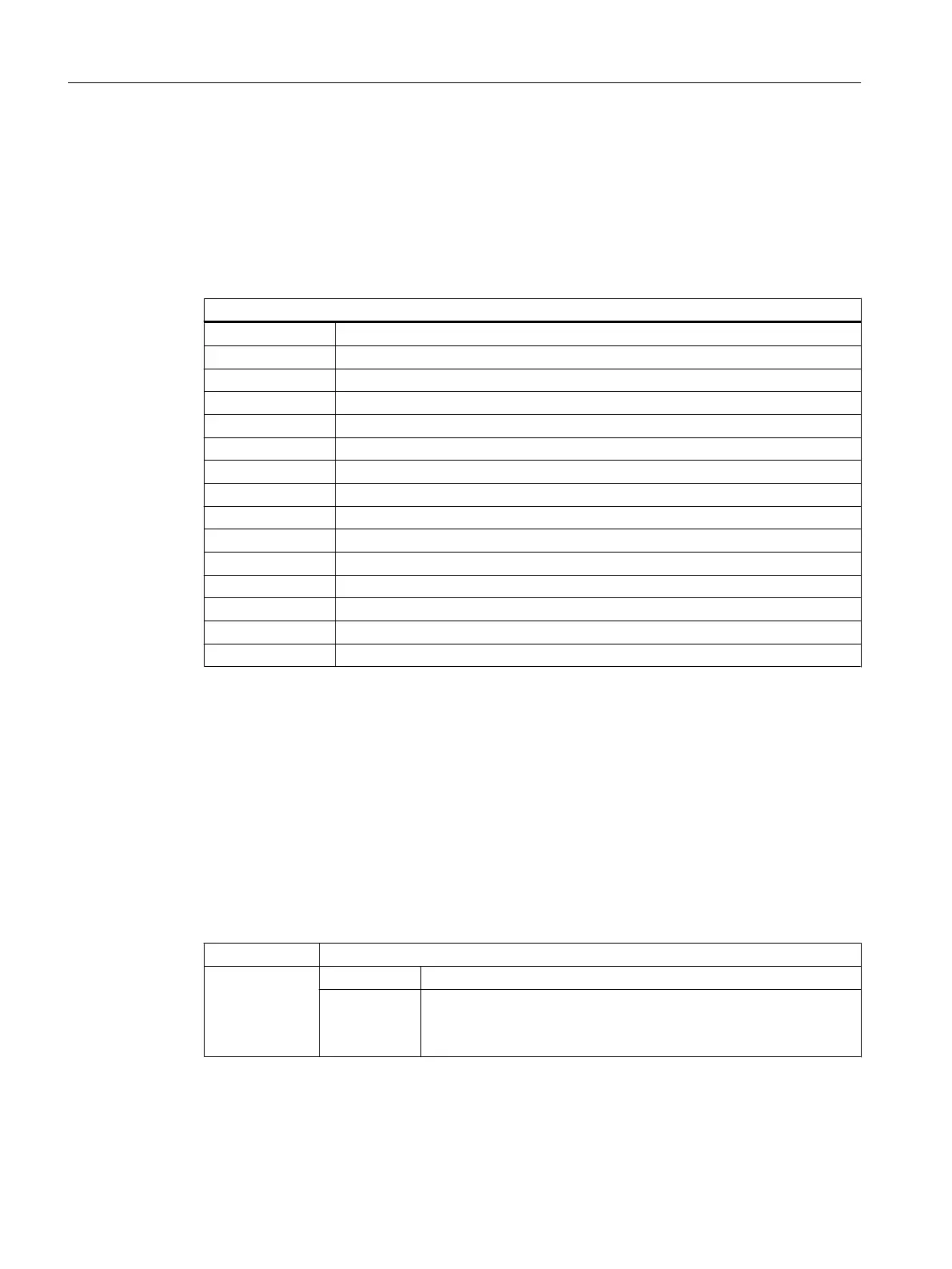
Sequence of characters in the INTEGER data type
1.
"I" Basic INTEGER designation
2. Display format
3. Memory utilization
4. "U" Unsigned
Valid INTEGER type specifications:
IB Integer variable 32 bits in binary notation
IBD Integer variable 32 bits in binary notation
IBW Integer variable 16 bits in binary notation
IBB Integer variable 8 bits in binary notation
I Integer variable 32 bits in decimal notation signed
IDD Integer variable 32 bits in decimal notation signed
IDW Integer variable 16 bits in decimal notation signed
IDB Integer variable 8 bits in decimal notation signed
IDDU Integer variable 32 bits in decimal notation unsigned
IDWU Integer variable 16 bits in decimal notation unsigned
IDBU Integer variable 8 bits in decimal notation unsigned
IH Integer variable 32 bits in hexadecimal notation
IHDU Integer variable 32 bits in hexadecimal notation
IHWU Integer variable 16 bits in hexadecimal notation
IHBU Integer variable 8 bits in hexadecimal notation
VARIANT variable type
The VARIANT variable type is determined by the data type of the last value assignment. If the
assigned or entered value starts with '-', '+', '.' or a number ('0'-'9'), then the value is interpreted
as numeric. In all other cases as a string.
It can be scanned using the ISNUM or ISSTR functions. The VARIANT type is mainly suited
to the purpose of writing either variable names or numerical values to the NC code.
Programming
The data type of variables can be checked:
Syntax: ISNUM
(VAR)
Parameter:
VAR Name of the variable whose data type is to be checked.
FALSE =
TRUE =
The result of the scan can be:
not a numerical variable (data type = STRING)
numerical variable (data type = REAL)
Variables
5.11 Details on the variable type
SINUMERIK Integrate Run MyScreens
76 Programming Manual, 10/2015, 6FC5397-3DP40-5BA3

 Loading...
Loading...


















