98 (327) BRUKER BIOSPIN User Manual Version 002
Decoupling Techniques
References:
1. D. Sakellariou, A. Lesage, P. Hodgkinson, and L. Emsley, Homonuclear dipolar decoupling in solid-
state NMR using continuous phase modulation, Chem. Phys. Lett. 319, 253-260 (2000).
2. Lyndon Emsley’s home page: http://www.ens-lyon.fr/STIM/NMR/NMR.html
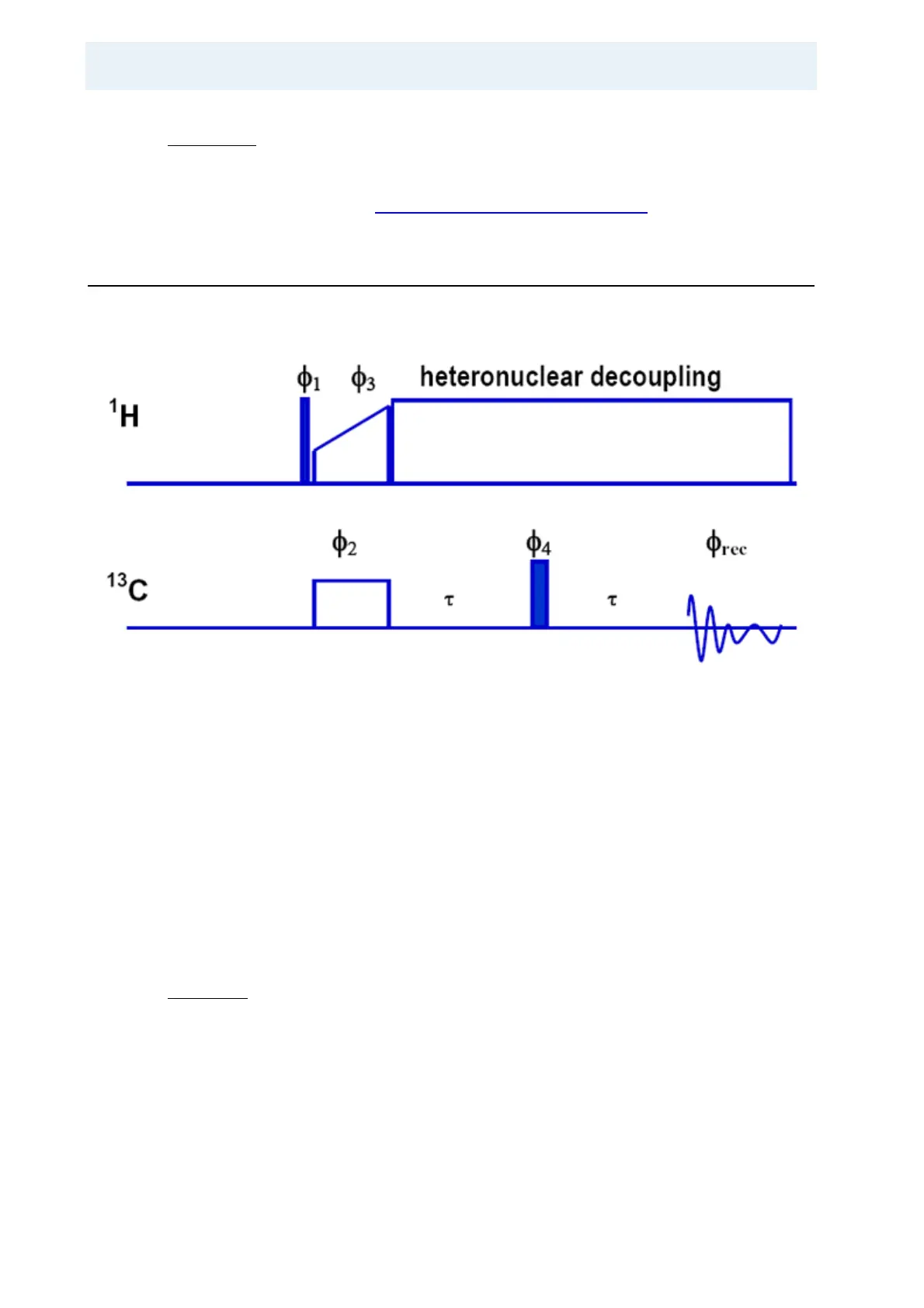
Transverse Dephasing Optimized Spectroscopy 5.3
Decoupling optimized under refocused conditions:
Figure 5.6. Pulse Program for Hahn Echo Sequence
Transverse Dephasing Optimized spectroscopy (G. De Paepe et al. 2003) uses a
spin echo sequence for optimizing heteronuclear decoupling. The idea behind it is
simply the removal of the normally dominant J
0
term (describing coherent residual
line broadening effects) in the transverse relaxation rate R
2
(A. Abragam chapter
8). With the normal CP experiment the observed line broadening (coherence de
-
cay time T
*
2
) might be caused by other heterogeneous effects, such as distribu-
tion of chemical shifts or susceptibility effects and not reflect the true T’
2
(coherence lifetime). The true T’
2
achieved through good heteronuclear decou-
pling can then be observed with a hahn-echo experiment. Optimization is done by
looking for the maximum signal amplitude of the decoupled resonances of inter
-
est. Be careful not to exceed the maximum decoupling time with high power de-
coupling.
Reference:
1. G. De Paepe, N. Giraud, A. Lesage, P. Hodgkinson, A. Böckmann, and L. Emsley, Transverse De-
phasing Optimized Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy, JACS 125, 13938 – 13939 (2003).
 Loading...
Loading...