Section 8. Operation
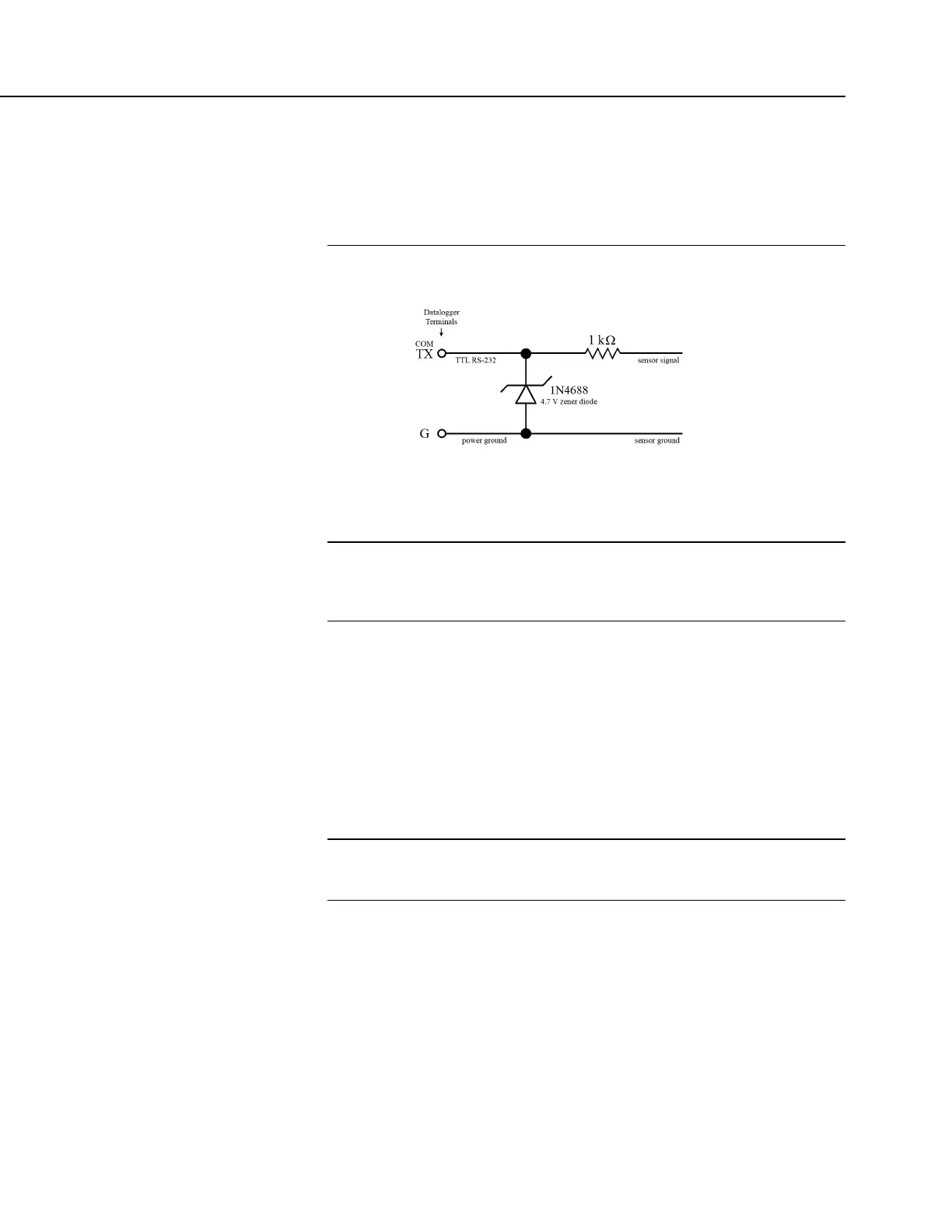
When connecting serial sensors to a C terminal configured as Rx, the
sensor power consumption may increase by a few milliamps due to
voltage clamps in the CR800. An external resistor may need to be added
in series to the Rx line to limit the current drain, although this is not
advisable at very high baud rates. See Circuit to Limit C Terminal Input to
5 Volts
(p. 385).
FIGURE 91: Circuit to Limit C Terminal Input to 5 Vdc
8.1.6.2 SDI-12 Sensor Support — Details
Related Topics:
• SDI-12 Sensor Support — Overview (p. 74)
• SDI-12 Sensor Support — Details (p. 385)
• Serial I/O: SDI-12 Sensor Support — Programming Resource (p. 240)
SDI-12 is a communication protocol developed to transmit digital data from smart
sensors to data-acquisition units. It is a simple protocol, requiring only a single
communication wire. Typically, the data-acquisition unit also supplies power (12
Vdc and ground) to the SDI-12 sensor. SDI12Recorder() instruction
communicates with SDI-12 sensors on terminals configured for SDI-12 input.
See the table CR800 Terminal Definitions
(p. 58) to determine those terminals
configurable for SDI-12 communications.
8.1.7 Field Calibration — Overview
Related Topics:
• Field Calibration — Overview (p. 75)
• Field Calibration — Details
(p. 214)
Calibration increases accuracy of a measurement device by adjusting its output, or
the measurement of its output, to match independently verified quantities.
Adjusting sensor output directly is preferred, but not always possible or practical.
By adding FieldCal() or FieldCalStrain() instructions to the CR800 CRBasic
program, measurements of a linear sensor can be adjusted by modifying the
programmed multiplier and offset applied to the measurement without modifying
or recompiling the CRBasic program.

 Loading...
Loading...