14.2 Measurement Range and Accuracy
347
14
Chapter 14 Specifications
• Impedance (Z=50 ) basic accuracy
(For example) Measurement conditions: measurement frequency=10 kHz, measurement speed=SLOW2
Example calculation of basic accuracy
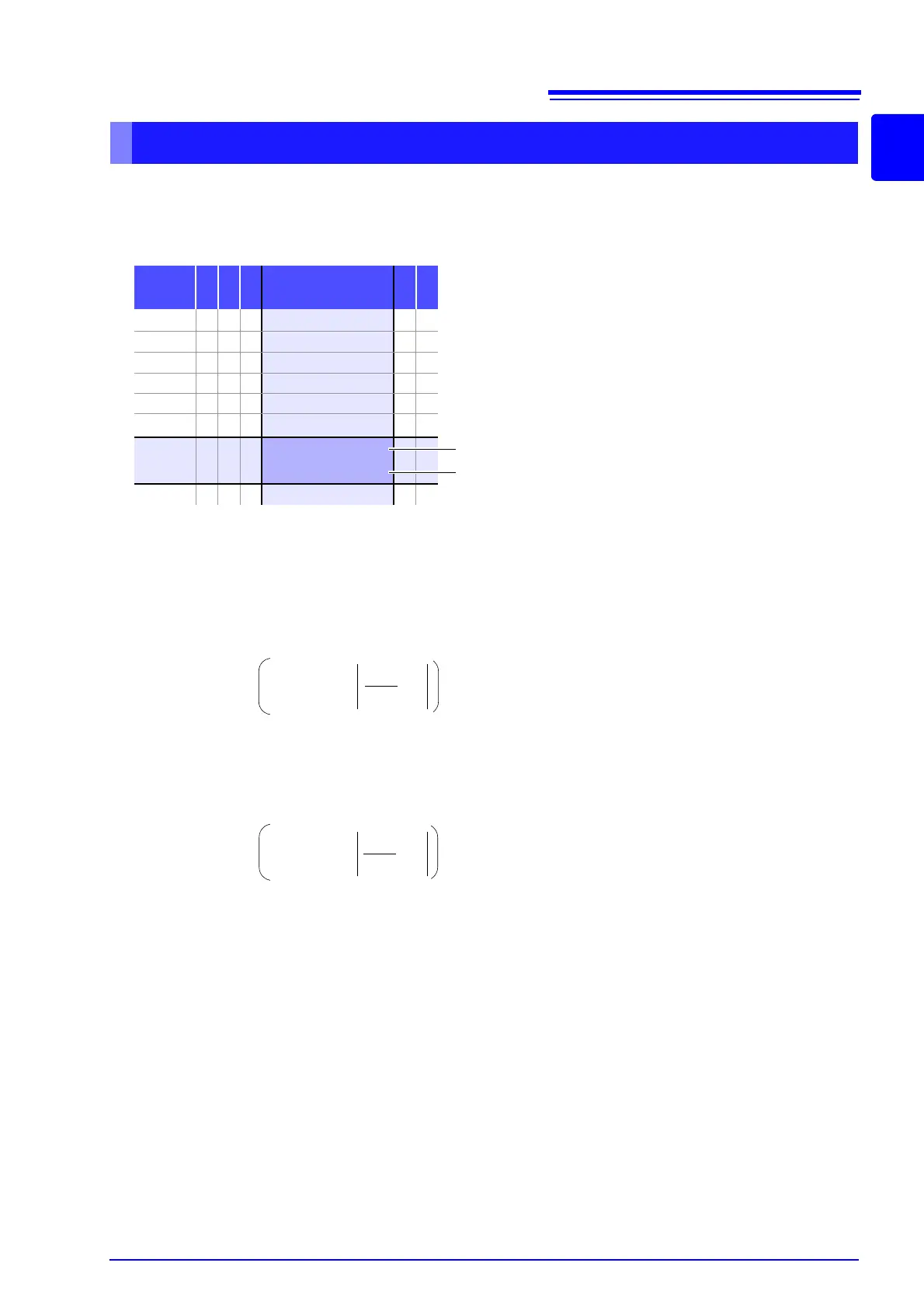
Accuracy table (p.343)
range
1.0000 kHz to
10.000 kHz
10 k
100
A= 0.15 B= 0.02
A= 0.1 B= 0.01
10
1. Because Z is 50 , the 100 measurement range will be used.
2. Obtain the Z coefficients A and B from the accuracy table (p.343) and then calculate the basic
accuracy of Z.
In the 10 kHz/100 range, the accuracy table (p.343) yields the values A = 0.15 and B = 0.02.
Using the basic accuracy formula (p.342) for 100 or less ranges,
Z
3. Similarly, calculate the basic accuracy of
The accuracy table (p.343) yields the values A = 0.1 and B = 0.01
Using the basic accuracy formula (p.342) for 100 and lower ranges,
Z accuracy=±
accuracy=±
100
50
- 1
0.15+ 0.02 ×
=±0.17%
100
50
- 1
0.1+ 0.01 ×
=±0.11°
 Loading...
Loading...