Operation Manual – Multicast Protocol
Quidway S3900 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 7 PIM Configuration
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
7-3
Server
Multicast
User A
User B
User C
User D
User E
Source
Receiver
Receiver
Receiver
packets
SPT
Prune
Prune
Prune
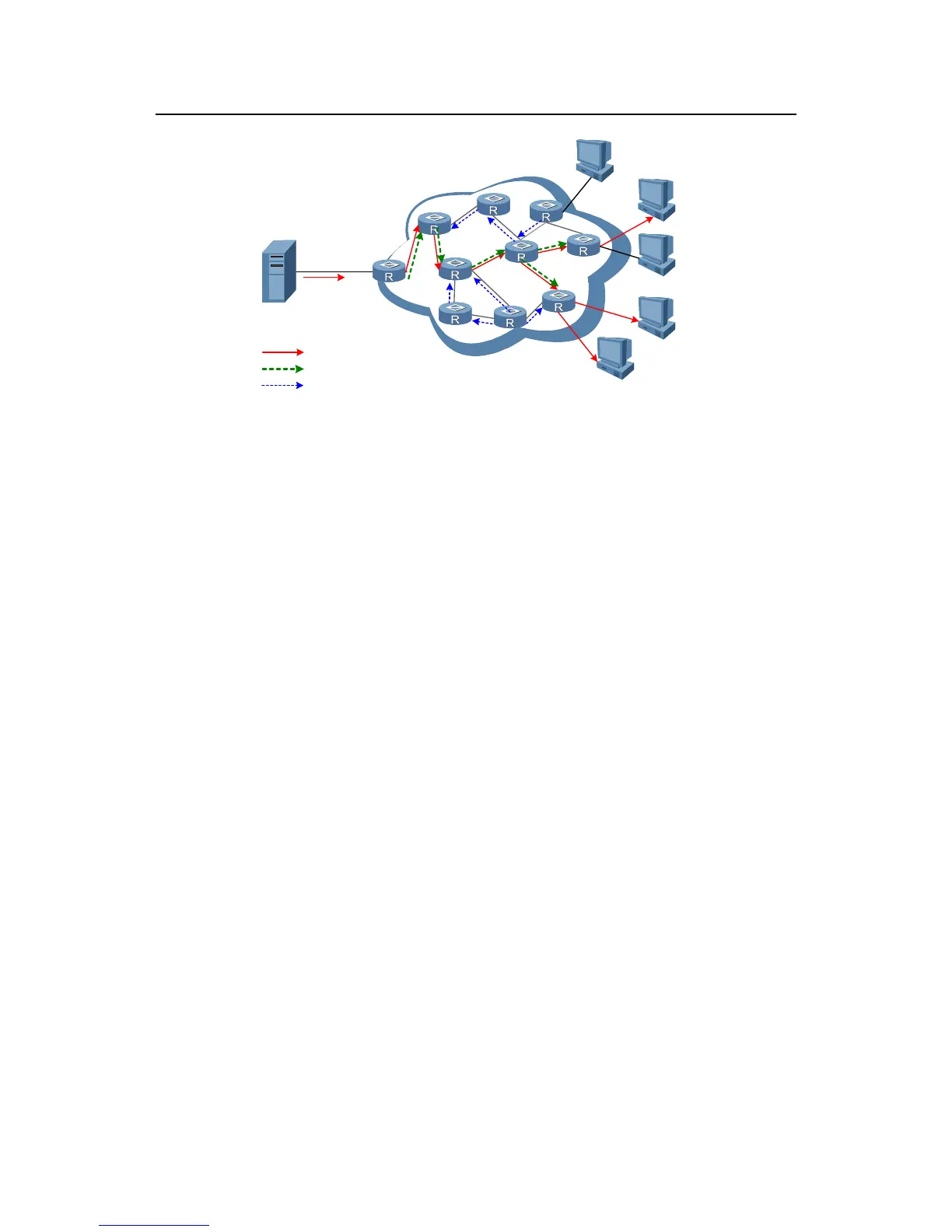
Figure 7-1 Diagram for SPT establishment in PIM-DM
The process above is called "Flooding and Pruning". Every pruned node also provides
timeout mechanism. If pruning behavior times out, the router will initiate another
flooding and pruning process. This process is performed periodically for PIM-DM.
III. Graft
When a pruned downstream node needs to be restored to the forwarding state, it may
send a graft packet to inform the upstream node. As shown in
Figure 7-1, user A
receives multicast data again. Graft messages will be sent hop by hop to the multicast
source S. The intermediate nodes will return acknowledgements when receiving Graft
messages. Thus, the pruned branches are restored to the information transmission
state.
IV. RPF check
PIM-DM adopts the RPF check mechanism to establish a multicast forwarding tree
from the data source S based on the existing unicast routing table, static multicast
routing table, and MBGP routing table.
The procedure is as follows:
z When a multicast packet arrives, the router first checks the path.
z If the interface this packet reaches is the one along the unicast route towards the
multicast source, the path is considered as correct.
z Otherwise, the multicast packet will be discarded as a redundant one.
The unicast routing information on which the path judgment is based can be of any
unicast routing protocol such as RIP or OSPF. It is independent of the specified unicast
routing protocol. The static multicast routing table needs to be configured manually, and
the MBGP routing table is provided by the MBGP protocol.

 Loading...
Loading...








