Design Guide 151
EMI and Mechanical Design Considerations
11.2.2 Differential Clocking
Differential clocking requires that the clock generator supply both clock and clock-bar traces.
Clock-bar has equal and opposite current as the primary clock, and is also 180 degrees out of
phase. To maximize the benefit of differential clocking, both clock lines must be routed parallel to
each other for their entire length. Devices connected to the clock must also be designed to accept
both the clock and clock-bar signals.
EMI reduction due to differential clocking is caused by H-field cancellation. Since H-field
orientation is generated by and is dependent upon current flow, two equal currents flowing in
opposite directions and 180 degrees out of phase will have their H-fields cancelled (see
Figure 11-3). Lower H-fields will result in reduced EMI radiation.
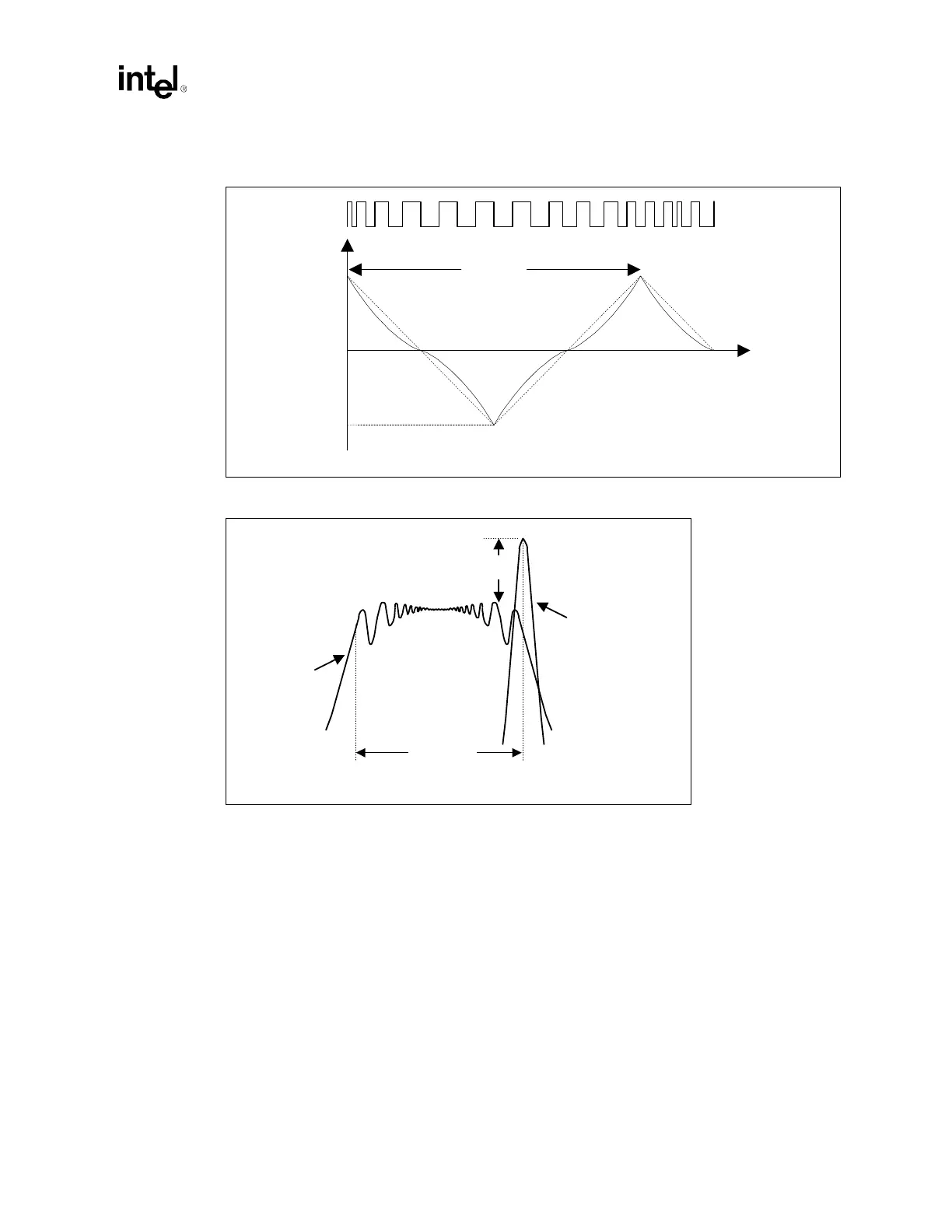
Figure 11-1. Spread Spectrum Modulation Profile
Figure 11-2. Impact of Spread Spectrum Clocking on Radiated Emissions
(1-δ)fnom
time
f
nom
1/fm
∆
SCC
non-SSC
(1-δ)f
nom
f
nom

 Loading...
Loading...











