Operation Manual - DHCP
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 2
DHCP Server Configuration
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
2-10
You can configure domain names to be used by DHCP clients for address pools. After
you do this, the DHCP server provides the domain names to the DHCP clients as well
while the former assigns IP addresses to the DHCP clients.
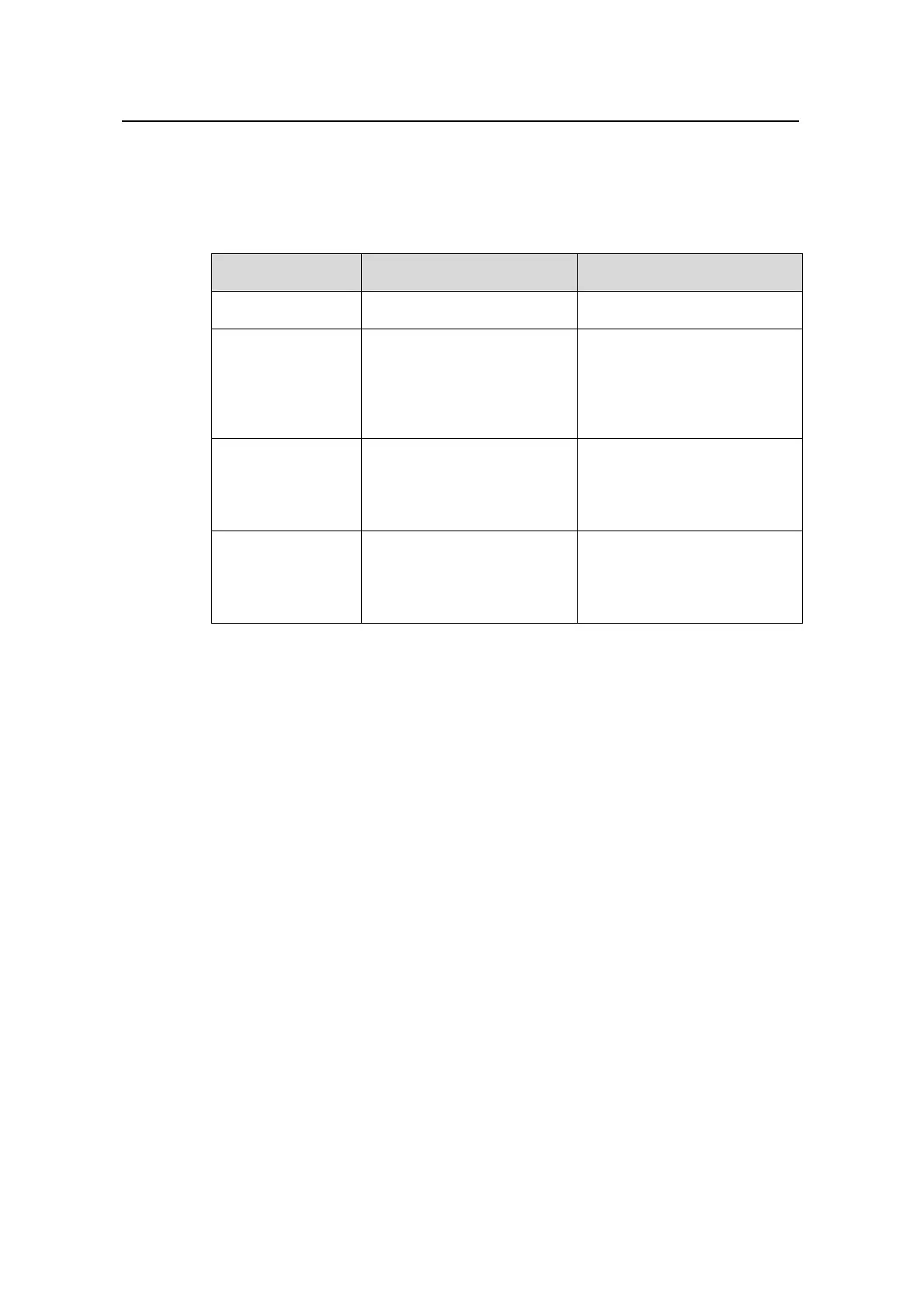
Table 2-6 Configure DNS services for the DHCP server
Operation Command Description
Enter system view
system-view
—
Create a DHCP
address pool and
enter DHCP
address pool view
dhcp server ip-pool
pool-name
Required
By default, no global DHCP
address pool is created
Configure a
domain name for
DHCP clients
domain-name
domain-name
Required
By default, no domain name is
configured for DHCP clients
Configure DNS
server addresses
for DHCP clients
dns-list ip-address&<1-8>
Required
By default, no DNS server
address is configured
2.2.6 Configuring NetBIOS Services for the DHCP Server
For Microsoft Windows-based DHCP clients that communicate through NetBIOS
protocol, the host name-to-IP address translation is carried out by Windows internet
naming service (WINS) servers. So you need to perform WINS-related configuration
for most Windows-based hosts. Currently, you can configure up to eight WINS
addresses for a DHCP address pool.
Host name-to-IP address mappings are needed for DHCP clients communicating
through NetBIOS protocol. According to the way to establish the mapping, NetBIOS
nodes fall into the following four categories:
z B-node. Nodes of this type establish their mappings through broadcasting (The
character b stands for the word broadcast). The source node obtains the IP
address of the destination node by sending the broadcast packet containing the
host name of the destination node. After receiving the broadcast packet, the
destination node returns its IP address to the source node.
z P-node. Nodes of this type establish their mappings by sending unicast packets
to WINS servers. (The character p stands for peer-to-peer). The source node
sends the unicast packet to the WINS server. After receiving the unicast packet,
the WINS server returns the IP address corresponding to the destination node
name to the source node.

 Loading...
Loading...











