261
DHCP overview
After the DHCP client is enabled on an interface, the interface can dynamically obtain an IP address and
other configuration parameters from the DHCP server. This facilitates configuration and centralized
management. For more information about the DHCP client configuration, see "Configuring VLAN
in
terfaces" and "Managing interfaces."
On certain device models, if requesting for an IP address fails several times, a DHCP client enabled
interface uses a default IP address.
DHCP
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) provides a framework to assign configuration
information to network devices.
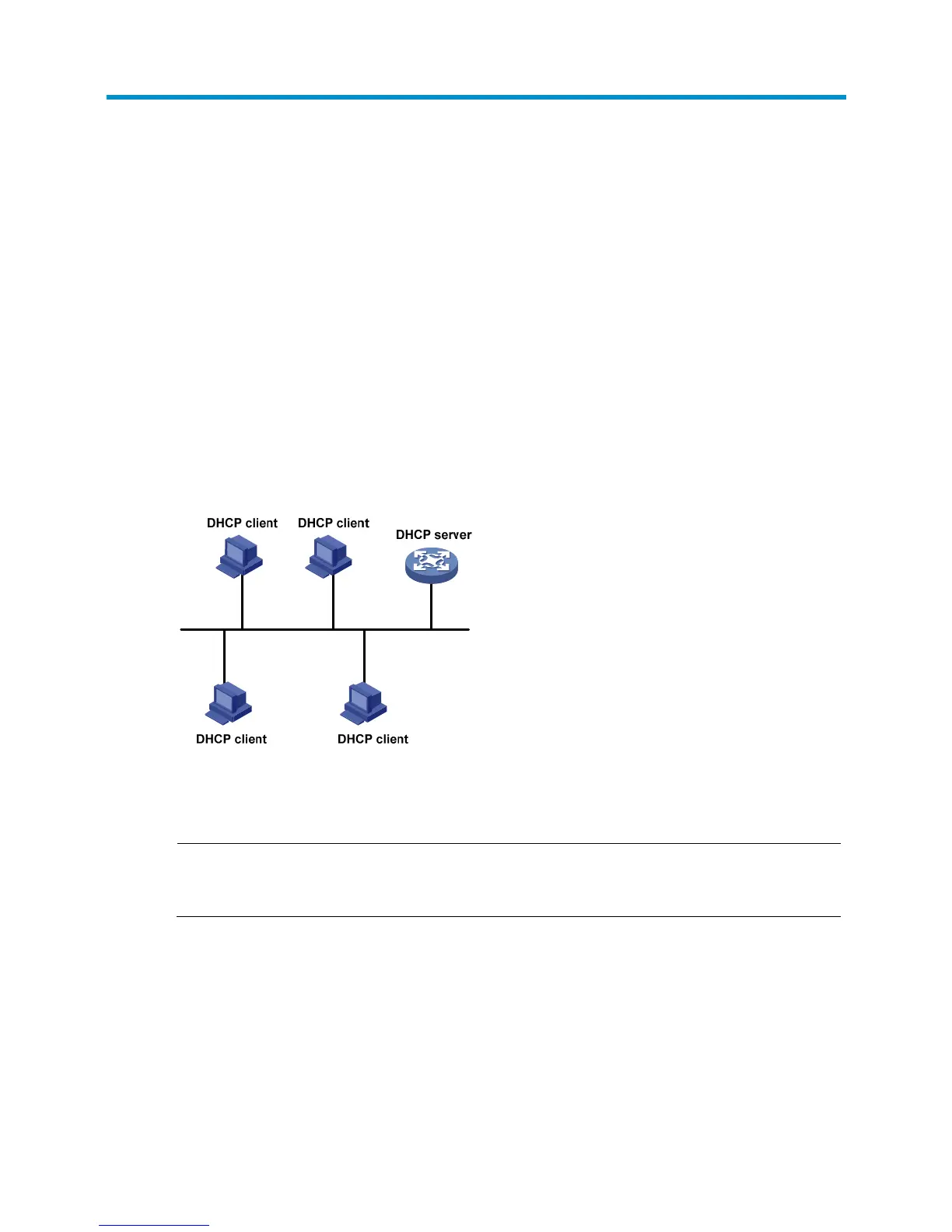
DHCP uses the client-server model. Figure 245
shows a typical DHCP application.
Figure 245 A typical DHCP application
DHCP snooping
NOTE:
The DHCP snooping-enabled device must be either between the DHCP client and relay agent, or between
the DHCP client and server. It does not work if it is between the DHCP relay agent and DHCP server.
As a DHCP security feature, DHCP snooping can implement the following:
• Recording IP-to-MAC mappings of DHCP clients
• Ensuring DHCP clients to obtain IP addresses from authorized DHCP servers
Recording IP-to-MAC mappings of DHCP clients
DHCP snooping reads DHCP-REQUEST messages and DHCP-ACK messages from trusted ports to record
DHCP snooping entries, including MAC addresses of clients, IP addresses obtained by the clients, ports
that connect to DHCP clients, and VLANs to which the ports belong.

 Loading...
Loading...











