Chapter 1 Specications Check 1.2 Mechanical Specications
57
[Example for Duty Calculation for TTA]
In below, shows an example for operation of the four-axis model TTA-A4SLG-WA-50-50-15B///.
Example 1) X-axis
Calculate the duty of when;
Set Payload Mr [kg] : 30 [kg]
Set Acceleration / Deceleration αr [G] : 0.15 [G]
Transported Weight at Operation M [kg] : 30 [kg]
Acceleration / Deceleration at Operation α [G] : 0.15 [G]
Stroke St [mm] : 500 [mm]
Set Velocity V [mm/s] : 600 [mm/s]
Positioning convergence time [s] : 0.15 [s]
Check the operation pattern in a).
Reached Velocity Vmax [mm/s] = √[Stroke St ×Set Acceleration α ]
= √[ St [mm] x 9,800 [mm/s
2
] ×Set Acceleration α [G] ] [mm/s]
= √[ 500 x 9800 x 0.15] = 857 [mm/s]
Set Velocity V < Reached Velocity Vmax …1) Trapezoid Pattern
Figure out the load factor LF in b).
Load Factor LF = (M x α) / (Mr x αr) [%]
= (30 x 0.15 x 9800) / (30 x 0.15 x 9800) = 1 (100 [%])
Figure out the acceleration/deceleration time ta (tb) /
constant velocity range movement distance S / cycle time tcr.
Acceleration / Deceleration Time ta(tb) = [Set Velocity V [mm/s] /
Acceleration / deceleration at operation α [mm/s
2
] ] = [ 600 / (0.15x9800) ] = 0.41 [s]
Acceleration/deceleration movement distance Sa (Sb) =
(Acceleration / deceleration at operation α[G] x 9800 [mm/s
2
]) x
(Acceleration/deceleration time ta (tb) [s])
2
/ 2 = (0.15 x 9800) x 0.41
2
/ 2 = 123.55 [mm]
Acceleration/deceleration Time Ratio
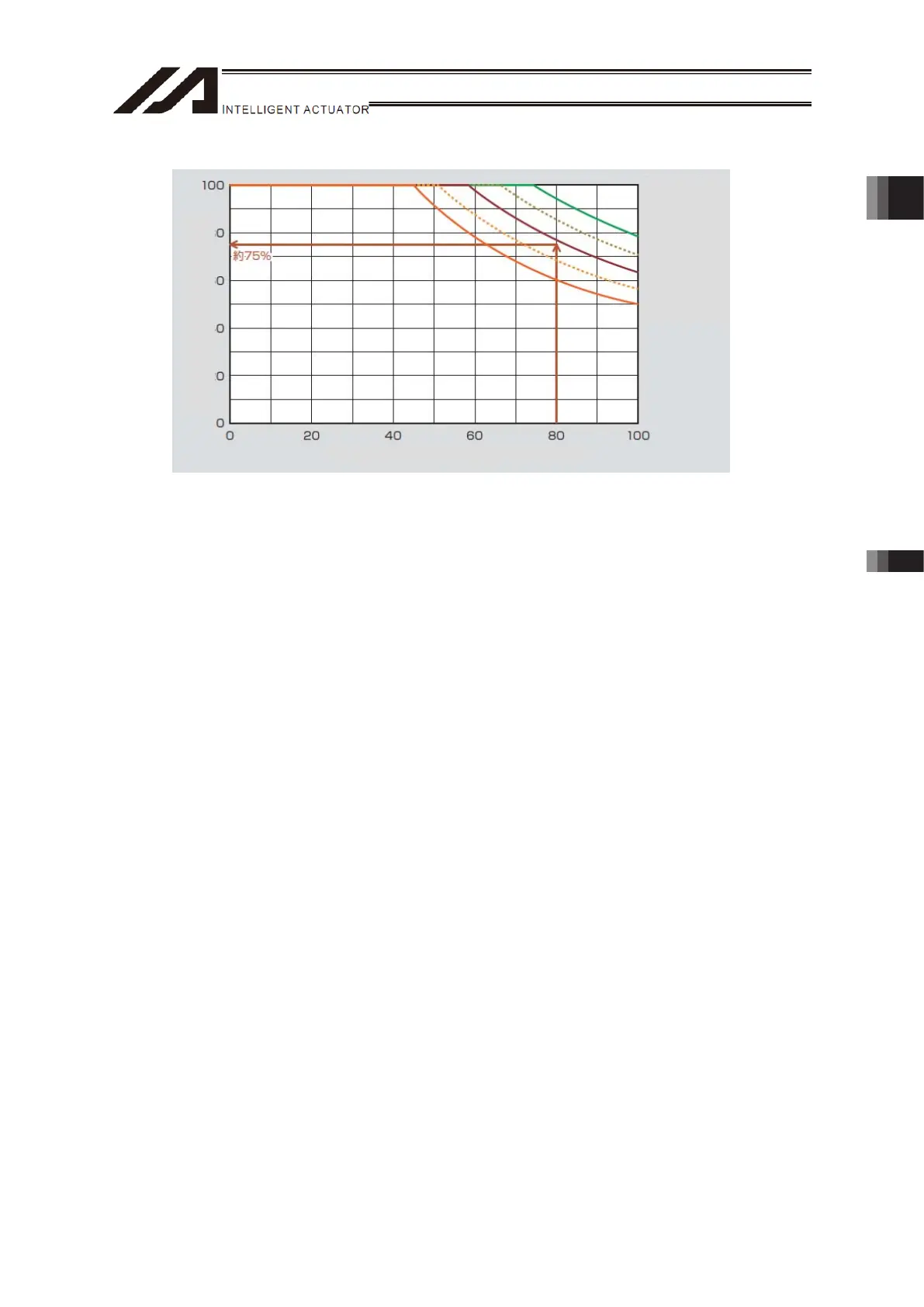
Reference for Duty of the Operation
LF=50% less than
LF=50% less than
LF=50% less than
LF=50% less than
LF=50% less than
LF=50% less than

 Loading...
Loading...