Basic Setup Procedures
User Manual Version 002 BRUKER BIOSPIN 85 (327)
Some Practical Hints for CPMAS Spectroscopy 4.8
Some general recommendations for reasonable RF-fields used in WB probes:
Note: Higher RF power levels should only be applied if necessary and within
specifications. For special probes, max. allowed RF fields may be lower. Check
with your Bruker BioSpin applications support if in doubt.
In order to have quantitative information about the precision of your magic angle,
one may measure the line width of the KBr central peak and compare it with the
line width of the 5
th
spinning sideband. If the linewidths compare within ± 8% then
the MA-setting is acceptable. The line-width comparison is conveniently achieved
with the command peakw, expanding the display first around the center line, typ
-
ing peakw and then repeating this with the 5
th
sideband to either side.
Most cp/mas probes are tunable over a large range of X-frequencies. It can some-
times be fairly difficult to retune a probe to an arbitrary frequency within the tuning
range. NEVER just load a nucleus and blindly tune and match the probe, using a
small wobble width (wbsw) of 10 MHz or less. Instead, either note the current tun
-
ing position of the probe into the lab notebook and start retuning to the new nucle-
us frequency from this frequency on, following the probe response over the whole
frequency range using a large wbsw of 50 MHz. Alternately, check the microme
-
ter setting of the X-tuning adjustment and conclude from that to which nucleus the
probe is tuned. Make a list of micrometer settings for the most frequently mea
-
sured nuclei.
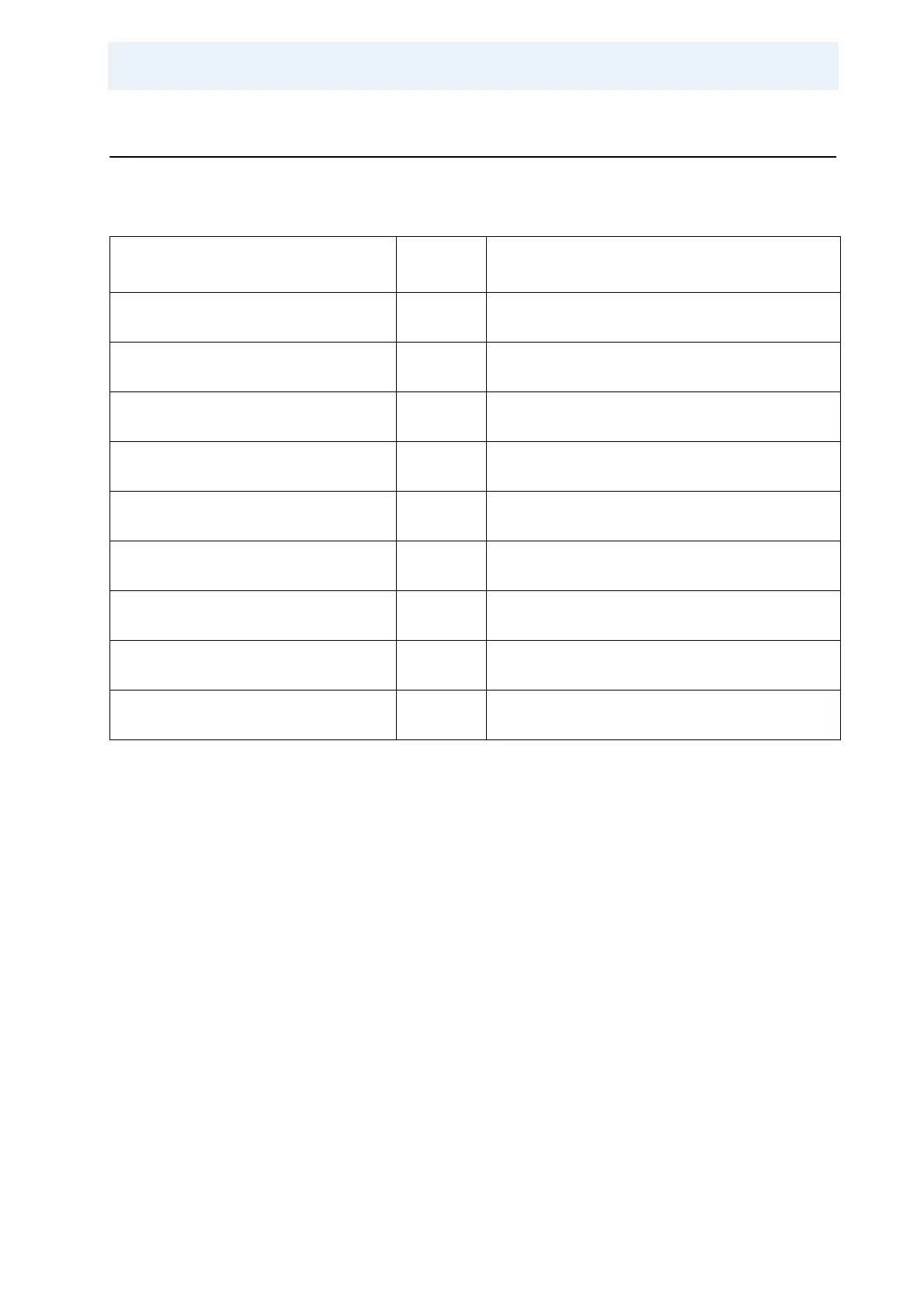
Table 4.3. Reasonable RF-fields for Max. 2% Duty Cycle
Probe Nucleus
Decoupling power over 50 ms, 200ms,
500ms. Contact pulse up to 10 ms
2.5mm CPMAS double resonance 35
kHz max sample rotation
1
H 115 kHz (2.2µs 90º pulse), 75 kHz, 40 kHz
71 kHz (3.5 µs) contact
2.5mm CPMAS double resonance 35
kHz max sample rotation
13
C 83 kHz (3 µs 90º pulse)
71 kHz (3.5 µs)
3.2mm CPMAS double resonance 24
kHz max sample rotation
1
H 110 kHz (2.3 µs), 60 kHz, 35 kHz
68 kHz (3.7 µs)
3.2mm CPMAS double resonance 24
kHz max sample rotation
13
C 78 kHz (3.2 µs)
68 kHz (3.7 µs)
4 mm CPMAS double resonance
probe (15 kHz max. sample rotation)
1
H 92.5 kHz (2.7us 90º), 50 kHz, 30 kHz
62 kHz (4 µs)
4 mm CPMAS double resonance
probe (15 kHz max. sample rotation)
13
C 71 kHz (3.5 µs)
62 kHz (4 µs)
4 mm CPMAS triple resonance probe
(15 kHz max. sample rotation)
13
C 66 kHz (3.8 µs)
50 kHz (5 µs)
7mm CPMAS double resonance probe
(7 kHz sample rotation)
1
H 70 kHz (3.6 µs 90º pulse), 35 kHz, 20 kHz
50 kHz (5 µs)
7mm CPMAS double resonance probe
(7 kHz sample rotation)
13
C 55 kHz (4.5 µs)
50 kHz (5 µs)
 Loading...
Loading...