2-6 IM 701450-01E
Relationship between the Specified Record Length, Time Axis Setting, Sample
Rate, and Display Record Length
If you change the time axis setting with respect to the specified record length of the
acquisition memory, the sample rate and display record length change. (For more
details about this relationship, see appendix 1.
Relationship between the Time Axis Setting and Sampling Mode
Depending on the time axis setting, you can switch the mode used to sample the input
signal (sampling mode). The time axis settings that allow the sampling mode to be
changed vary depending on the acquisition mode and other settings. For details, see
appendix 1.
Realtime Sampling Mode
Changing the time axis setting changes the sample rate. Data can be sampled at up to 2
GS/s (1 GS/s when interleave mode is OFF. For a description of interleave mode, see
section 2.4). The input signal is sampled sequentially, and the data is stored in the
acquisition memory. In this mode, the DL7400 can only display waveforms correctly up
to one-half the frequency of the sample rate (the number of samples per second, in units
of S/s) as defined by the sampling theorem.* Therefore, this mode is best suited for
observing waveforms whose frequency is low relative to the sample rate.
* If the sample rate is comparatively low with respect to the input signal frequency, the
harmonics contained in the signal are lost. In this case, some of the harmonics will appear at
low frequencies due to the effects described by the Nyquist sampling theorem. This
phenomenon is called
aliasing
. You can prevent aliasing by acquiring waveforms with the
acquisition mode set to envelope.
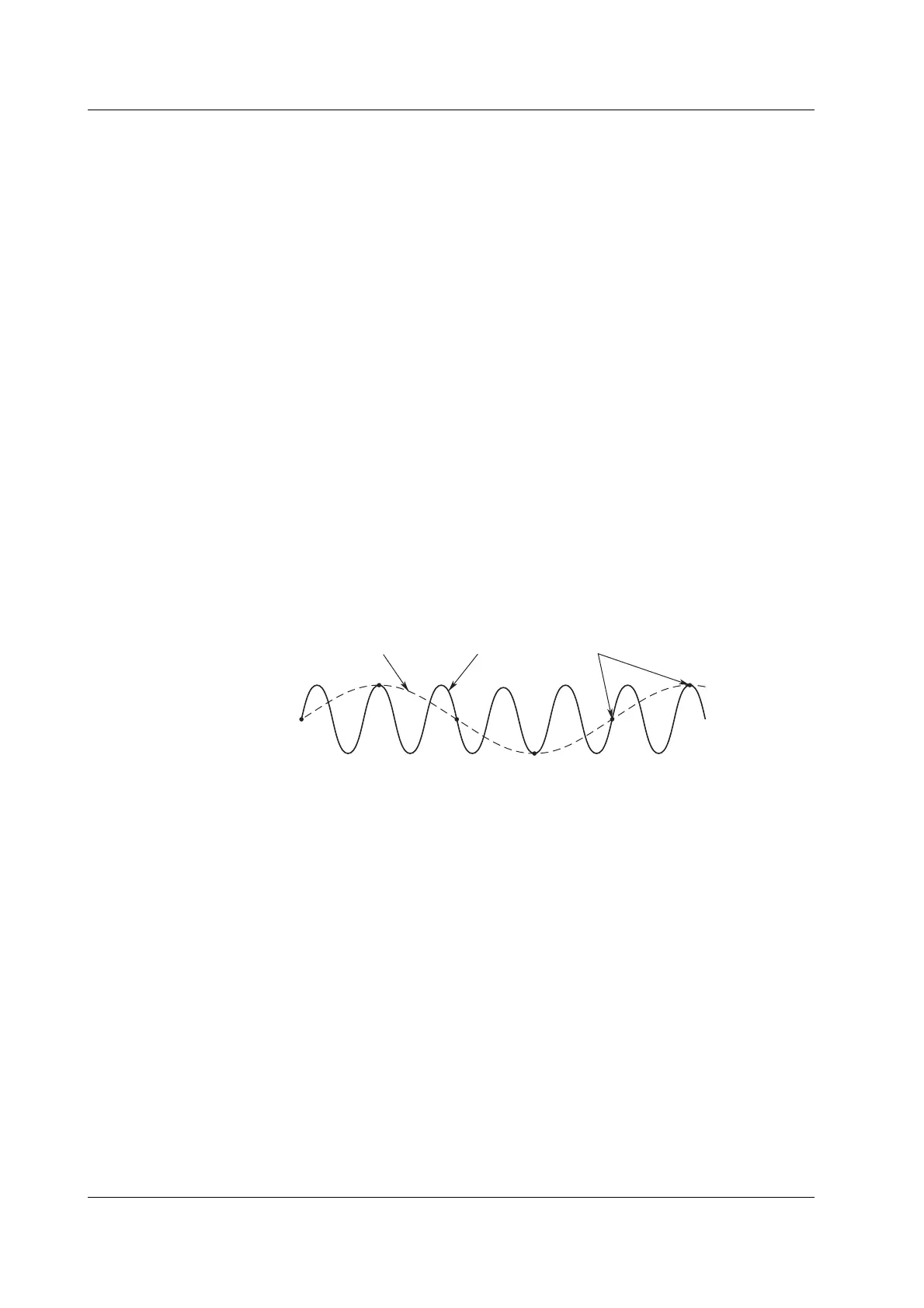
Aliased signal Input signal Sampling point
Repetitive Sampling Mode
In repetitive sampling mode, you can set the time axis to a setting that will cause the
sample rate to exceed 2 GS/s (5 GS/s when interleave mode is ON). In this mode, one
waveform is created from several cycles of a repetitive signal. This is equivalent to
sampling the signal at a higher sample rate than the actual sample rate. The maximum
apparent sample rate is 100 GS/s on the DL7400. In addition, even in realtime sampling
mode, if the relationship of the time axis and the display record length would cause the
sample rate to exceed 2 GS/s (5 GS/s when interleave mode is ON), the mode
automatically switches to repetitive sampling.
There are two types of repetitive sampling. One is
sequential sampling
in which the data
is sampled by intentionally offsetting the sampling points by a certain time with respect to
the trigger point. The other is
random sampling
in which the data that is offset randomly
from the trigger point is sampled and resorted with respect to the trigger point. The
DL7400 employs random sampling which enables the waveform before the trigger point
(trigger position, see section 2.3) to be observed.
2.2 Vertical and Horizontal Axes

 Loading...
Loading...