Operation Manual – Routing Protocol
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 5 BGP Configuration
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
5-5
5.1.2 BGP Route Attributes
I. Routes attributes classification
BGP route attributes describe route, so that BGP can filter and choose the routes.
In fact, all the BGP route attributes can be classified into the following four categories.
z Well-known mandatory attributes, which can be identified by any BGP routers.
Route attributes of this type are carried in Update messages. Without these
attributes, routing information goes wrong.
z Well-known discretionary attributes, which can be identified by any BGP routers.
An Update message can travel with or without this type of attributes.
z Optional transitive attributes, which can be transmitted among ASs. Although
attributes of this type may not be supported by any BGP routers, routes with them
can still be received and be forwarded to BGP speakers.
z Optional non-transitive attributes, which is dropped on the BGP routers that do not
support them. In this case, the attributes are not forwarded to other BGP routers.
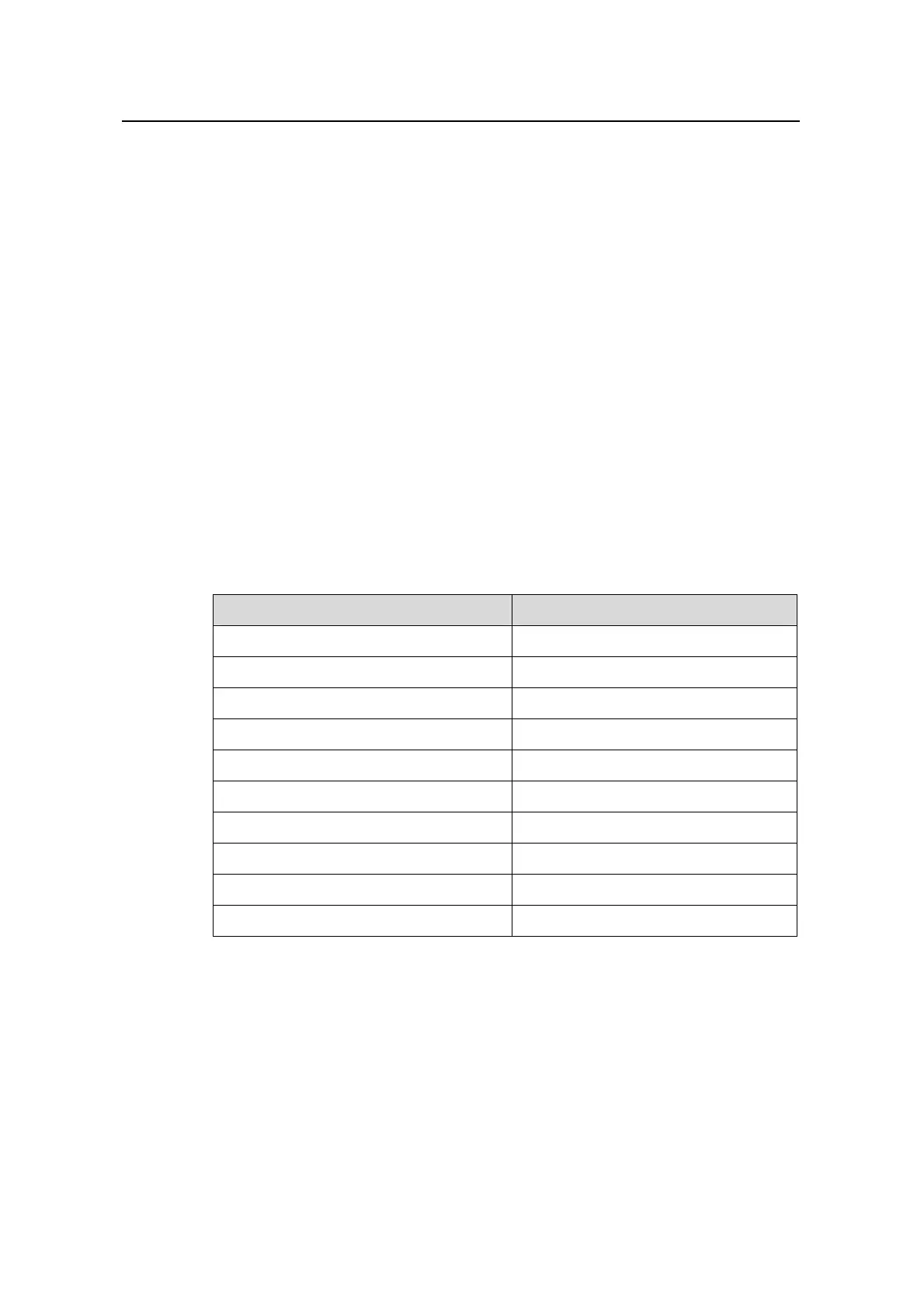
Table 5-1 lists basic BGP route attributes and the categories they belong to.
Table 5-1 BGP route attributes and the corresponding categories
BGP route attribute Category
Origin Well-known mandatory
As_Path Well-known mandatory
Next_Hop Well-known mandatory
Local_Pref Well-known discretionary
Atomic_Aggregate Well-known discretionary
Aggregator Optional transitive
Community Optional transitive
Multi_Exit_Disc(MED) Optional non-transitive
Originator_ID Optional non-transitive
Cluster_List Optional non-transitive
II. Primary route attributes
1) Origin
The Origin attribute holds the source of routing information. It indicates how a route
becomes a BGP route. The following describes the possible values of the Origin
attribute.
z IGP: BGP routes with their Origin attributes being IGP have the highest priority.
They are added to the BGP routing table through the network command.

 Loading...
Loading...











