Engineering via SICAM WEB
SICAM RTUs, User Manual SICAM CMIC 241
DC8-001-2.09, Edition 08.2016
5.2.1.2 Syntax for Instructions
5.2.1.2.1 General
Each instruction command must be in one line. Each line must be concluded with a paragraph
break, line break or both (done automatically by the text editor).
An instruction command consists of the command (operation) and an operand.
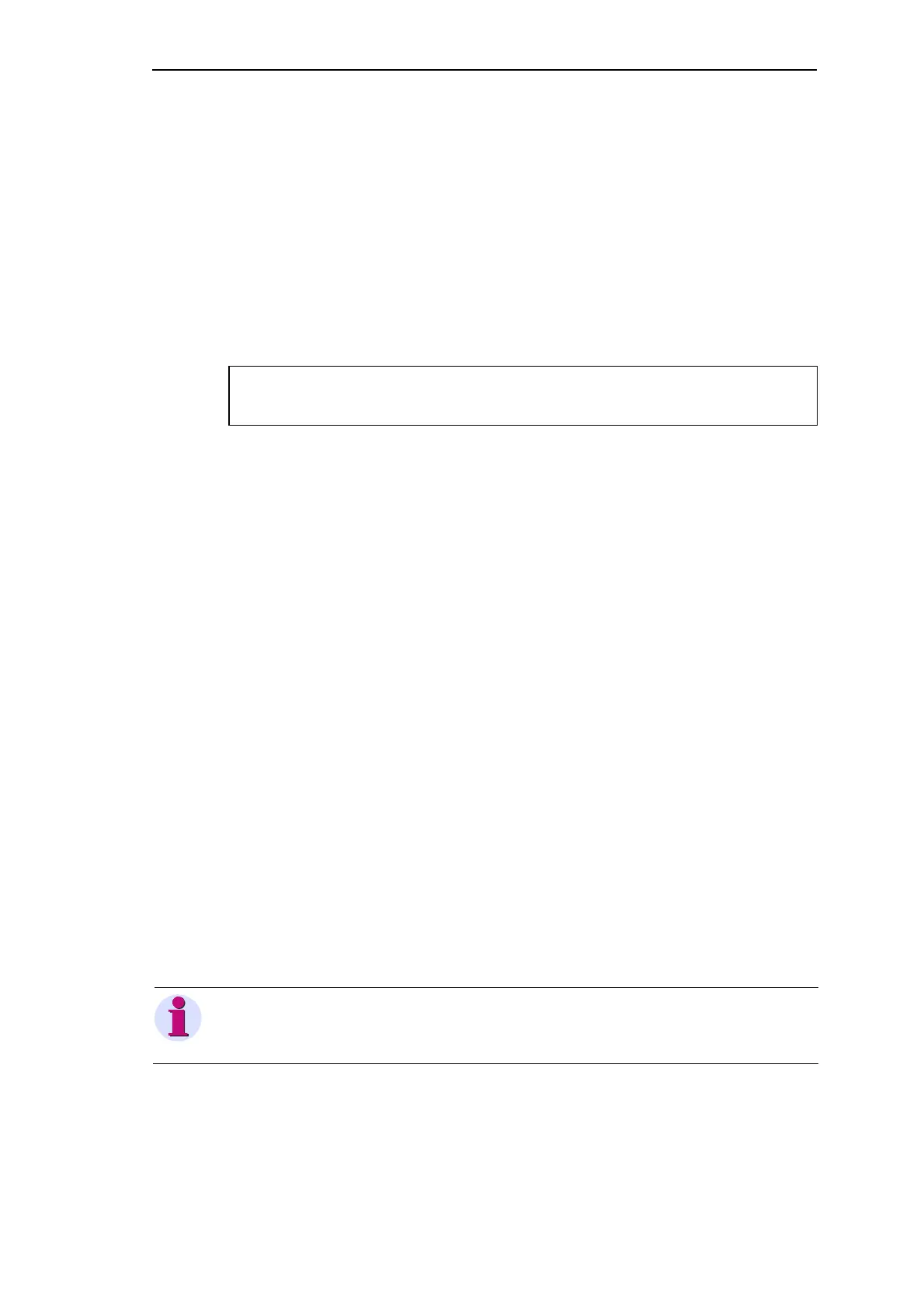
Example:
LD M_BOOL_TEST (*command: LD operand: M_BOOL_TEST*)
Each operation produces a calculated value (result). The following operation can calculate fur-
ther with this result.
5.2.1.2.2 Adressing of I/O Variables
The format of an I/O variable must correspond with the respective input/output of the periph-
ery.
A command or setpoint value is assigned to an I/O variable by an ST operation and the ad-
dress of the operand. A state or value of an I/O variable is read by an LD operation and the
address of the operand.
Example for the simple syntax:
I_030_001_000_000_TEST.VALUE
0_031_005_001_000.OFF
Example for the expanded syntax:
E_045_001_001_001_002_003_TEST.VALUE or
E_045_001_001_001_002_003.VALUE
The attribute of the I/O variable must be separated by a ".". An I/O variable without attribute is
not allowed.
Note
If the same IOA is used input- and output side, the freely definable Name must be different.
Special signs are not allowed.

 Loading...
Loading...