Protection parameter group06
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION 152
Current stalling protection
When heavy load and motor starts or target frequency changes (increases), the rotating speed of motor often
cannot keep up with the speed of output frequency change. When the rotation speed of motor is lower than output
frequency, output current will increase to enhance output torque. However, if the difference between output
frequency and motor speed is too large, motor torque will be reduced, which is called “stall”
06-01
P.22
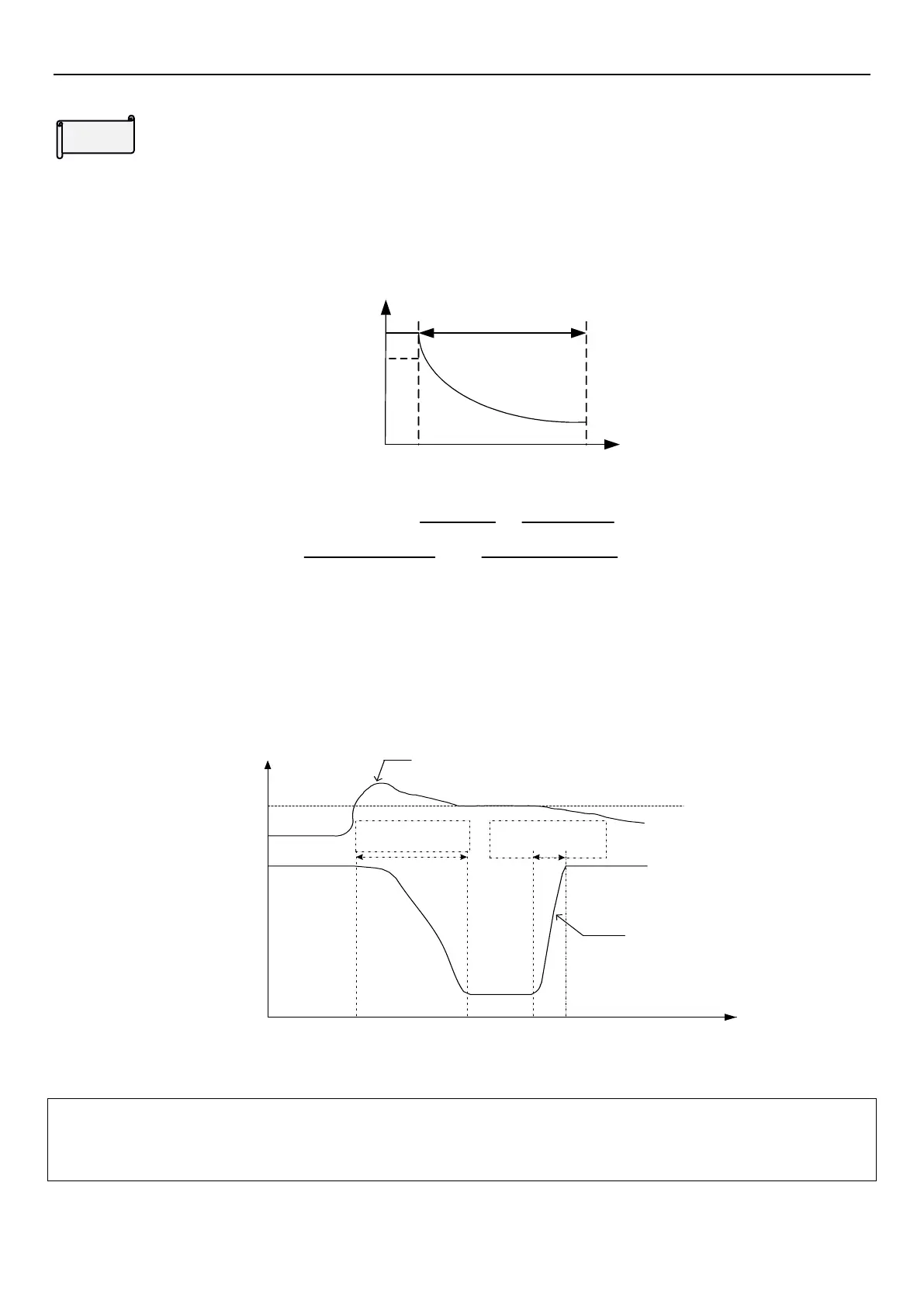
Output frequency
Level decreasing
region
100%
Output current
percentage
06-03
(P.66)
(Full load
current)
Formula for stall prevention level:
Level percentage=A+B×
06-01(P.22)-A
06-01(P.22)-B
×
06-02(P.23)-100
B=
100
400
A=
Output frequency
(06-23(P.66))x(06-01(P.22))
(06-23(P.66))x(06-01(P.22))
When load is heavy, the output current of inverter will increase. Once the percentage of output current exceeds
curve shown in the diagram below, inverter will reduce output frequency according to deceleration time selected in
06-04
(P.220)
. After rotation speed of motor keeps up (output current of inverter will decrease accordingly), inverter
will accelerate and recover to original output frequency (output frequency at stall) according to acceleration time
selected in 06-04
(P.220)
, and then continue to increase output frequency.
120%
06-01
(P.22)
Level
Time
deceleration time
according to 06-
04(P.220)
acceleration time
according to 06-
04(P.220)
Current
Output
frequency
Current in the figure refers to the current amplitude
Note: 1. If set 00-21(P.300) to 3 sensorless vector control, 06-01 (P.22) will act as torque limit level operation.
2. When 06-04(P.220)=2, if 01-22(P.44) is not set, acceleration time will be 01-07(P.8); If 01-23(P.45) is not set,
deceleration time will be 01-07(P.8).

 Loading...
Loading...