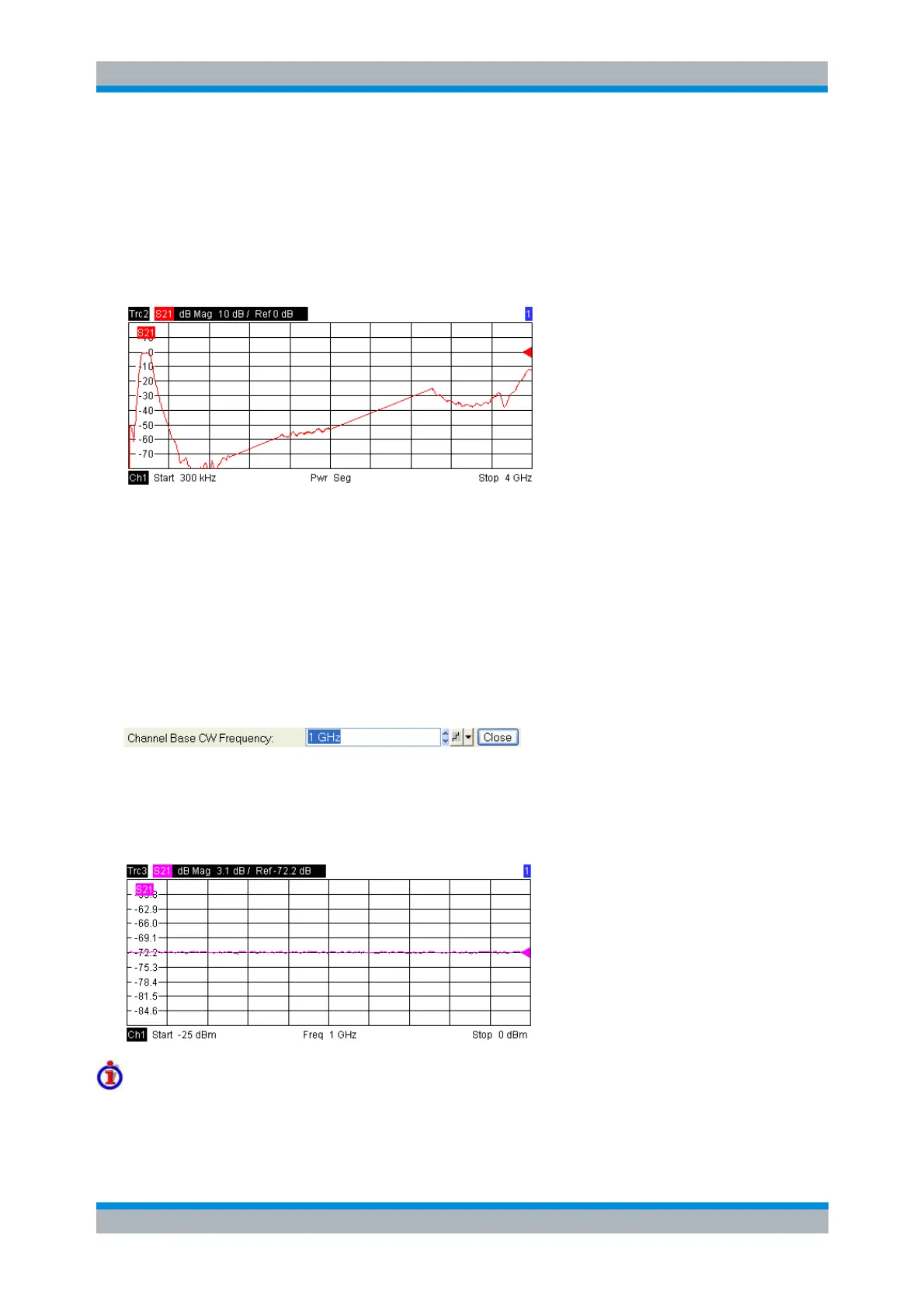
In a Power sweep the internal generator power is swept in linear, equidistant steps over a continuous
power range. The generator power range (sweep range) is defined via Channel - Stimulus - Start and
Channel - Stimulus - Stop; see Stimulus and Sweep Types. The numeric entry bar for the fixed frequency
(CW Frequency) appears as soon as Power is activated.
Power sweeps are particularly suitable for the analysis of non-linear effects (saturation, compression) on
active and passive DUTs (e.g. power amplifiers, mixers).
In a Cartesian diagram the measurement result is displayed as a trace over a dB-linear power scale. The
following example shows a Power sweep with a linear DUT:
Generator power
The power range defined for a power sweep replaces the internal generator power setting in the Power
Bandwidth Average submenu.
 Loading...
Loading...