6241A/6242 DC Voltage Current Source/Monitor Operation Manual
5.1.3 Preventing Oscillation
5-4
5.1.3 Preventing Oscillation
The 6241A/6242 itself may oscillate due to cases where the tested device itself oscillates, or the capaci-
tance or inductance exceeding the specified value is connected
(due to stray capacitance or retained inductance from connected cables, a scanner, or a fixture).
With the oscillation frequency, the difference between the oscillations of the device and that of the 6241A/
6242 is evident. The 6241A/6242 does not oscillate at 2 MHz or over.
5.1.3.1 Preventing 6241A/6242 Oscillation
1. Causes of Oscillation
• Oscillation may occur because of the capacitive load while the voltage source or voltage-limiter
is activated.
• Oscillation may occur because of the inductive load while the current source or current-limiter
is activated.
2. Solution
Remove the causes of oscillation by following the procedure below.
1. Verify if the load capacitance and load inductance are within the maximum load
capacitance and the maximum load inductance indicated in Chapter 9, “SPECI-
FICATIONS.”
2. Check if the 6241A/6242 still oscillates when cables of the shortest lengths are
connected.
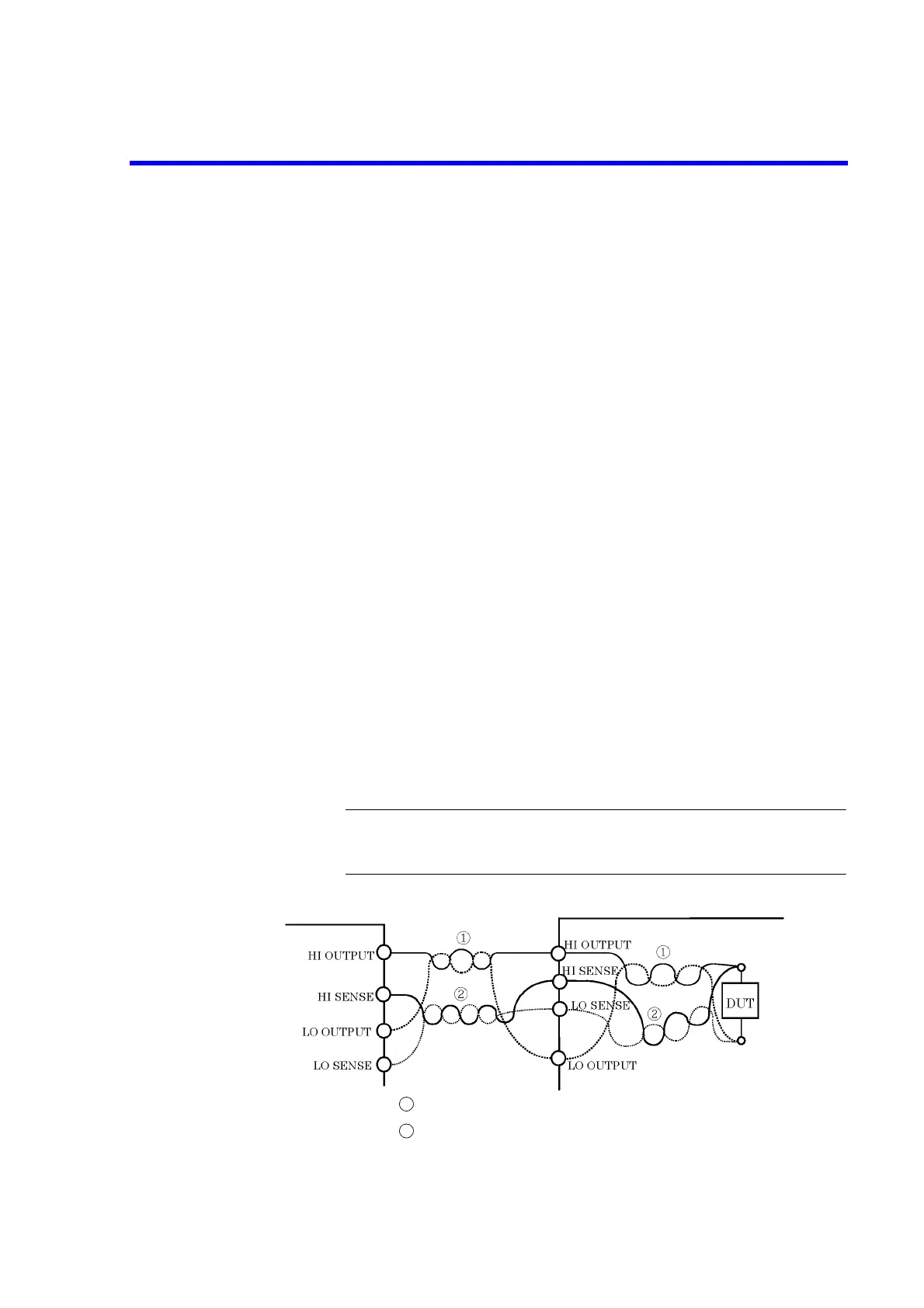
3. If the shorter cables stop the oscillation, then connect the 6241A/6242 and DUT
as shown in Figure 5-3 to reduce the capacitance and inductance of cables and
other devices.
4. If the oscillation does not stop even if the cables are the shortest possible, insert
an allowable resistor for a load as shown in Figure 5-5.
NOTE: When more than one power supply unit is used, oscillation in one unit may
cause oscillation in other units. Then find the particular power supply that
may stop the oscillation, following the procedure in 1 to 4 above.
Figure 5-3 Reducing Stray Capacitance and Lead Inductor
6241A/6242
Wire HI OUTPUT and LO OUTPUT in twisted pairs.
Wire HI SENSE and LO SENSE in twisted pairs.
1
2

 Loading...
Loading...