R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT GUI Reference
Channel Menu
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 258
The analyzer tries to keep the time intervals between any two consecutive time sweep points equal: The
time sweep samples are equidistant. For unidirectional measurements, time sweeps up to the maximum
number of 60001 sweep points are generally equidistant. For measurements with 4 drive ports, you can
acquire between 18000 and 20000 equidistant results for each partial measurement. Equidistance also
holds for sweeps which range over several channels.
If equidistance is no longer ensured, a tooltip is displayed. Reduce the number of points to restore
equidistance. Equidistance is also impaired if an external power meter is active during the sweep.
Trigger settings
The Time sweep is incompatible with the Periodic Trigger: If Periodic... is selected while a time sweep is
active, the analyzer generates an error message:
To continue, click OK and select any other trigger source.
In Time sweep mode the Start, Center and Stop softkeys are inactive, still you can use the START
CENTER hardkey to select the fixed CW frequency.
[SENSe<Ch>:]SWEep:TYPE CW
[SENSe<Chn>:]FUNCtion[:ON] "XTIMe:..."
SOURce<Ch>:FREQuency<Pt>:CW|FIXed
SOURce<Ch>:POWer[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPlitude]
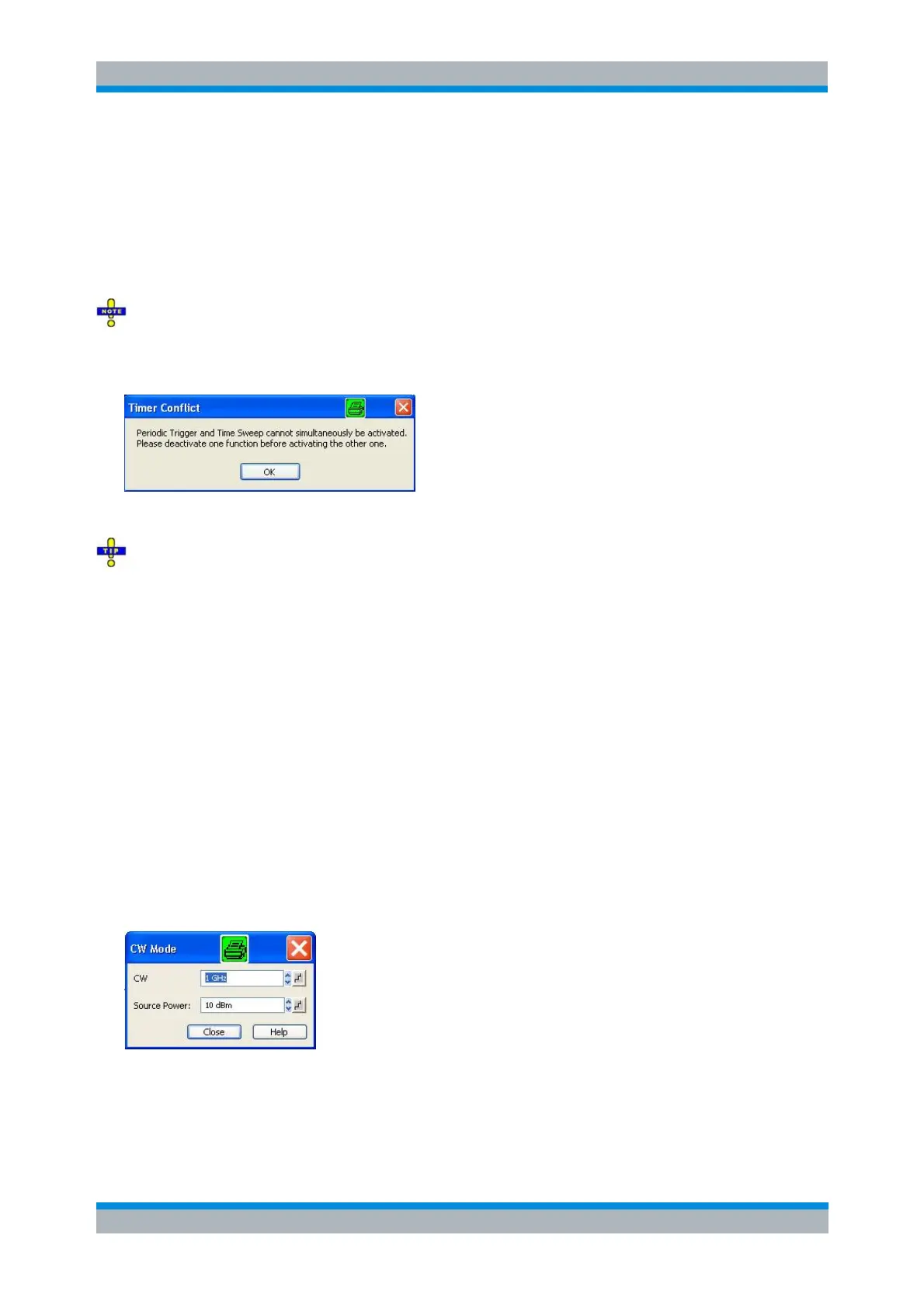
CW Mode
CW Mode sweeps, like Time sweeps, are performed at constant frequency and stimulus power. The
measurement is triggered according to the current trigger settings; each trigger event triggers the first
partial measurement of a measurement point. The total number of measurement points is defined via
Channel - Stimulus - Stop; see Stimulus and Sweep Types. The time interval between two consecutive
measurements depends on the trigger settings. Any trigger mode is allowed.
The frequency (CW) and internal generator power (Source Power) is fixed and entered into a field which
pops up as soon as CW Mode is activated.
A CW Mode sweep corresponds to the analysis of a signal over the time with a time scale and resolution
that is determined by the trigger events. In a Cartesian diagram the measurement result is displayed as a
trace over a linear time scale (oscillographic representation). The diagram is analogous to the Time
diagram. The following example shows a CW Mode sweep with a DUT that does not change its
 Loading...
Loading...