390
AAA can be implemented through multiple protocols, such as RADIUS, HWTACACS, and LDAP. The
device supports RADIUS, which is most commonly used. For more information about RADIUS, see
"Configuring RADIUS."
Domain-based user management
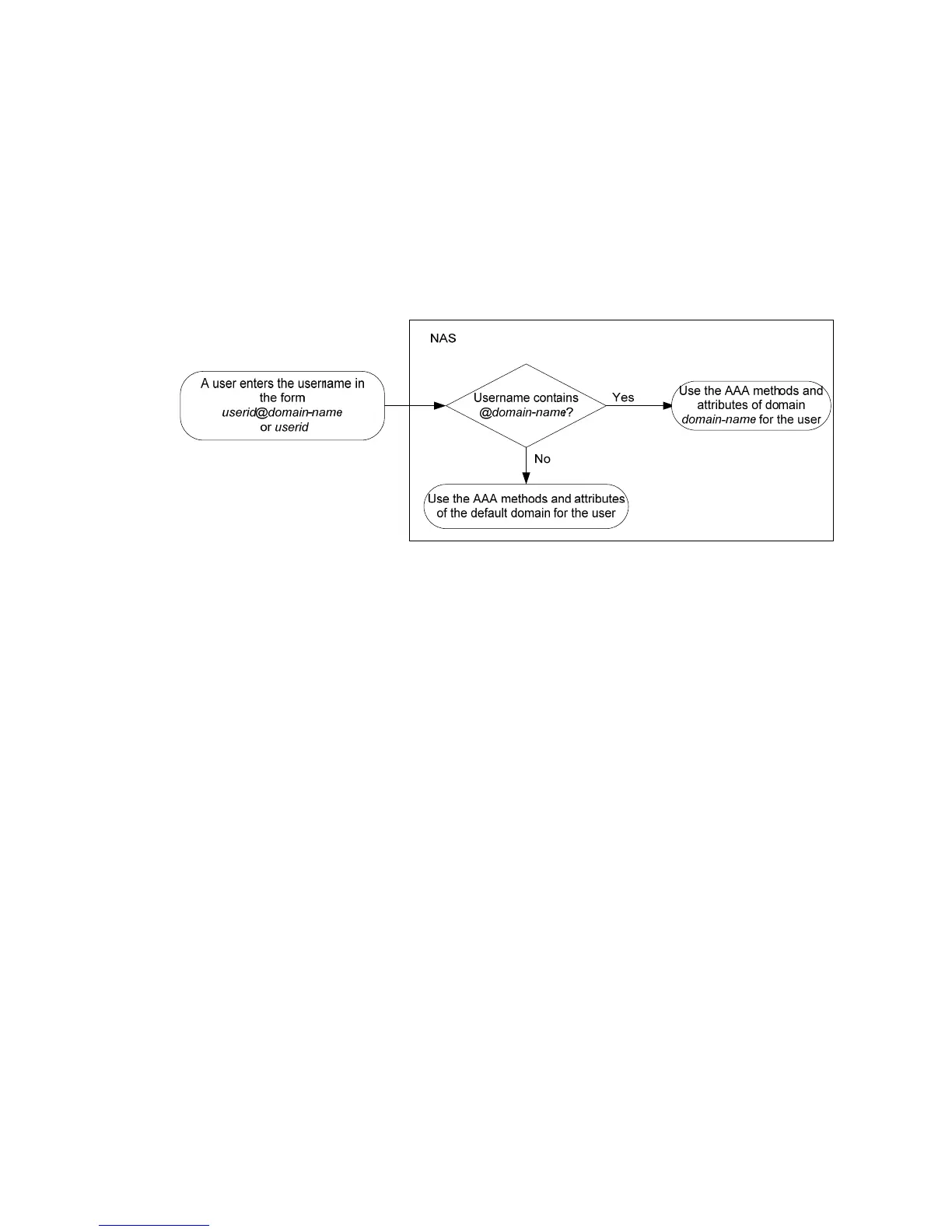
A NAS manages users based on ISP domains. On a NAS, each user belongs to one ISP domain. A NAS
determines the ISP domain for a user by the username entered by the user at login, as shown in Figure
405.
Figure 405 Det
ermining the ISP domain of a user by the username
User authentication, authorization, and accounting depends on the AAA methods configured for the
domain that the user belongs to. If no specific AAA methods are configured for the domain, the default
methods are used: local authentication, local authorization, and local accounting.
AAA allows you to manage users based on their access types:
• LAN users—Users on a LAN who must pass 802.1X or MAC address authentication to access the
network.
• Login users—Users who want to log in to the device, including SSH users, Telnet users, Web users,
FTP users, and terminal users.
• Portal users—Users who must pass portal authentication to access the network.
• PPP users—Users who access through PPP.
In addition, AAA provides command authorization for login users to improve device security. Command
authentication enables the NAS to defer to the authorization server to determine whether a command
entered by a login user is permitted for the user, and allows login users to execute only authorized
commands.
Configuration prerequisites
To deploy local authentication, configure local users on the access device. See "Configuring users."
To deploy remote authentication, authorization, or accounting, create the RADIUS schemes to be
referenced. See "Configuring RADIUS."

 Loading...
Loading...











