RL78/G1H CHAPTER 15 SERIAL INTERFACE IICA
R01UH0575EJ0120 Rev. 1.20 Page 512 of 920
Dec 22, 2016
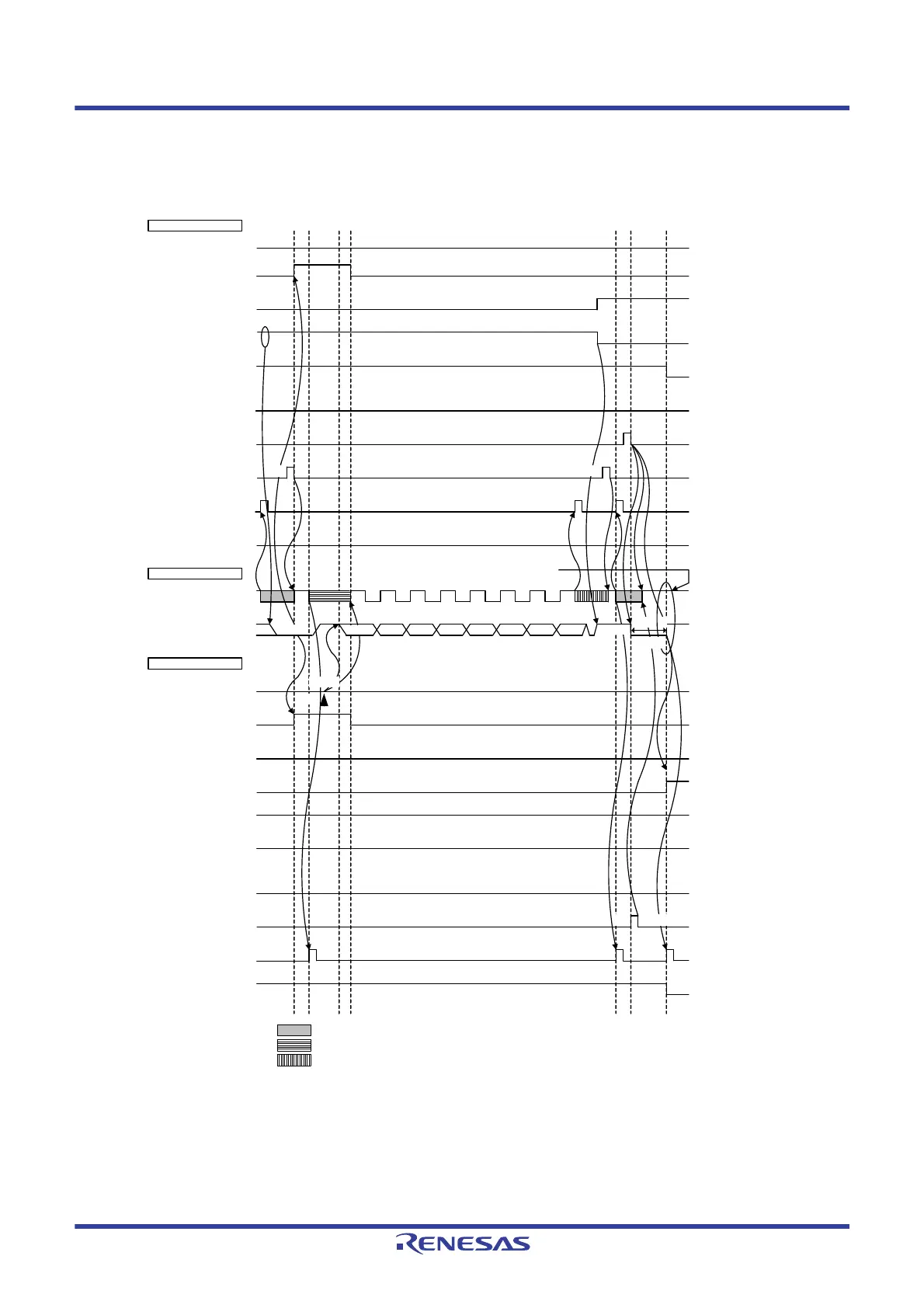
Figure 15 - 46 Example of Slave to Master Communication
(When 8-Clock and 9-Clock Wait Is Selected for Master, 9-Clock Wait Is Selected for Slave) (3/3)
(3) Data ~ data ~ stop condition
Note 1. To cancel a wait state, write “FFH” to IICAn or set the WRELn bit.
Note 2. Make sure that the time between the rise of the SCLAn pin signal and the generation of the stop condition after a stop
condition has been issued is at least 4.0
μs when specifying standard mode and at least 0.6 μs when specifying fast
mode.
Note 3. Write data to IICAn, not setting the WRELn bit, in order to cancel a wait state during transmission by a slave device.
Note 4. If a wait state during transmission by a slave device is canceled by setting the WRELn bit, the TRCn bit will be
cleared.
Remark n = 0, 1
ACKDn
(ACK detection)
IICAn
WTIMn
(8 or 9 clock wait)
ACKEn
(ACK control)
MSTSn
(communication status)
STTn
(ST trigger)
SPTn
(SP trigger)
WRELn
(wait cancellation)
INTIICAn
(interrupt)
Bus line
TRCn
(transmit/receive)
Master side
SCLAn (bus)
(clock line)
SDAAn (bus)
(data line)
Slave side
IICAn
ACKDn
(ACK detection)
STDn
(ST detection)
SPDn
(SP detection)
WTIMn
(8 or 9 clock wait)
ACKEn
(ACK control)
MSTSn
(communication status)
WRELn
(wait cancellation)
INTIICAn
(interrupt)
TRCn
(transmit/receive)
<14>
<13>
D160
: Wait state by master device
: Wait state by slave device
: Wait state by master and slave devices
D166D165D164D163D162D161
<16><8>
<15>
D150
D167
ACK
<9>
<10>
<12>
<17>
Note 4
<18>
<11>
Note 1
Note 3
Note 1
NACK
Note 2
Notes 1, 4
<19>
Stop condition
H
H
L
L
L
L

 Loading...
Loading...