RL78/G1H CHAPTER 15 SERIAL INTERFACE IICA
R01UH0575EJ0120 Rev. 1.20 Page 466 of 920
Dec 22, 2016
Figure 15 - 31 shows the Communication Reservation Timing.
Figure 15 - 31 Communication Reservation Timing
Remark IICAn: IICA shift register n
STTn: Bit 1 of IICA control register n0 (IICCTLn0)
STDn: Bit 1 of IICA status register n (IICSn)
SPDn: Bit 0 of IICA status register n (IICSn)
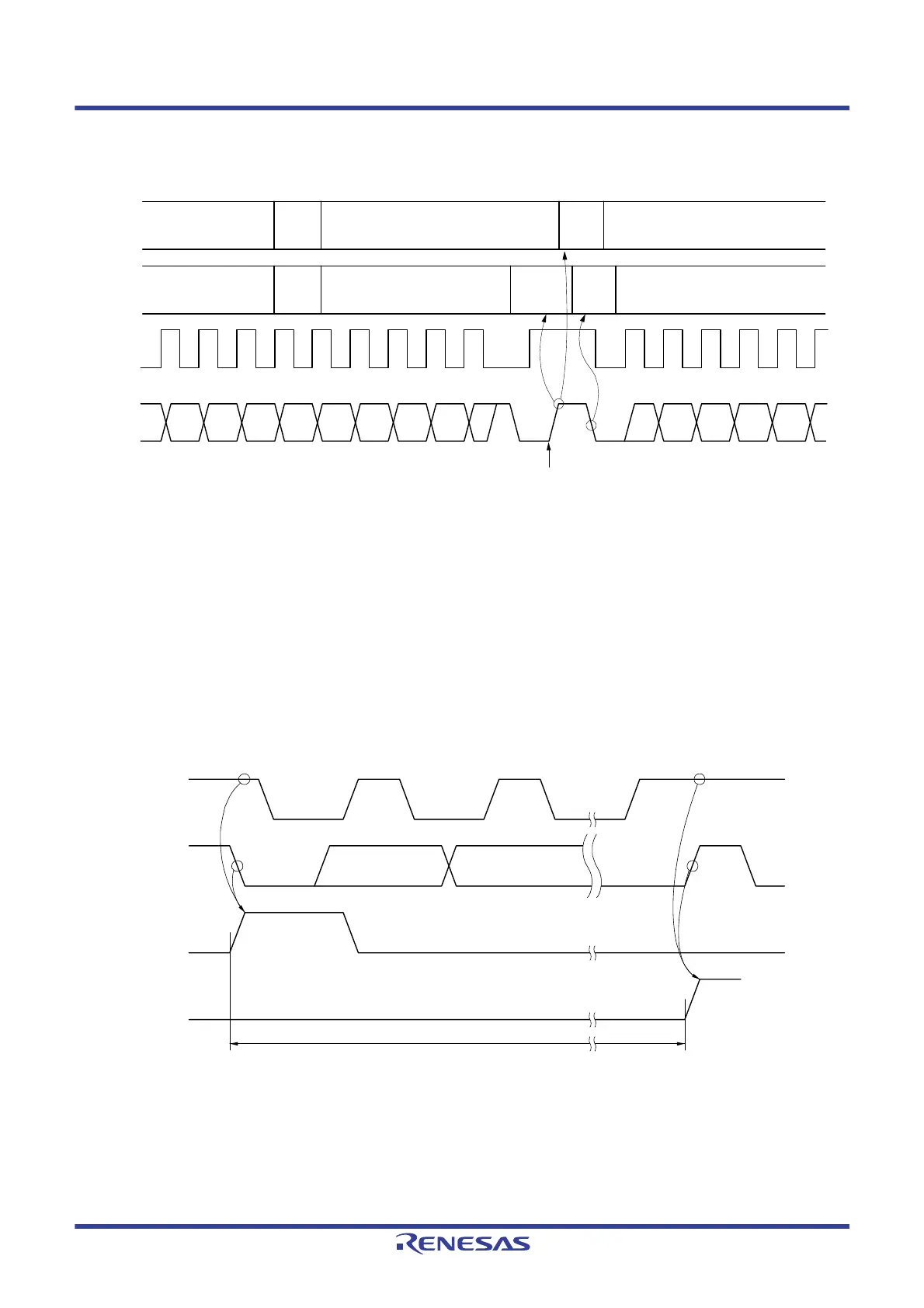
Communication reservations are accepted via the timing shown in Figure 15 - 32. After bit 1 (STDn) of the IICA
status register n (IICSn) is set to 1, a communication reservation can be made by setting bit 1 (STTn) of IICA
control register n0 (IICCTLn0) to 1 before a stop condition is detected.
Figure 15 - 32 Timing for Accepting Communication Reservations
Remark n = 0, 1
1SCLAn
SDAAn
Program processing
Hardware processing
Generate by master device with bus mastership
STTn = 1
Write to
IICAn
Communication
reservation
Set SPDn
and
INTIICAn
Set
STDn
23456789 123456
SCLAn
SDAAn
STDn
SPDn
Standby mode (Communication can be reserved by setting STTn to 1 during this period.)

 Loading...
Loading...