tion
0 000 best-effort
1 001 background
2 010 spare
3 011 excellent-effort
4 100 controlled-load
5 101 video
6 110 voice
7 111 network-management
Queue scheduling
In general, congestion management uses queuing technology. The system uses a queuing algorithm for
traffic classification, and then uses a precedence algorithm to send the traffic. Each queuing algorithm
handles a particular network traffic problem and has significant impacts on bandwidth resource
assignment, delay, and jitter.
In this section, two common hardware queue scheduling algorithms are introduced: Strict Priority (SP)
queuing and Weighted Round Robin (WRR) queuing.
SP queuing
SP queuing is designed for mission-critical applications that require preferential service to reduce
response delay when congestion occurs.
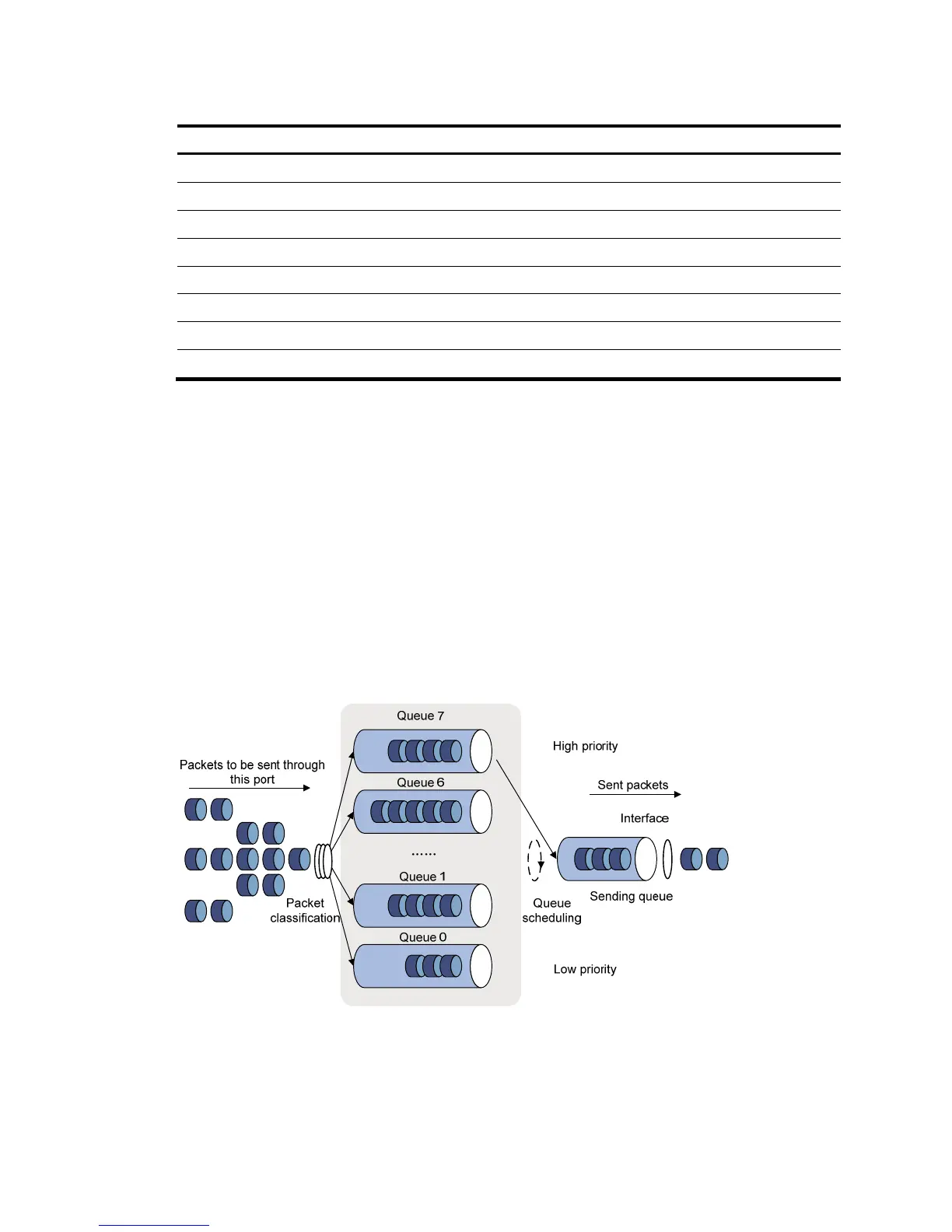
Figure 481 SP queuing
A typical switch provides eight queues per port. As shown in Figure 481, SP queuing classifies eight
queues on a port into eight classes, numbered 7 to 0 in descending priority order.
SP queuing schedules the eight queues according to the descending order of priority. It sends packets in
the queue with the highest priority first. When the queue with the highest priority is empty, it sends

 Loading...
Loading...











