165
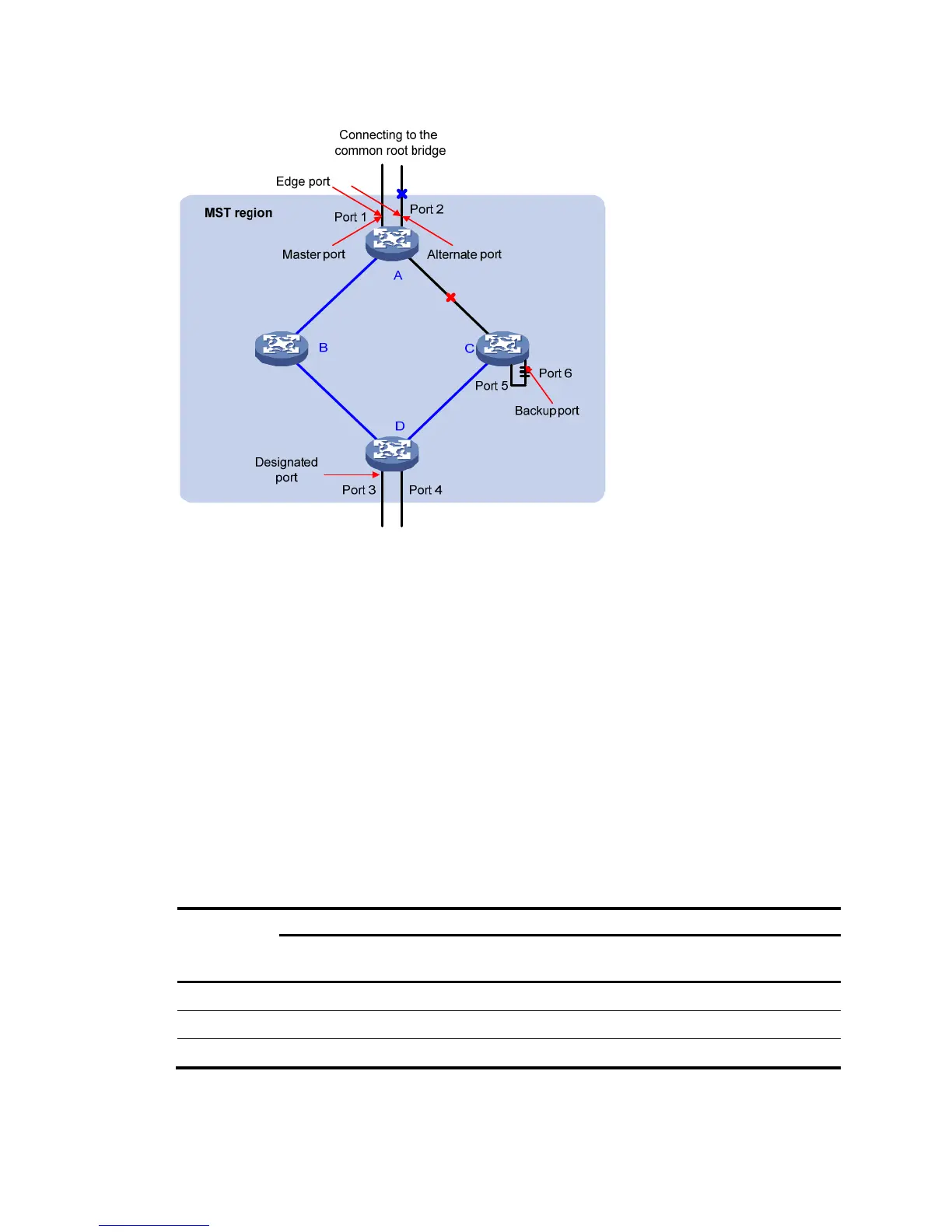
Figure 160 Port roles
In Figure 160, devices A, B, C, and D constitute an MST region. Port 1 and port 2 of device A are
connected to the common root bridge, port 5 and port 6 of device C form a loop, and port 3 and port
4 of Device D are connected downstream to the other MST regions.
Port states
In MSTP, a port can be in one of the following states:
• Forwarding—The port learns MAC addresses and forwards user traffic.
• Learning—The port learns MAC addresses but does not forward user traffic.
• Discarding—The port does not learn MAC addresses or forwards user traffic.
A port can have different port states in different MSTIs. A port state is not exclusively associated with a
port role. Table 54 lists the por
t states supported by each port role. ("√" indicates that the port state is
available for the corresponding port role, and "—" indicates that the port state is not available for the
corresponding port role.)
Table 54 Ports states supported by different port roles
Port state
Port role
Root port/master

 Loading...
Loading...











