Description of the Software Modules and Parameters
Parameter manual b maXX BM3000
Document no.: 5.12001.07
715
of 820
4
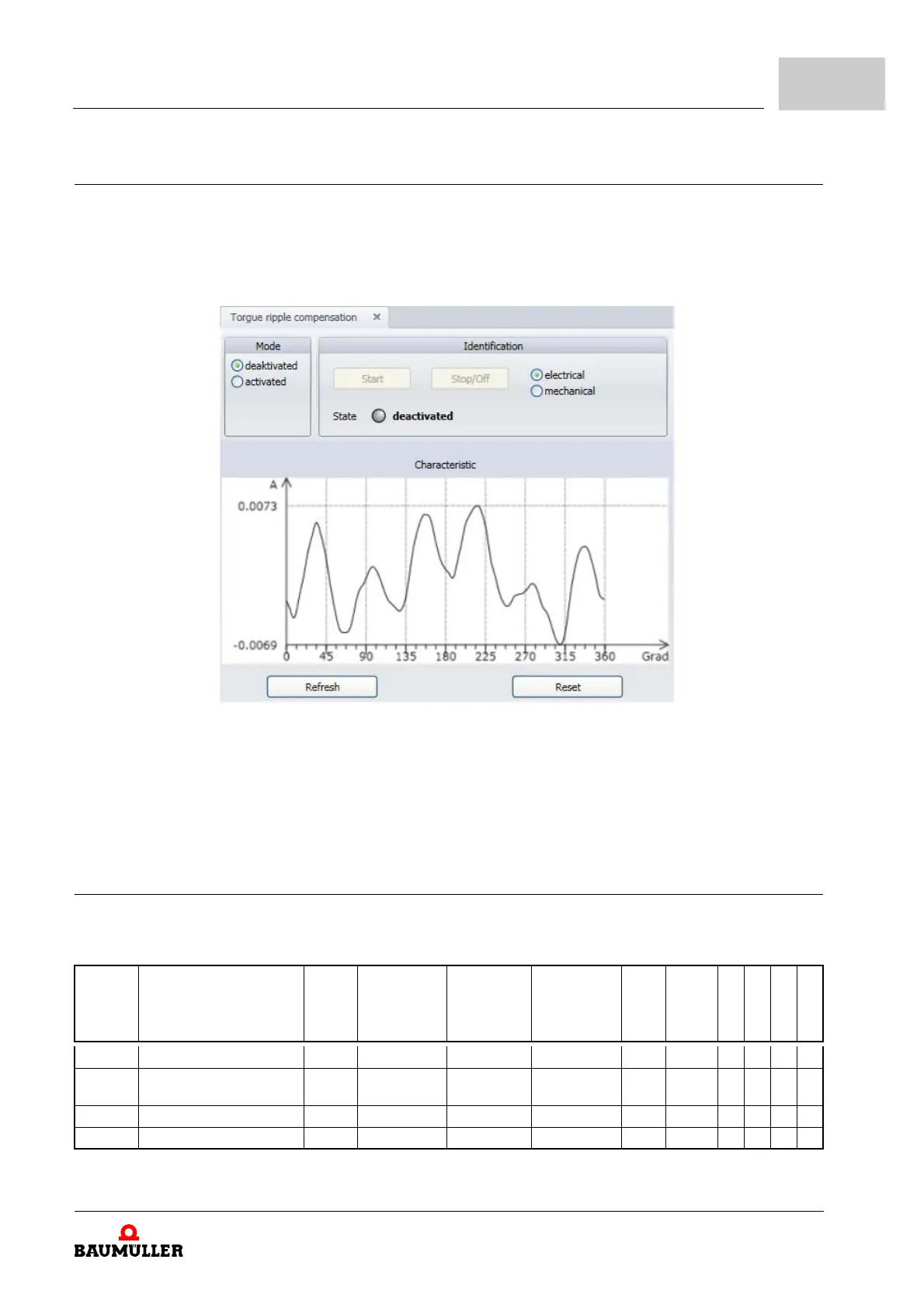
4.10.2 Torque ripple compensation
Synchronous motors normally have ripple torques. This can cause speed variations in the
speed control, because the torques cannot be adjusted quickly enough. The controller
can compensate these ripple torques. A feedforward of an additional current torque is
generated, in which an additional current torque is generated in dependence of an electric
or mechanic angle.
Figure 222: Torque ripple compensation
Before operation of the controller, an identification of the torque ripples can be made. The
required currents are measured here and then are preprocessed. Then the additional cur
-
rent set values are saved in the table.
4.10.2.1 Parameter overview
Functional block: FbOptimization [157]
Number Name Type Min Max Default Value Unit Factor
Read only
Storage
DS Support
Cyclic Write
157.1 Mode optimization UINT 0 0xFFFF 0 1:1 X
157.2 State Identification torque rip-
ple compensation
UINT 0 0xFFFF 0 1:1 X
157.3 Table torque ripple current FLOAT -1000 1000 0 A 1:1 X
157.6 Actual torque ripple current FLOAT -1000 1000 0 A 1:1 X
 Loading...
Loading...