Using the Amp section
67
LFO modulation
YoucanmodulatethefilterviaLFO1,LFO2,andthe
CommonLFO.Amongotherapplications,LFO
modulationofthefiltercanproducetheclassic“auto‐
wah”effect.
TheFilterLFOModtabletsyousetupthefollowing
parametersseparatelyforeachLFO:
IntensitytoAandIntensitytoBspecifyhow
much
theLFOchangesthetone.
JS‐YIntensitytoAandJS‐YIntensitytoBspecifythe
depthofthewaheffectproducedbytheLFOwhenthe
joystickismovedtowardyourself,orwhenCC#2is
received.
TheAMSsettingselectsaAMSmodulationsourceto
scalethe
amountoftheLFOappliedtoFiltersAandB.
ThetwofiltersshareasingleAMSsource,with
separateintensitysettings.
Forexampleif,AMSissettoAfterTouch,applying
pressuretothekeyboardproducesan“auto‐wah”
effect.
Keyboard Track
Mostacousticinstrumentsgetbrighterasyouplay
higherpitches.Atitsmostbasic,keyboardtrackingre‐
createsthiseffectbyincreasingthecutofffrequencyof
alowpassfilterasyouplayhigheronthekeyboard.
Usually,someamountofkeytrackingisnecessaryin
ordertomakethetimbreconsistent
acrosstheentire
range.
TheOASYSkeyboardtrackingcanalsobemuchmore
complex,sinceitallowsyoutocreatedifferentratesof
changeoveruptofourdifferentpartsofthekeyboard.
Forinstance,youcan:
•Makethefiltercutoffincreaseveryquicklyoverthe
middleofthekeyboard,and
thenopenmore
slowly–ornotatall–inthehigheroctaves.
•Makethecutoffincreaseasyouplayloweronthe
keyboard.
• Createabruptchangesatcertainkeys,forsplit‐like
effects.
How Key Track works: Keys and Ramps
Thekeyboardtrackingworksbycreatingfourramps,
orslopes,betweenfivekeysonthekeyboard.The
bottomandtopkeysarefixedatthebottomandtopof
theMIDIrange,respectively.Youcansettheother
threekeys–namedLowBreak,Center,andHigh
Break–tobeanywhereinbetween.
The
fourRampvaluescontroltherateofchange
betweeneachpairofkeys.Forinstance,iftheLow‐
CenterRampissetto0,thevaluewillstaythesame
betweentheLowBreakkeyandtheCenterkey.
Youcanthinkoftheresultingshapeasbeingliketwo
folding
doorsattachedtoahingeinthecenter.Atthe
Centerkey(themainhinge),thekeyboardtrackinghas
noeffect.Thetwofoldingdoorsswingoutfromthis
centerpointtocreatechangesinthehigherandlower
rangesofthekeyboard.
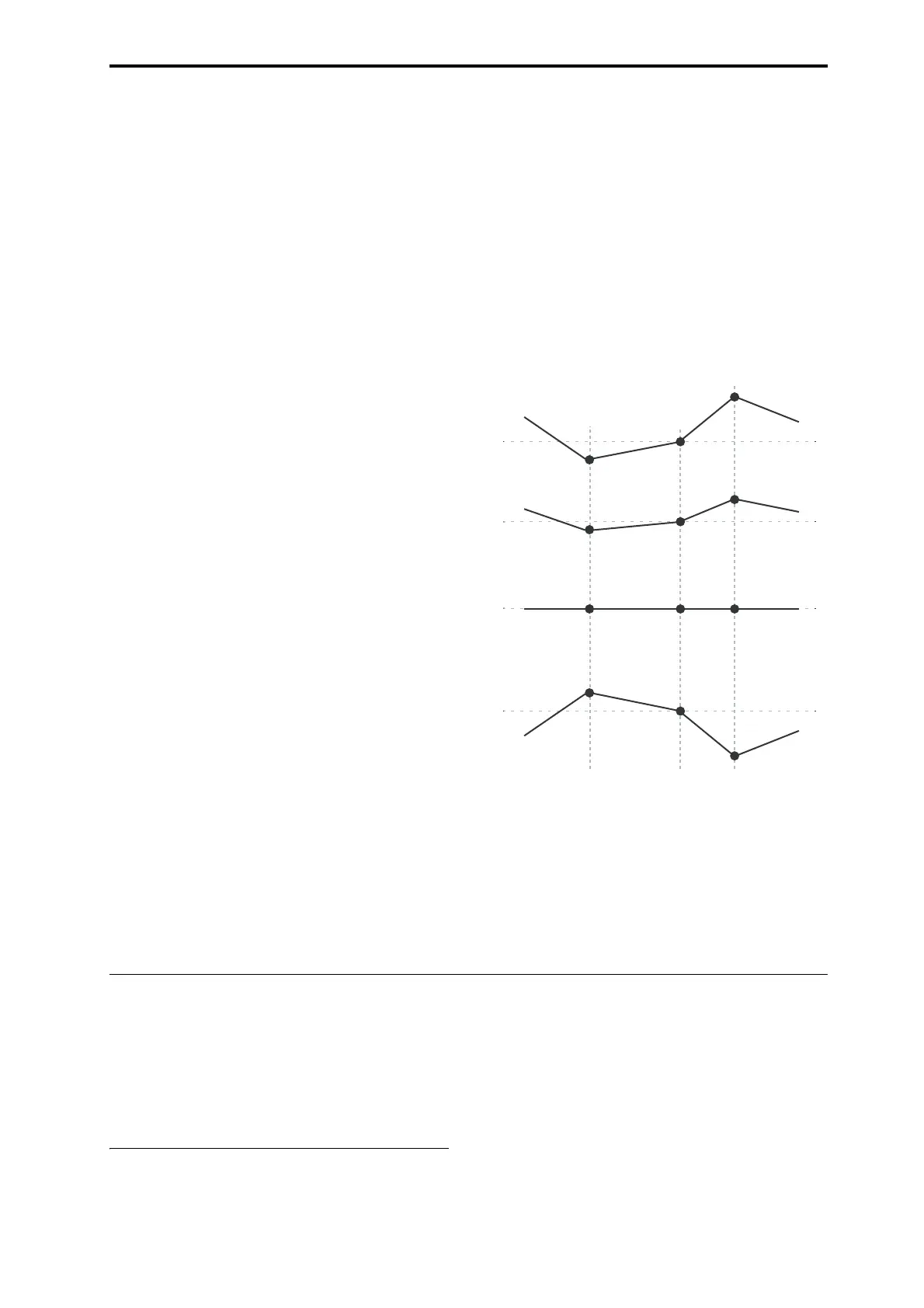
KeyboardTrackShapeandIntensity
IntensitytoA
andIntensitytoBadjusttheeffectthat
keyboardtrackingwillhaveonfiltersAandB.For
moreinformation,see“3–2a:KeyboardTrack,”on
page 64oftheParameterGuide.
AMS Modulation
InadditiontotheEG,LFOs,andKeyTrack,youcan
usetwoAMSsourcestomodulatethefilters.For
instance,youcouldusetheribbontochangethe
brightness,orusetheAMSoutputofaWaveSequence.
Using the Amp section
TheAmpsectionincludescontrolsforvolume,pan,
andthedrivercircuit.Youcancontrolthevolume
usingtheAmpEG,LFO1/2,KeyTrack,andvelocity,
alongwithotherAMSsources.
EachOscillatorhasitsownAmpsection:Amp1for
OSC1,andAmp2forOSC2.
Background: what does “Amp” mean?
Differentsoundshavecharacteristicshapestotheir
volumelevels.
Forexample,thevolumeofapianonotebeginsata
highvolumetheinstantyouplaythenote,andthen
decreasesgradually.
Thevolumeofanorgannote,ontheotherhand,
remainsconstantaslongasyoucontinuepressingthe
key.
Thevolumeofanoteonaviolinorwindinstrument
canbevariedduringthenotebythemusician(i.e.,by
regulatingtheamountofpressureontheboworthe
forceofthebreath).
ntensity = +99 (Original Shape)
ntensity = –99 (Inverted)
ntensity = +50 (Less Effect)
ntensity = 0 (No Effect)
 Loading...
Loading...











