Section 8. Operation
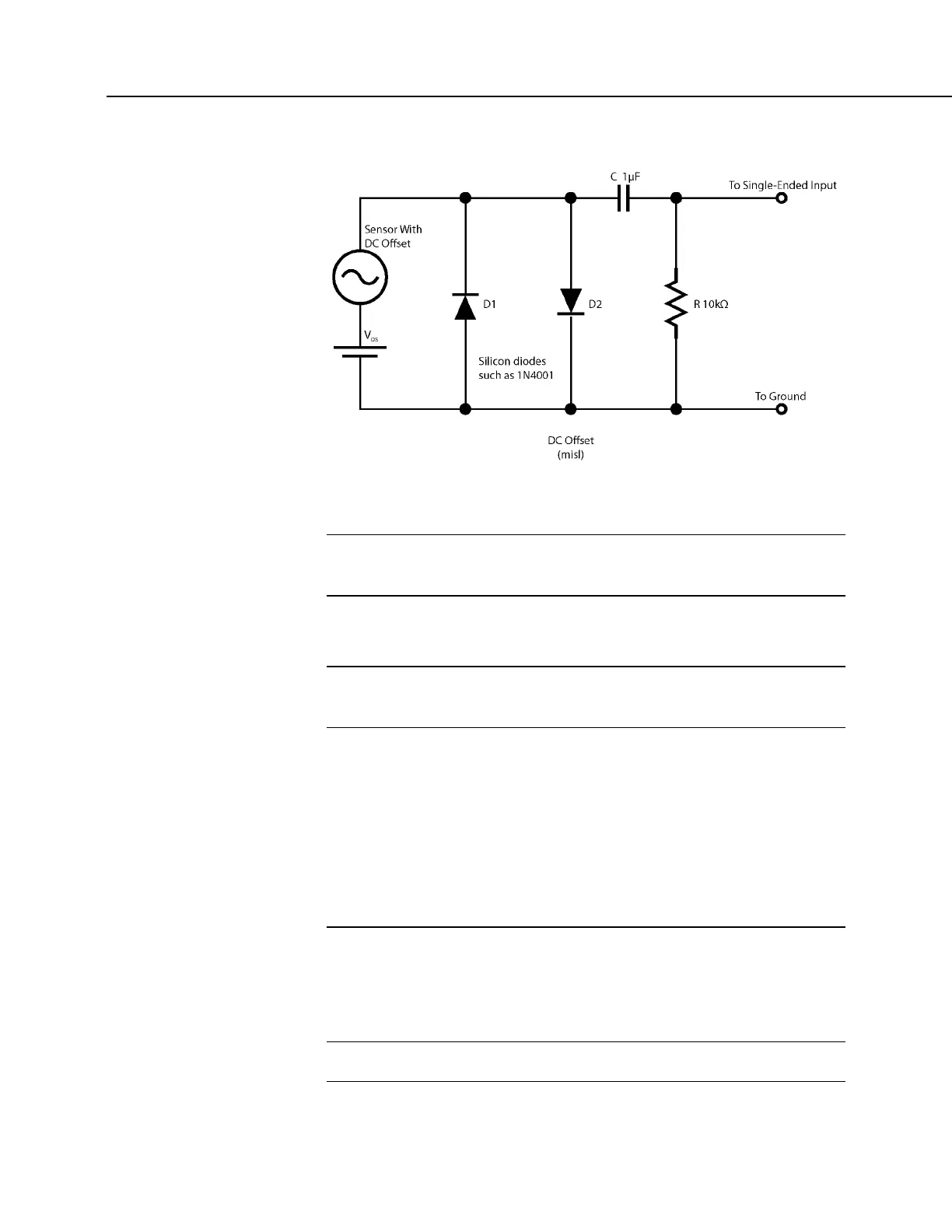
FIGURE 90: Input Conditioning Circuit for Period Averaging
8.1.6 Reading Smart Sensors — Details
Related Topics:
• Reading Smart Sensors — Overview (p. 74)
• Reading Smart Sensors — Details
(p. 384)
8.1.6.1 RS-232 and TTL — Details
Related Topics:
• RS-232 and TTL — Details (p. 384)
• Serial I/O (p. 279)
The CR800 can receive and record most TTL (0 to 5 Vdc) and true RS-232 data
from devices such as smart sensors. See the table CR800 Terminal Definitions
(p.
58)
for those terminals and serial ports configurable for either TTL or true RS-232
communications. Use of the CS I/O port for true RS-232 communications
requires use of an interface device. See Hardware, Single-Connection Comms
Devices — List
(p. 569). If additional serial inputs are required, serial input
expansion modules can be connected. See Serial I/O Modules — List
(p. 563).
Serial data are usually captured as text strings, which are then parsed (split up) as
defined in the CRBasic program.
Note When connecting serial sensors to a C terminal configured as Rx,
the sensor power consumption may increase by a few milliamps due to
voltage clamps in the CR800. An external resistor may need to be added
in series to the Rx line to limit the current drain, although this is not
advisable at very high baud rates. See figure Circuit to Limit C Terminal
Input to 5 Volts Dc
(p. 385).
Note C terminals configured as Tx transmit only 0 to 5 Vdc logic.
However, C terminals configured as Rx read most true RS-232 signals.

 Loading...
Loading...