Operation Manual - Reliability
Quidway S6500 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 VRRP Configuration
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-2
Ethernet
Master
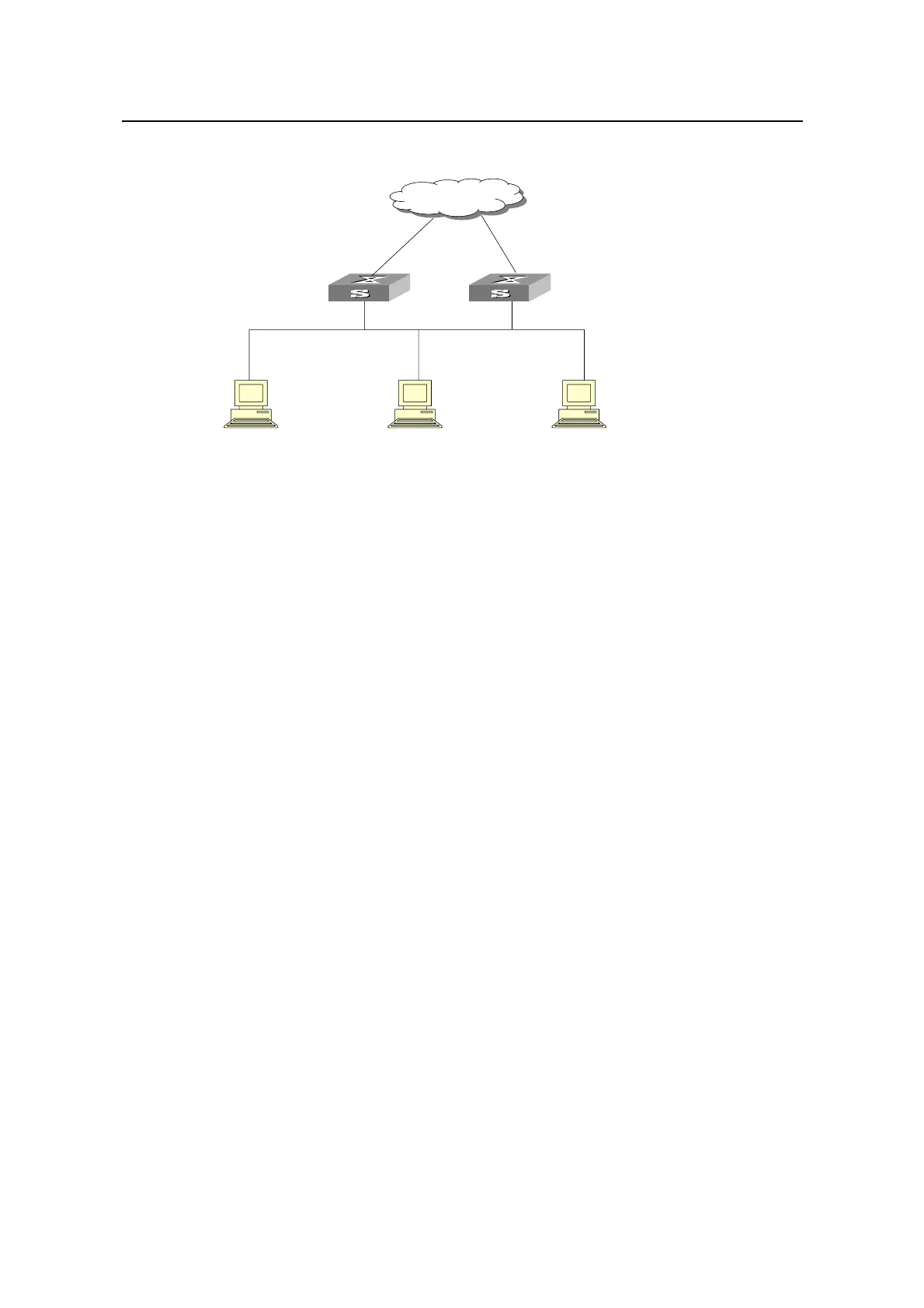
Host 1 Host 2 Host 3
10.100.10.7 10.100.10.8 10.100.10.9
Virtual IP address10.100.10.1
Network
Backup
Virtual IP address10.100.10.1
Actual IP address10.100.10.2 Actual IP address10.100.10.3
Figure 1-2 Virtual router
This virtual router has its own IP address: 10.100.10.1 (which can be the interface
address of a switch within the virtual router). The switches within the virtual router
have their own IP addresses (such as 10.100.10.2 for the master switch and
10.100.10.3 for the backup switch). Hosts on the LAN only know the IP address of
this virtual router, that is, 10.100.10.1 (which is usually known as the virtual IP
address of the virtual router), but not the specific IP addresses 10.100.10.2 of the
master switch and 10.100.10.3 of the backup switch. They configure their own default
routes as the IP address of this virtual router: 10.100.10.1. Therefore, hosts within the
network will communicate with the external network through this virtual router. If a
master switch in the virtual group goes down, the higher priority backup switch will
function as the new master switch to continue serving the host with routing to avoid
interrupting the communication between the host and the external networks.
1.2 VRRP Configuration
VRRP configuration tasks are described in the following sections:
z Enabling/Disabling the Function to Ping the Virtual IP Address
z Setting Correspondence Between Virtual IP Address and MAC Address
z Adding/Deleting a Virtual IP Address
z Configuring the Priority of Switches in the Virtual Router
z Configuring Preemption and Delay for a Switch Within a Virtual Router
z Configuring Authentication Type and Authentication Key
z Configuring VRRP Timer
z Configuring the Switch to Track a Specified Interface

 Loading...
Loading...











