Chapter 1 Specications Check1.3 Electrical Specications
62
1.3.1 Protection Circuit
Although there are fuses mounted in this robot for purpose of protecting the circuit, it is not what a
customer can replace.
With sufficient margin in design, it is a rear case that the fuses get broken, but please make sure to
set up a breaker shown below external before starting to use.
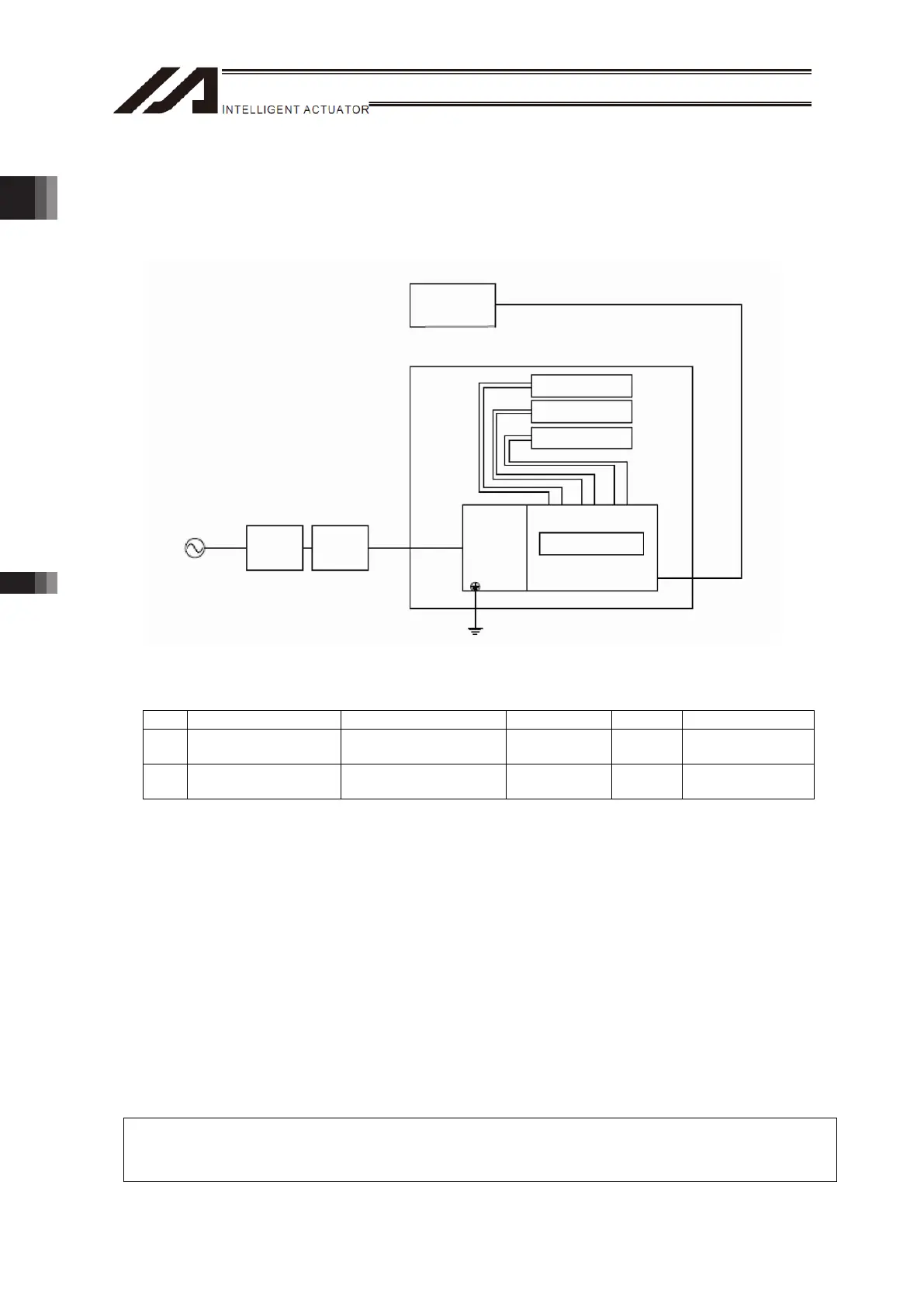
The figure shows the case of three-axis type. Take the same countermeasure for two-axis type.
[Example for protection equipment in order to secure safety]
No. Name Model Manufacturer Quantity Remarks
1) Circuit Breaker (1) NF32-SVF-3P-15A Mitsubishi 1
AC100/200V
Input common
2) Leakage Breaker (1)
NV32-SVF-3P-15A-
AC100-240V-30mA-CE
Same as
above
1
AC100/200V
Input common
* Number in brackets ( ) show the drawing number described later.
[1] Selection of Circuit Breaker
Follow the description below for selection of the circuit breaker.
• 3 times of the rated current may flow to the controller during the acceleration/deceleration.
Select one that would not trip when this current flows.
If it trips, select a breaker in rated current one rank higher.
(Check in the operation characteristics curve shown in the supplier catalog)
• Select one that would not trip at in-rush current.
(Check in the operation characteristics curve shown in the supplier catalog)
• Select a rated cutoff current with the current value that can cut off the flow of current even when
short-circuit current flows.
Rated cutoff current > Short-circuit current = Primary current amperage / Power voltage
Have margin to select the rated current of a circuit breaker.
Rated current of circuit breaker>
(Rated Motor Power Capacity [VA] + Control Power Capacity [VA]) ÷ AC Input Voltage ×Margin (1.2
to 1.4 for reference)
Single-phase
C100/200V
Circuit
breaker
Leakage
breaker
1
2)
Protection Grounding (PE)
TT controller
Power
supply
connector
Actuato
Actuator
Actuator
Host controller
DeviceNet/CC-Link/PROFIBUS/Ethernet
Network connector

 Loading...
Loading...