Inter-integrated circuit (I2C) interface RM0440
1896/2126 RM0440 Rev 4
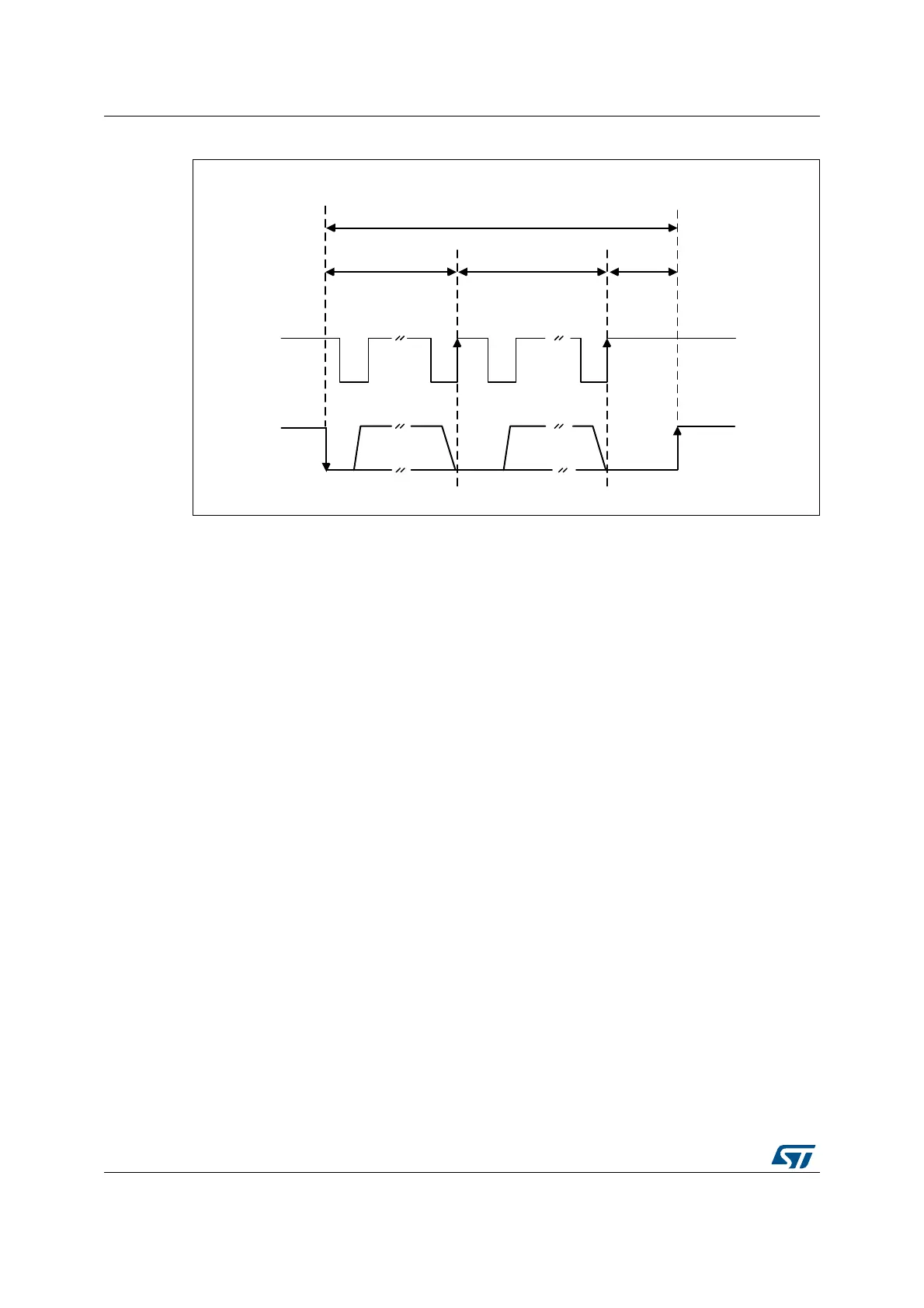
Figure 652. Timeout intervals for t
LOW:SEXT
, t
LOW:MEXT
.
Bus idle detection
A master can assume that the bus is free if it detects that the clock and data signals have
been high for t
IDLE
greater than t
HIGH
,
MAX
. (refer to Table 377: I2C-SMBus specification data
setup and hold times)
This timing parameter covers the condition where a master has been dynamically added to
the bus and may not have detected a state transition on the SMBCLK or SMBDAT lines. In
this case, the master must wait long enough to ensure that a transfer is not currently in
progress. The peripheral supports a hardware bus idle detection.
41.4.12 SMBus initialization
This section is relevant only when SMBus feature is supported. Refer to Section 41.3: I2C
implementation.
In addition to I2C initialization, some other specific initialization must be done in order to
perform SMBus communication:
Received Command and Data Acknowledge control (Slave mode)
A SMBus receiver must be able to NACK each received command or data. In order to allow
ACK control in slave mode, the Slave Byte Control mode must be enabled by setting the
SBC bit in the I2C_CR1 register. Refer to Slave Byte Control mode on page 1873 for more
details.
MS19866V1
Start Stop
t
LOW:SEXT
t
LOW:MEXT
t
LOW:MEXT
t
LOW:MEXT
Clk
Ack
Clk
Ack
SMBCLK
SMBDAT

 Loading...
Loading...