Pump characteristics and data
l V_g:Geometricdisplacementvolume(P 2851[0](ccm/rev))
l eta_Vol,N:Volumetricefficiencyatthepump’sratingpoint(P 2851[4](%))
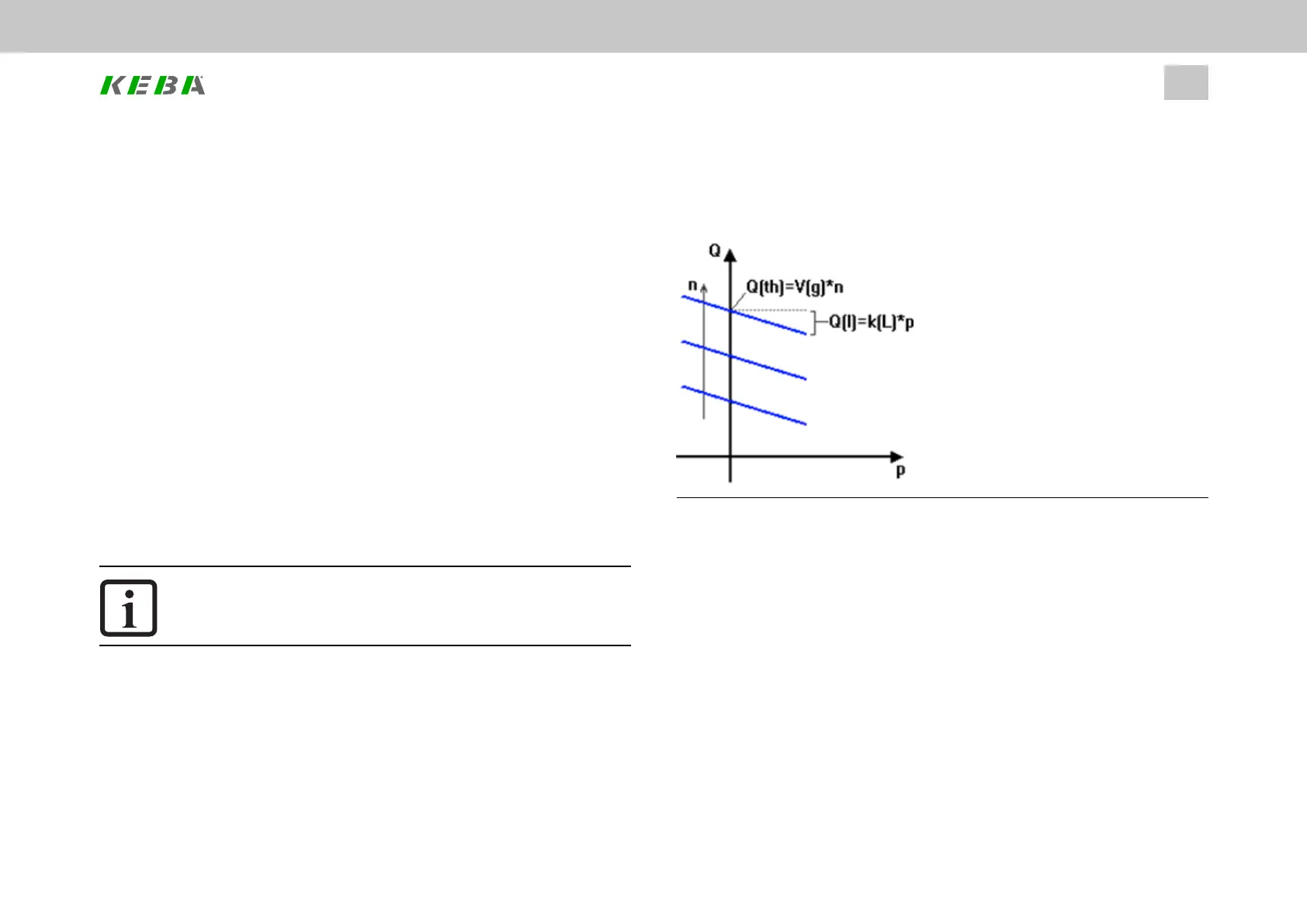
Theoretical volumetric flow rate Q_th is proportional to the speed:
l Q_th=V_g∙n
Internal pump leakage volumetric flow rate Q_L must be subtracted from the actual
volumetric flow rate:
l Q=Q_th-Q_L=V_g∙n-Q_L
It will typically be proportional to the pressure:
l Q_L=p∙k_L(ϑ)
However, pump data sheets often do not specify the leakage volume rate constant,
but instead specify a “volumetric efficiency” ηvol,N for the pump’s rated point, in
which case:
l Q_N=V_g∙n_N∙η_(vol,N)
l Q_N[l/min]=V_g[cm³/rev]∙n_N[rev/min]∙eta_(Vol,N)[100%]
NOTE
l MakesuretoconverttoSIunits!
Example
l eta_(Vol,N)=95%,n_N=1500rev/min,v_G=10cm³/rev->Q_N=
14,2l/min
ID No.: 0842.26B.5-01Date: 09.2020
ServoOne- Device Help
177
7 Control
If you specify eta_(Vol,N), the drive controller will internally calculate k_L
automatically as follows:
l k_L=V_g∙n_N∙(1-eta_(Vol,N))∙p_N
Image 7.52: Pump characteristic curves
For the torque at the pump (= motor torque):
l M=V_g/2π∙p+(M_friction);(makesuretouseSIunits)
The friction torque is normally unknown and negligible (M_friction ~ 0). This means
that a “torque constant” c_M in [Nm/bar] can be calculated using the following
formula:
l c_M[Nm/bar]=1/(20pi)*V_g[cm^3/rev]=M[Nm]/p[bar]
Displacement volume V_g is usually specified in data sheets. In contrast, if there is a
pressure measurement available, the torque constant is easier to determine
experimentally if necessary. In this case, a constant pressure can be built up on the
drive in a steady state and the delivered motor torque can be used to calculate the
displacement volume.
 Loading...
Loading...