User's Manual 310 Document #: LTRT-68822
Mediant 2000
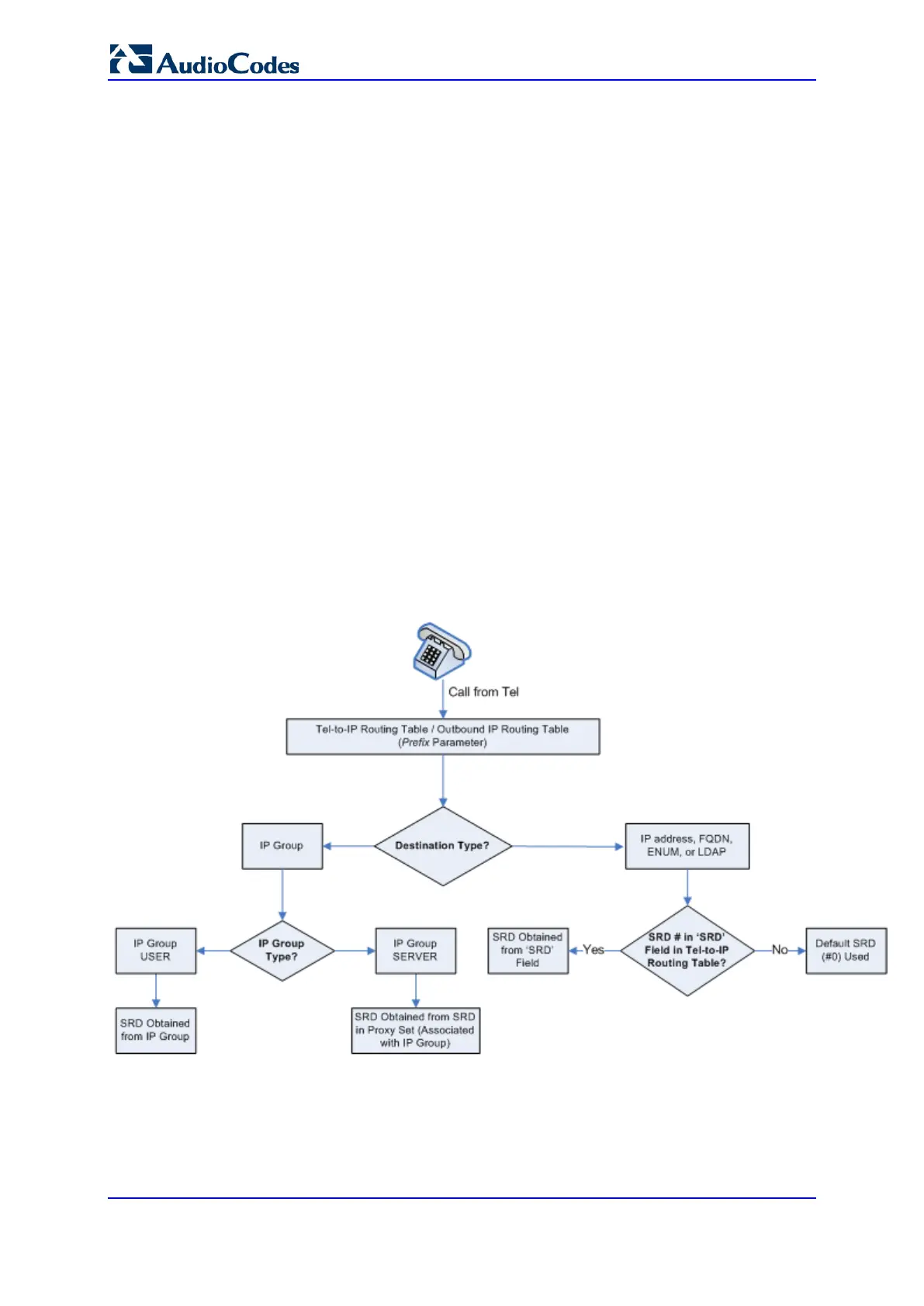
Destination: If the call matches the configured characteristics, the device routes the
call to an IP destination. If no characteristics match is found in the table, the call is
rejected. The destination can be any of the following:
• IP address in dotted-decimal notation.
• Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).
• E.164 Telephone Number Mapping (ENUM service - NRENum.net or e164.arpa).
• Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). For a description, see 'Routing
Based on LDAP Active Directory Queries' on page 183.
• IP Group, where the call is routed to the IP address configured for the Proxy Set
or SRD associated with the IP Group (configured in 'Configuring IP Groups' on
page 204). If the device is configured with multiple SRDs, you can also indicate
(in the table's 'Dest. SRD' field) the destination SRD for routing to one of the
following destination types - IP address, FQDN, ENUM, or LDAP. If the SRD is
not specified, then the default SRD (0) is used. In scenarios where routing is to
an IP Group, the destination SRD is obtained from the SRD associated with the
IP Group (in the IP Group table). The specified destination SRD determines the:
♦ Destination SIP interface (SIP port and control IP interface) - important when
using multiple SIP control VLANs
♦ Media Realm (port and IP interface for media / RTP voice)
♦ Other SRD-related interfaces and features on which the call is routed
Since each call must have a destination IP Group (even in cases where the
destination type is not to an IP Group), in cases when the IP Group is not specified,
the SRD's default IP Group is used, which is the first configured IP Group that belongs
to the SRD.
Figure 24-2: Locating SRD
 Loading...
Loading...











